Abstract
BACKGROUND—In patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis, endotoxaemia is a frequent finding. Unknown mechanisms, however, prevent typical clinical symptoms of endotoxaemia in many patients. METHODS—We determined plasma levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators, ex vivo cytokine secretion capacity, and expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptors on phagocytic blood cells in 49 patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and 41 age matched healthy controls. RESULTS—In addition to increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines in cirrhotic patients, we observed consistent upregulation of the anti-inflammatory mediators interleukin 10 (IL-10) (plasma 15.75 (1.6) v 6.6 (1.3) pg/ml (p<0.001); ex-vivo 108.4 (22.0) v 40.1 (7.4) pg/ml (p<0.05)), interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (plasma 527.1 (83) v 331.4 (56) pg/ml (p<0.05); ex vivo 19.9 (3.4) v 10.2 (2.7) ng/ml (p<0.01)), and soluble TNF receptors (sTNF-R) in plasma (sTNF-RI 3157.2 (506.2) v 607.9 (300.3) pg/ml; sTNF-RII 3331.0 (506.2) v 1066.4 (225.1) pg/ml (p<0.001 for both)). Desensitisation at the target cell level was indicated by reduced expression of TNF receptor I on granulocytes (64.8 (6.5) v 40.1 (7.3)% positive cells; p<0.05) and unaltered plasma levels of soluble E-selectin. CONCLUSION—In patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis, upregulation of the pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine system and simultaneous desensitisation of effector cells could explain the restricted systemic inflammatory response to chronic endotoxaemia. This alteration in immune status may lead to impairment of host defences against infections which are frequent complications of alcoholic cirrhosis. Keywords: liver cirrhosis; lipopolysaccharide; lipopolysaccharide desensitisation; anti-inflammatory cytokines; tumour necrosis factor
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (167.9 KB).
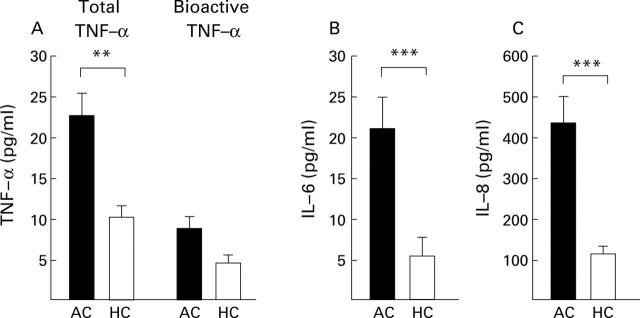
Figure 1 .
Elevated plasma levels (mean (SEM)) of the proinflammatory cytokines total tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and bioactive TNF-α (A), interleukin (IL)-6 (B), and IL-8 (C) in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (AC, n=14) compared with healthy controls (HC, n=10) in group I. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, AC v HC.
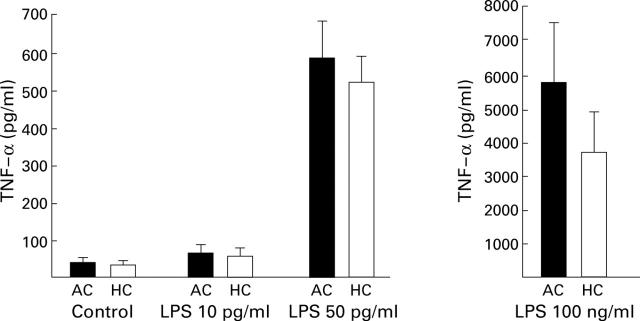
Figure 2 .
The ex vivo total tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) secretion capacity of peripheral blood leucocytes from patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (AC, n=12) was not reduced compared with that of controls (HC, n=10), irrespective of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) concentration used (group III). TNF-α concentrations (mean (SEM)) were measured in supernatants from cultures stimulated with LPS at 10 pg/ml, 50 pg/ml, and 100 ng/ml.
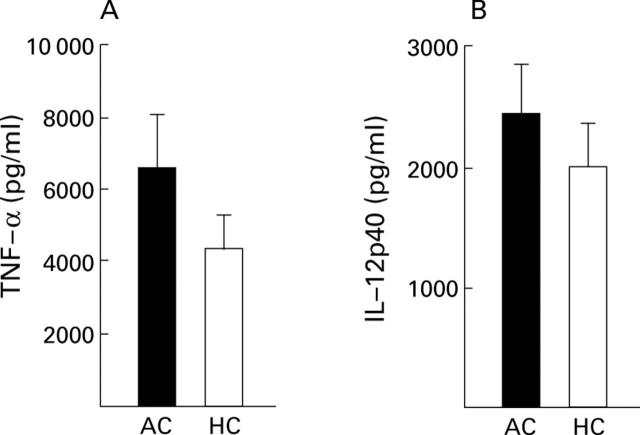
Figure 3 .
Tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) (A) and interleukin (IL)-12p40 (B) secretion capacity of peripheral blood leucocytes was not altered in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (AC, n=23) compared with healthy controls (HC, n=19) in group II. Cytokine concentrations (mean (SEM)) were determined in supernatants from cultures after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (100 ng/ml).
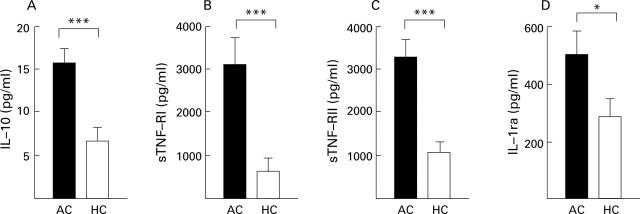
Figure 4 .
Elevated plasma levels (mean (SEM)) of anti-inflammatory mediators interleukin (IL)-10 (A), soluble tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptors I (sTNF-RI) (B) and II (sTNF-RII) (C), and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) (D) in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (AC, n=14) compared with healthy controls (HC, 10) in group I. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, AC v HC.
Figure 5 .
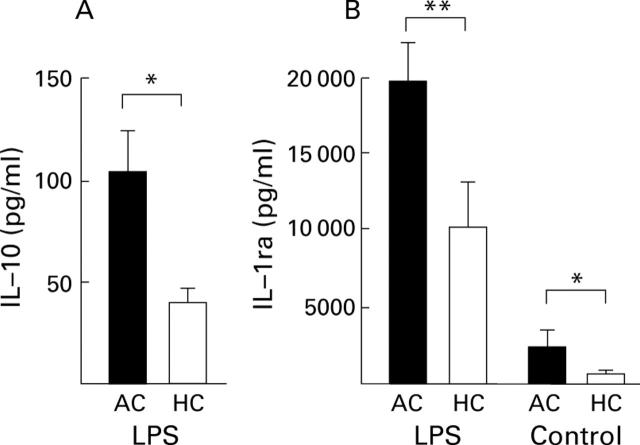
Interleukin (IL)-10 (A) and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) (B) secretion capacity of peripheral blood leucocytes was elevated in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (AC, n=23) compared with healthy controls (HC, n=19) in group II. Cytokine concentrations were measured in supernatants of whole blood cultures after stimulation with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/ml). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, AC v HC.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatti M., Chapman P., Peters M., Haskard D., Hodgson H. J. Visualising E-selectin in the detection and evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1998 Jul;43(1):40–47. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. L., Sheron N., Goka A. K., Alexander G. J., Williams R. S. Increased plasma tumor necrosis factor in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 15;112(12):917–920. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-12-917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh D. S., Barsig J., Hartung T., Randow F., Döcke W. D., Volk H. D., Wendel A. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IFN-gamma restore the systemic TNF-alpha response to endotoxin in lipopolysaccharide-desensitized mice. J Immunol. 1997 Mar 15;158(6):2862–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A., Aste-Amezaga M., Valiante N. M., Ma X., Kubin M., Trinchieri G. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) inhibits human lymphocyte interferon gamma-production by suppressing natural killer cell stimulatory factor/IL-12 synthesis in accessory cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deviere J., Content J., Denys C., Vandenbussche P., Le Moine O., Schandene L., Vaerman J. P., Dupont E. Immunoglobulin A and interleukin 6 form a positive secretory feedback loop: a study of normal subjects and alcoholic cirrhotics. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1296–1301. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91519-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deviere J., Content J., Denys C., Vandenbussche P., Schandene L., Wybran J., Dupont E. High interleukin-6 serum levels and increased production by leucocytes in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Correlation with IgA serum levels and lymphokines production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):221–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Thompson R. C. Blocking IL-1: interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in vivo and in vitro. Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90142-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floch M. H., Katz J., Conn H. O. Qualitative and quantitative relationships of the fecal flora in cirrhotic patients with portal systemic encephalopathy and following portacaval anastomosis. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jul;59(1):70–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui H., Brauner B., Bode J. C., Bode C. Plasma endotoxin concentrations in patients with alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver disease: reevaluation with an improved chromogenic assay. J Hepatol. 1991 Mar;12(2):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90933-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz E. V., Porat R., Mier J. W., Orencole S. F., Kaplanski G., Lynch E. A., Ye K., Vannier E., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Intravenous endotoxin suppresses the cytokine response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy humans. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1637–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. B., Marsano L. S., McClain C. J. Increased plasma interleukin-8 concentrations in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1993 Sep;18(3):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J. P., Jarrar D., Steckholzer U., Ertel W. Interleukin-1, -6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release is down-regulated in whole blood from septic patients. Acta Haematol. 1996;95(3-4):268–273. doi: 10.1159/000203895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffi G., Carloni V., Baldi E., Rossi M. E., Azzari C., Gresele P., Marra F., Gentilini P. Impaired superoxide anion, platelet-activating factor, and leukotriene B4 synthesis by neutrophils in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):170–177. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine O., Marchant A., De Groote D., Azar C., Goldman M., Devière J. Role of defective monocyte interleukin-10 release in tumor necrosis factor-alpha overproduction in alcoholics cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1995 Nov;22(5):1436–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., Dentener M. A., Buurman W. A. Lipopolysaccharide LPS-mediated soluble TNF receptor release and TNF receptor expression by monocytes. Role of CD14, LPS binding protein, and bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):5070–5076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim A. G., Jazrawi R. P., Levy J. H., Petroni M. L., Douds A. C., Maxwell J. D., Northfield T. C. Soluble E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1995 Apr;22(4):416–422. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. S., Lee F. Y., Lee S. D., Tsai Y. T., Lin H. C., Lu R. H., Hsu W. C., Huang C. C., Wang S. S., Lo K. J. Endotoxemia in patients with chronic liver diseases: relationship to severity of liver diseases, presence of esophageal varices, and hyperdynamic circulation. J Hepatol. 1995 Feb;22(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden A. B., Henderson J. M., Kutner M. H. Endotoxin levels measured by a chromogenic assay in portal, hepatic and peripheral venous blood in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):232–236. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackensen A., Galanos C., Wehr U., Engelhardt R. Endotoxin tolerance: regulation of cytokine production and cellular changes in response to endotoxin application in cancer patients. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 Nov-Dec;3(6):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malyak M., Smith M. F., Jr, Abel A. A., Arend W. P. Peripheral blood neutrophil production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1 beta. J Clin Immunol. 1994 Jan;14(1):20–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01541172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martich G. D., Boujoukos A. J., Suffredini A. F. Response of man to endotoxin. Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):403–416. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough A. J., O'Connor J. F. Alcoholic liver disease: proposed recommendations for the American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Nov;93(11):2022–2036. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., O'Garra A., de Waal Malefyt R., Vieira P., Mosmann T. R. Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:165–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman W., Beall L. D., Carson C. W., Hunder G. G., Graben N., Randhawa Z. I., Gopal T. V., Wiener-Kronish J., Matthay M. A. Soluble E-selectin is found in supernatants of activated endothelial cells and is elevated in the serum of patients with septic shock. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):644–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P. The role of endotoxin in liver injury. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1346–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson J., Berg N. O., Sjölund K., Stenling R., Magnusson P. H. Morphologic changes in the small intestine after chronic alcohol consumption. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1990 Feb;25(2):173–184. doi: 10.3109/00365529009107940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platzer C., Meisel C., Vogt K., Platzer M., Volk H. D. Up-regulation of monocytic IL-10 by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cAMP elevating drugs. Int Immunol. 1995 Apr;7(4):517–523. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst T., Propst A., Herold M., Judmaier G., Braunsteiner H., Vogel W. High levels of interleukin 6 and its secondary mediators in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):310–311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90060-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkovic I. A., Williams R. Abnormalities of neutrophil phagocytosis, intracellular killing and metabolic activity in alcoholic cirrhosis and hepatitis. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):252–262. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer C., Schips I., Landig J., Bode J. C., Bode C. Tumor-necrosis-factor and interleukin-6 response of peripheral blood monocytes to low concentrations of lipopolysaccharide in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Z Gastroenterol. 1995 Sep;33(9):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley A. J., MacGregor I. R., Dillon J. F., Bouchier I. A., Hayes P. C. Neutrophil activation in chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Feb;8(2):135–138. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199602000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R., Boyer T. D., Levin J. Portal and systemic bacteraemia and endotoxaemia in liver disease. Gut. 1978 Oct;19(10):935–939. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.10.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zee K. J., Kohno T., Fischer E., Rock C. S., Moldawer L. L., Lowry S. F. Tumor necrosis factor soluble receptors circulate during experimental and clinical inflammation and can protect against excessive tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4845–4849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Holtmann H., Engelmann H., Nophar Y. Sensitization and desensitization to lethal effects of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2994–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Jansen P. M., Montegut W. J., Braxton C. C., Calvano S. E., Stackpole S. A., Smith S. R., Swanson S. W., Hack C. E., Lowry S. F. Effects of IL-10 on systemic inflammatory responses during sublethal primate endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1997 Feb 15;158(4):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]