Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (135.4 KB).
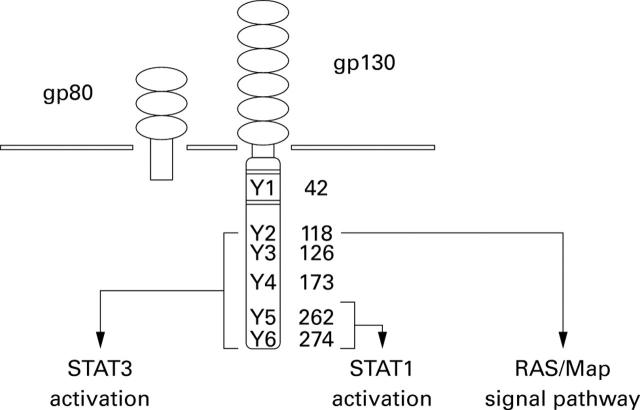
Figure 1 .
Intracellular cascades of the gp130 receptor. After interleukin 6 (IL-6) binding to gp80, two gp130 molecules homodimerise and activate JAK kinases which in turn phosphorylate the intracellular tyrosines of the gp130 receptor. Via the different phosphotyrosines, STAT1/3 and Ras dependent pathways are activated in the cell.
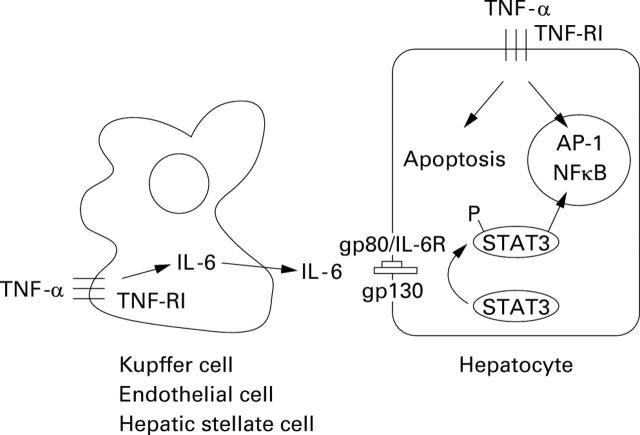
Figure 2 .
The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6) in hepatocyte proliferation after partial hepatectomy. After partial hepatectomy, tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) activates IL-6 expression, most likely in Kupffer cells. TNF-α and IL-6 via the gp80/gp130 receptor complex in turn activate intracellular pathways in liver cells which are essential for triggering hepatocyte proliferation after hepatectomy.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrejko K. M., Chen J., Deutschman C. S. Intrahepatic STAT-3 activation and acute phase gene expression predict outcome after CLP sepsis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1998 Dec;275(6 Pt 1):G1423–G1429. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.6.G1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellido T., O'Brien C. A., Roberson P. K., Manolagas S. C. Transcriptional activation of the p21(WAF1,CIP1,SDI1) gene by interleukin-6 type cytokines. A prerequisite for their pro-differentiating and anti-apoptotic effects on human osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 14;273(33):21137–21144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.33.21137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz U. A., Bloch W., van den Broek M., Yoshida K., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Addicks K., Rajewsky K., Müller W. Postnatally induced inactivation of gp130 in mice results in neurological, cardiac, hematopoietic, immunological, hepatic, and pulmonary defects. J Exp Med. 1998 Nov 16;188(10):1955–1965. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg J. F., Wrzeszczynska M. H., Devgan G., Zhao Y., Pestell R. G., Albanese C., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999 Aug 6;98(3):295–303. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81959-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. T., Ades I. Z., Nordan R. P. An acute phase response factor/NF-kappa B site downstream of the junB gene that mediates responsiveness to interleukin-6 in a murine plasmacytoma. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 29;270(52):31129–31135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.31129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo C. A., Jr, Madden J. F., Gao W., Selvan R. S., Clavien P. A. Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology. 1997 Dec;26(6):1513–1520. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J., Klapproth J., Gross V., Walter E., Andus T., Snyers L., Content J., Heinrich P. C. Fate of interleukin-6 in the rat. Involvement of skin in its catabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 20;189(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlett-Falcone R., Landowski T. H., Oshiro M. M., Turkson J., Levitzki A., Savino R., Ciliberto G., Moscinski L., Fernández-Luna J. L., Nuñez G. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity. 1999 Jan;10(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Chang M. C., Su Y. H., Tsai Y. T., Kuo M. L. Interleukin-6 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathways. J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 13;274(33):23013–23019. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.33.23013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cressman D. E., Diamond R. H., Taub R. Rapid activation of the Stat3 transcription complex in liver regeneration. Hepatology. 1995 May;21(5):1443–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cressman D. E., Greenbaum L. E., DeAngelis R. A., Ciliberto G., Furth E. E., Poli V., Taub R. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science. 1996 Nov 22;274(5291):1379–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997 Sep 12;277(5332):1630–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5332.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., Goldschmitt J., Peschel C., Brakenhoff J. P., Kallen K. J., Wollmer A., Grötzinger J., Rose-John S. I. A bioactive designer cytokine for human hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion. Nat Biotechnol. 1997 Feb;15(2):142–145. doi: 10.1038/nbt0297-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flørenes V. A., Lu C., Bhattacharya N., Rak J., Sheehan C., Slingerland J. M., Kerbel R. S. Interleukin-6 dependent induction of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 is lost during progression of human malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 1999 Jan 28;18(4):1023–1032. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada T., Hibi M., Yamanaka Y., Takahashi-Tezuka M., Fujitani Y., Yamaguchi T., Nakajima K., Hirano T. Two signals are necessary for cell proliferation induced by a cytokine receptor gp130: involvement of STAT3 in anti-apoptosis. Immunity. 1996 Nov;5(5):449–460. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80501-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada T., Ohtani T., Yoshida Y., Shirogane T., Nishida K., Nakajima K., Hibi M., Hirano T. STAT3 orchestrates contradictory signals in cytokine-induced G1 to S cell-cycle transition. EMBO J. 1998 Nov 16;17(22):6670–6677. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.22.6670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhartz C., Heesel B., Sasse J., Hemmann U., Landgraf C., Schneider-Mergener J., Horn F., Heinrich P. C., Graeve L. Differential activation of acute phase response factor/STAT3 and STAT1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. I. Definition of a novel phosphotyrosine motif mediating STAT1 activation. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):12991–12998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.12991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum L. E., Li W., Cressman D. E., Peng Y., Ciliberto G., Poli V., Taub R. CCAAT enhancer- binding protein beta is required for normal hepatocyte proliferation in mice after partial hepatectomy. J Clin Invest. 1998 Sep 1;102(5):996–1007. doi: 10.1172/JCI3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlund A. C., Farrar M. A., Viviano B. L., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced IFN gamma receptor tyrosine phosphorylation couples the receptor to its signal transduction system (p91). EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1591–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16(3-4):249–284. doi: 10.3109/08830189809042997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota H., Chen J., Betz U. A., Rajewsky K., Gu Y., Ross J., Jr, Müller W., Chien K. R. Loss of a gp130 cardiac muscle cell survival pathway is a critical event in the onset of heart failure during biomechanical stress. Cell. 1999 Apr 16;97(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80729-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara S., Nakajima K., Fukada T., Hibi M., Nagata S., Hirano T., Fukui Y. Dual control of neurite outgrowth by STAT3 and MAP kinase in PC12 cells stimulated with interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1997 Sep 1;16(17):5345–5352. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 1995 Feb;11(2):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89000-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya A., Kinoshita T., Ito Y., Matsui T., Morikawa Y., Senba E., Nakashima K., Taga T., Yoshida K., Kishimoto T. Fetal liver development requires a paracrine action of oncostatin M through the gp130 signal transducer. EMBO J. 1999 Apr 15;18(8):2127–2136. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki K., Gao Y. H., Yokose S., Kaji Y., Nakamura T., Suda T., Yoshida K., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Kataoka H. Osteoclasts are present in gp130-deficient mice. Endocrinology. 1997 Nov;138(11):4959–4965. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.11.5534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortylewski M., Heinrich P. C., Mackiewicz A., Schniertshauer U., Klingmüller U., Nakajima K., Hirano T., Horn F., Behrmann I. Interleukin-6 and oncostatin M-induced growth inhibition of human A375 melanoma cells is STAT-dependent and involves upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27/Kip1. Oncogene. 1999 Jun 24;18(25):3742–3753. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon L. R., White A. A., Kluger M. J. Role of IL-6 and TNF in thermoregulation and survival during sepsis in mice. Am J Physiol. 1998 Jul;275(1 Pt 2):R269–R277. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.1.R269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maione D., Di Carlo E., Li W., Musiani P., Modesti A., Peters M., Rose-John S., Della Rocca C., Tripodi M., Lazzaro D. Coexpression of IL-6 and soluble IL-6R causes nodular regenerative hyperplasia and adenomas of the liver. EMBO J. 1998 Oct 1;17(19):5588–5597. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.19.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuhara H., O'Neill E., Seki N., Ogawa T., Kusunoki C., Otsuka K., Satoh S., Niwa M., Senoh H., Fujiwara H. T cell activation-associated hepatic injury: mediation by tumor necrosis factors and protection by interleukin 6. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1529–1537. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Newen G., Küster A., Hemmann U., Keul R., Horsten U., Martens A., Graeve L., Wijdenes J., Heinrich P. C. Soluble IL-6 receptor potentiates the antagonistic activity of soluble gp130 on IL-6 responses. J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6347–6355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narazaki M., Yasukawa K., Saito T., Ohsugi Y., Fukui H., Koishihara Y., Yancopoulos G. D., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Soluble forms of the interleukin-6 signal-transducing receptor component gp130 in human serum possessing a potential to inhibit signals through membrane-anchored gp130. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1120–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehof M., Manns M. P., Trautwein C. CREB controls LAP/C/EBP beta transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jul;17(7):3600–3613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.7.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakemann T., Niehof M., Kubicka S., Fischer M., Manns M. P., Rose-John S., Trautwein C. The designer cytokine hyper-interleukin-6 is a potent activator of STAT3-dependent gene transcription in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jan 15;274(3):1257–1266. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.3.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz R., Lee C. K., Cannizzaro L. A., d'Eustachio P., Levy D. E. Essential role of STAT3 for embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 16;96(6):2846–2851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose-John S., Heinrich P. C. Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: generation and biological function. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj3000281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:621–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmacher P., Peters M., Ciliberto G., Blessing M., Lotz J., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Rose-John S. Hepatocellular hyperplasia, plasmacytoma formation, and extramedullary hematopoiesis in interleukin (IL)-6/soluble IL-6 receptor double-transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1998 Aug;153(2):639–648. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65605-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Kirschning C. J., Unbehaun A., Aberle H. P., Knope H. P., Lamping N., Ulevitch R. J., Herrmann F. The lipopolysaccharide-binding protein is a secretory class 1 acute-phase protein whose gene is transcriptionally activated by APRF/STAT/3 and other cytokine-inducible nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;16(7):3490–3503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.7.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Willson T. A., Viney E. M., Murray L. J., Rayner J. R., Jenkins B. J., Gonda T. J., Alexander W. S., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A. A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):917–921. doi: 10.1038/43206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Kishimoto T. Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:797–819. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Kaisho T., Yoshida N., Takeda J., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Stat3 activation is responsible for IL-6-dependent T cell proliferation through preventing apoptosis: generation and characterization of T cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1998 Nov 1;161(9):4652–4660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Böker K., Manns M. P. Hepatocyte and immune system: acute phase reaction as a contribution to early defence mechanisms. Gut. 1994 Sep;35(9):1163–1166. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.9.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Caelles C., van der Geer P., Hunter T., Karin M., Chojkier M. Transactivation by NF-IL6/LAP is enhanced by phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):544–547. doi: 10.1038/364544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Rakemann T., Malek N. P., Plümpe J., Tiegs G., Manns M. P. Concanavalin A-induced liver injury triggers hepatocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest. 1998 May 1;101(9):1960–1969. doi: 10.1172/JCI504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Rakemann T., Niehof M., Rose-John S., Manns M. P. Acute-phase response factor, increased binding, and target gene transcription during liver regeneration. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jun;110(6):1854–1862. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8964411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein C., Ramadori G., Gerken G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Manns M. Regulation of cytochrome P450 IID by acute phase mediators in C3H/HeJ mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):617–623. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91777-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Fausto N. Deficient liver regeneration after carbon tetrachloride injury in mice lacking type 1 but not type 2 tumor necrosis factor receptor. Am J Pathol. 1998 Jun;152(6):1577–1589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Kirillova I., Peschon J. J., Fausto N. Initiation of liver growth by tumor necrosis factor: deficient liver regeneration in mice lacking type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 18;94(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Taga T., Saito M., Suematsu S., Kumanogoh A., Tanaka T., Fujiwara H., Hirata M., Yamagami T., Nakahata T. Targeted disruption of gp130, a common signal transducer for the interleukin 6 family of cytokines, leads to myocardial and hematological disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Sun M., Samols D., Kushner I. STAT3 participates in transcriptional activation of the C-reactive protein gene by interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 19;271(16):9503–9509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.16.9503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Jones S., Hagood J. S., Fuentes N. L., Fuller G. M. STAT3 acts as a co-activator of glucocorticoid receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1997 Dec 5;272(49):30607–30610. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.49.30607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]