Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (213.0 KB).
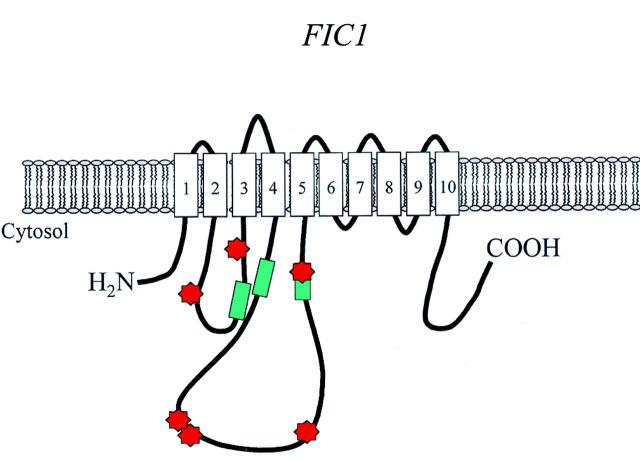
Figure 1 .
Putative structure of FIC1. The FIC1 gene has been demonstrated to be mutated in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) type 1 and benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC).20 It encodes a membrane protein with 10 putative transmembrane domains that exhibits homology with proteins with presumed aminophospholipid translocase activity. The green boxes represent P type ATPase signature domains; the red symbols mark mutations.
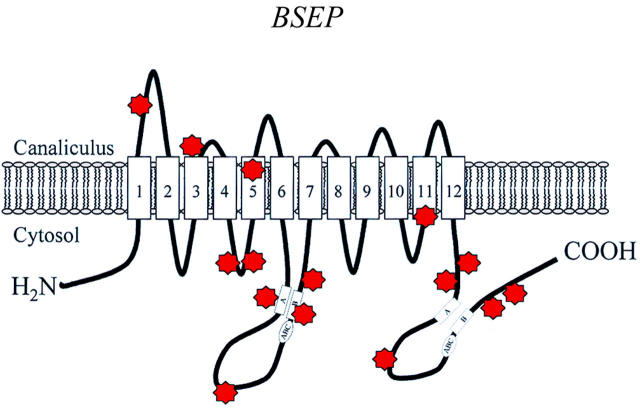
Figure 2 .
Putative structure of BSEP. The BSEP (bile salt export pump) gene has been demonstrated to be mutated in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) type 2.31 32 It encodes a membrane protein with 12 putative transmembrane domains that functions as a major bile salt export pump.32 33 The white boxes represent the Walker A and B motifs and the "ABC" signature; the red symbols mark mutations (modified after Strautnieks and colleagues31).
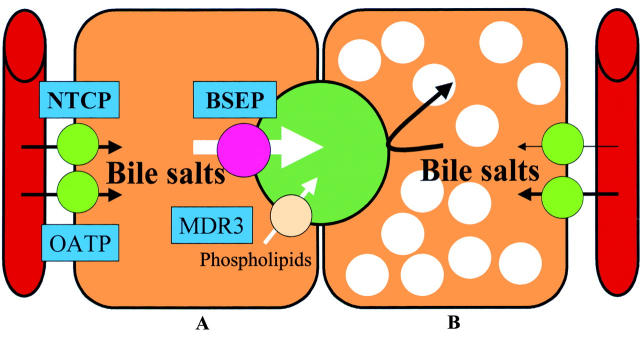
Figure 3 .
Bile salt transport. (A) Bile salts are taken up from the blood into the hepatocyte via carrier proteins in the basolateral membrane. These are NTCP or "sodium taurocholate cotransporting protein" and OATP or "organic anion transporting protein". At the canalicular membrane bile salts are transported into the bile canaliculus by the ATP dependent "bile salt export pump" (BSEP). Hepatocanalicular transport of phospholipids, mainly phosphatidylcholine, is mediated by the P-glycoprotein MDR3. (B) In patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2, BSEP is not expressed.
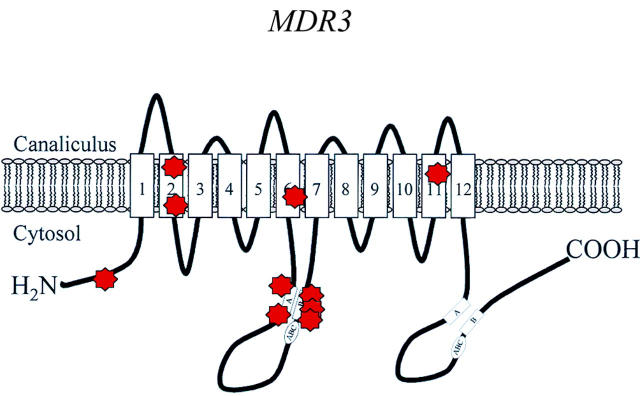
Figure 4 .
Putative structure of MDR3. The MDR3 gene has been demonstrated to be mutated in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) type 3.44 45 47 It encodes a membrane protein with 12 putative transmembrane domains that functions as a phosphatidylcholine translocator. The white boxes represent the Walker A and B motifs and the "ABC" signature; the red symbols mark mutations.
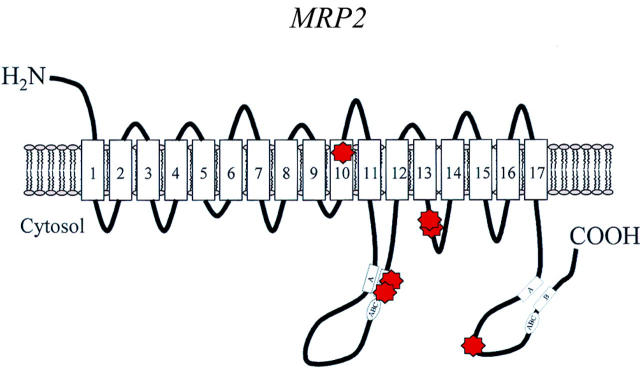
Figure 5 .
Putative structure of MRP2. The MRP2 gene has been demonstrated to be mutated in patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome6 52-54 It encodes a membrane protein with 17 putative transmembrane domains that functions as a major export pump for anionic conjugates. The white boxes represent the Walker A and B motifs and the "ABC" signature; the red symbols mark mutations.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aagenaes O. Hereditary cholestasis with lymphoedema (Aagenaes syndrome, cholestasis-lymphoedema syndrome). New cases and follow-up from infancy to adult age. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Apr;33(4):335–345. doi: 10.1080/00365529850170955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allikmets R., Gerrard B., Hutchinson A., Dean M. Characterization of the human ABC superfamily: isolation and mapping of 21 new genes using the expressed sequence tags database. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Oct;5(10):1649–1655. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.10.1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso E. M., Snover D. C., Montag A., Freese D. K., Whitington P. F. Histologic pathology of the liver in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):128–133. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnell H., Nemeth A., Annerén G., Dahl N. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC): evidence for genetic heterogeneity by exclusion of linkage to chromosome 18q21-q22. Hum Genet. 1997 Sep;100(3-4):378–381. doi: 10.1007/s004390050519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevers E. M., Comfurius P., Dekkers D. W., Zwaal R. F. Lipid translocation across the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Aug 18;1439(3):317–330. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourke B., Goggin N., Walsh D., Kennedy S., Setchell K. D., Drumm B. Byler-like familial cholestasis in an extended kindred. Arch Dis Child. 1996 Sep;75(3):223–227. doi: 10.1136/adc.75.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks-Wilson A., Marcil M., Clee S. M., Zhang L. H., Roomp K., van Dam M., Yu L., Brewer C., Collins J. A., Molhuizen H. O. Mutations in ABC1 in Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Nat Genet. 1999 Aug;22(4):336–345. doi: 10.1038/11905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull L. N., Carlton V. E., Stricker N. L., Baharloo S., DeYoung J. A., Freimer N. B., Magid M. S., Kahn E., Markowitz J., DiCarlo F. J. Genetic and morphological findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler disease [PFIC-1] and Byler syndrome): evidence for heterogeneity. Hepatology. 1997 Jul;26(1):155–164. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull L. N., Juijn J. A., Liao M., van Eijk M. J., Sinke R. J., Stricker N. L., DeYoung J. A., Carlton V. E., Baharloo S., Klomp L. W. Fine-resolution mapping by haplotype evaluation: the examples of PFIC1 and BRIC. Hum Genet. 1999 Mar;104(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/pl00008714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull L. N., van Eijk M. J., Pawlikowska L., DeYoung J. A., Juijn J. A., Liao M., Klomp L. W., Lomri N., Berger R., Scharschmidt B. F. A gene encoding a P-type ATPase mutated in two forms of hereditary cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998 Mar;18(3):219–224. doi: 10.1038/ng0398-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., König J., Brom M., Kartenbeck J., Spring H., Horie T., Keppler D. cDNA cloning of the hepatocyte canalicular isoform of the multidrug resistance protein, cMrp, reveals a novel conjugate export pump deficient in hyperbilirubinemic mutant rats. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 21;271(25):15091–15098. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.25.15091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton V. E., Knisely A. S., Freimer N. B. Mapping of a locus for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler disease) to 18q21-q22, the benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis region. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jun;4(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs S., Yeh R. L., Georges E., Ling V. Identification of a sister gene to P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res. 1995 May 15;55(10):2029–2034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Leonard J. V., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D., Andersson S., Egestad B., Sjövall J. Familial giant cell hepatitis associated with synthesis of 3 beta, 7 alpha-dihydroxy-and 3 beta,7 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acids. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1031–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI112915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. J., Iber F. L., Ruebner B. H., McKusick V. A. Byler disease. Fatal familial intrahepatic cholestasis in an Amish kindred. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jan;117(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., van Driel M., den Hollander A. I., van Haren F. J., Knoers N. V., Tijmes N., Bergen A. A., Rohrschneider K., Blankenagel A. Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy caused by splice site mutations in the Stargardt's disease gene ABCR. Hum Mol Genet. 1998 Mar;7(3):355–362. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.3.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleuze J. F., Jacquemin E., Dubuisson C., Cresteil D., Dumont M., Erlinger S., Bernard O., Hadchouel M. Defect of multidrug-resistance 3 gene expression in a subtype of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):904–908. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerloff T., Stieger B., Hagenbuch B., Madon J., Landmann L., Roth J., Hofmann A. F., Meier P. J. The sister of P-glycoprotein represents the canalicular bile salt export pump of mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):10046–10050. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.16.10046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner J., Moser H., Valle D. Mutations in the 70K peroxisomal membrane protein gene in Zellweger syndrome. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):16–23. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Cresteil D., Manouvrier S., Boute O., Hadchouel M. Heterozygous non-sense mutation of the MDR3 gene in familial intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Lancet. 1999 Jan 16;353(9148):210–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)77221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Hadchouel M. Genetic basis of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Hepatol. 1999 Aug;31(2):377–381. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Hermans D., Myara A., Habes D., Debray D., Hadchouel M., Sokal E. M., Bernard O. Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy in pediatric patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology. 1997 Mar;25(3):519–523. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Setchell K. D., O'Connell N. C., Estrada A., Maggiore G., Schmitz J., Hadchouel M., Bernard O. A new cause of progressive intrahepatic cholestasis: 3 beta-hydroxy-C27-steroid dehydrogenase/isomerase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83280-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L., Peters W. H., Lamers W. H. Hereditary chronic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia in mutant rats caused by defective hepatic anion transport. Hepatology. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):573–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L., Strautnieks S. S., Jacquemin E., Hadchouel M., Sokal E. M., Hooiveld G. J., Koning J. H., De Jager-Krikken A., Kuipers F., Stellaard F. Hepatocanalicular bile salt export pump deficiency in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1999 Dec;117(6):1370–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedlitschky G., Leier I., Buchholz U., Hummel-Eisenbeiss J., Burchell B., Keppler D. ATP-dependent transport of bilirubin glucuronides by the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 and its hepatocyte canalicular isoform MRP2. Biochem J. 1997 Oct 1;327(Pt 1):305–310. doi: 10.1042/bj3270305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagalwalla A. F., Al Amir A. R., Khalifa A., Sylven M., Al Ajaji S., Kagalwalla Y. A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler's disease) in Arab children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1995 Dec;15(4):321–327. doi: 10.1080/02724936.1995.11747792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisako T., Leier I., Cui Y., König J., Buchholz U., Hummel-Eisenbeiss J., Keppler D. Transport of monoglucuronosyl and bisglucuronosyl bilirubin by recombinant human and rat multidrug resistance protein 2. Hepatology. 1999 Aug;30(2):485–490. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Leuschner U., Mayer R., Keppler D. Absence of the canalicular isoform of the MRP gene-encoded conjugate export pump from the hepatocytes in Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Hepatology. 1996 May;23(5):1061–1066. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1996.v23.pm0008621134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Leier I., Jedlitschky G. Transport of glutathione conjugates and glucuronides by the multidrug resistance proteins MRP1 and MRP2. Biol Chem. 1997 Aug;378(8):787–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Alroy J., Gatmaitan Z., Inoue M., Mikami T., Jansen P., Arias I. M. Defective biliary excretion of epinephrine metabolites in mutant (TR-) rats: relation to the pathogenesis of black liver in the Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Corriedale sheep with an analogous excretory defect. Hepatology. 1992 Jun;15(6):1154–1159. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J., Lutz Y., Stoeckel M. E., Sarde C. O., Kretz C., Douar A. M., Lopez J., Aubourg P., Mandel J. L. The gene responsible for adrenoleukodystrophy encodes a peroxisomal membrane protein. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):265–271. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh Y., Bassan L., Rosenthal E., Berkowitz D., Jaffe M., Mandel H., Berant M. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis among the Arab population in Israel. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997 May;24(5):548–554. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199705000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Ikeda K., Takasaka T. Sensorineural hearing loss associated with Byler disease. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1999 Jan;187(1):83–88. doi: 10.1620/tjem.187.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oude Elferink R. P., de Haan J., Lambert K. J., Hagey L. R., Hofmann A. F., Jansen P. L. Selective hepatobiliary transport of nordeoxycholate side chain conjugates in mutant rats with a canalicular transport defect. Hepatology. 1989 Jun;9(6):861–865. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulusma C. C., Bosma P. J., Zaman G. J., Bakker C. T., Otter M., Scheffer G. L., Scheper R. J., Borst P., Oude Elferink R. P. Congenital jaundice in rats with a mutation in a multidrug resistance-associated protein gene. Science. 1996 Feb 23;271(5252):1126–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5252.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulusma C. C., Kool M., Bosma P. J., Scheffer G. L., ter Borg F., Scheper R. J., Tytgat G. N., Borst P., Baas F., Oude Elferink R. P. A mutation in the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter gene causes the Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Hepatology. 1997 Jun;25(6):1539–1542. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERSKILL W. H., WALSHE J. M. Benign recurrent intrahepatic "obstructive" jaundice. Lancet. 1959 Oct 31;2(7105):686–690. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Schwarz M., O'Connell N. C., Lund E. G., Davis D. L., Lathe R., Thompson H. R., Weslie Tyson R., Sokol R. J., Russell D. W. Identification of a new inborn error in bile acid synthesis: mutation of the oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene causes severe neonatal liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1998 Nov 1;102(9):1690–1703. doi: 10.1172/JCI2962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Suchy F. J., Welsh M. B., Zimmer-Nechemias L., Heubi J., Balistreri W. F. Delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 beta-reductase deficiency described in identical twins with neonatal hepatitis. A new inborn error in bile acid synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2148–2157. doi: 10.1172/JCI113837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shroyer N. F., Lewis R. A., Allikmets R., Singh N., Dean M., Leppert M., Lupski J. R. The rod photoreceptor ATP-binding cassette transporter gene, ABCR, and retinal disease: from monogenic to multifactorial. Vision Res. 1999 Jul;39(15):2537–2544. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(99)00037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Groen A. K., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Ottenhoff R., van der Lugt N. M., van Roon M. A. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., de Vree J. M., Ottenhoff R., Oude Elferink R. P., Schinkel A. H., Borst P. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the human MDR3 P-glycoprotein gene restores the biliary phosphatidylcholine excretion absent in Mdr2 (-/-) mice. Hepatology. 1998 Aug;28(2):530–536. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Zhang J., O'Neill B., Sjövall J., Meier P. J. Differential interaction of bile acids from patients with inborn errors of bile acid synthesis with hepatocellular bile acid transporters. Eur J Biochem. 1997 Feb 15;244(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strautnieks S. S., Bull L. N., Knisely A. S., Kocoshis S. A., Dahl N., Arnell H., Sokal E., Dahan K., Childs S., Ling V. A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998 Nov;20(3):233–238. doi: 10.1038/3034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strautnieks S. S., Kagalwalla A. F., Tanner M. S., Gardiner R. M., Thompson R. J. Locus heterogeneity in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Med Genet. 1996 Oct;33(10):833–836. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.10.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strautnieks S. S., Kagalwalla A. F., Tanner M. S., Knisely A. S., Bull L., Freimer N., Kocoshis S. A., Gardiner R. M., Thompson R. J. Identification of a locus for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis PFIC2 on chromosome 2q24. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Sep;61(3):630–633. doi: 10.1086/515501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang X., Halleck M. S., Schlegel R. A., Williamson P. A subfamily of P-type ATPases with aminophospholipid transporting activity. Science. 1996 Jun 7;272(5267):1495–1497. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5267.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. M., Wohllk N., Huang E., Kuhnle U., Rabl W., Gagel R. F., Cote G. J. Inactivation of the first nucleotide-binding fold of the sulfonylurea receptor, and familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Sep;59(3):510–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujii H., König J., Rost D., Stöckel B., Leuschner U., Keppler D. Exon-intron organization of the human multidrug-resistance protein 2 (MRP2) gene mutated in Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1999 Sep;117(3):653–660. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tygstrup N., Steig B. A., Juijn J. A., Bull L. N., Houwen R. H. Recurrent familial intrahepatic cholestasis in the Faeroe Islands. Phenotypic heterogeneity but genetic homogeneity. Hepatology. 1999 Feb;29(2):506–508. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Toh S., Taniguchi K., Nakamura T., Uchiumi T., Kohno K., Yoshida I., Kimura A., Sakisaka S., Adachi Y. Mutations in the canilicular multispecific organic anion transporter (cMOAT) gene, a novel ABC transporter, in patients with hyperbilirubinemia II/Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1998 Feb;7(2):203–207. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Freese D. K., Alonso E. M., Schwarzenberg S. J., Sharp H. L. Clinical and biochemical findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):134–141. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Kniazeva M., Hutchinson A., Han M., Dean M., Allikmets R. The ABCR gene in recessive and dominant Stargardt diseases: a genetic pathway in macular degeneration. Genomics. 1999 Sep 1;60(2):234–237. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.5896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Sims P. J., Wiedmer T. Production and characterization of a mutant cell line defective in aminophospholipid translocase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Jun 5;1357(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)00014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielenski J., Tsui L. C. Cystic fibrosis: genotypic and phenotypic variations. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:777–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.004021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter A. G., van Berge Henegouwen G. P., ten Bokkel Huinink J. A., Brandt K. H. Familial benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Interrelation with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and from oral contraceptives? Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vree J. M., Jacquemin E., Sturm E., Cresteil D., Bosma P. J., Aten J., Deleuze J. F., Desrochers M., Burdelski M., Bernard O. Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):282–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]