Abstract
BACKGROUND—The cytoskeleton actin network of intestinal microvilli has been found to be rapidly impaired after gluten challenge in coeliac disease (CD). The aim of this study was to investigate the presence of an immune reaction towards cytoskeleton structures such as actin filaments in CD. METHODS—Eighty three antiendomysial antibody positive CD patients (52 children and 31 adults) were studied at our outpatient clinics from 1996 to 1998 using indirect immunofluorescence, ELISA, and western blotting for antiactin (AAA) and antitissue transglutaminase (TGA) antibodies before and after a gluten free diet (GFD). Sixteen patients with smooth muscle antibody positive autoimmune hepatitis, 21 with inflammatory bowel diseases, seven with small bowel bacterial overgrowth, and 60 healthy subjects were studied as controls. RESULTS—Fifty nine of 83 CD patients (28/31 adults (90.3%); 31/52 children (59.6%)) were positive for IgA and/or IgG AAA. Seventy seven (92.7%) were positive for IgA TGA. IgA AAA were strongly correlated with more severe degrees of intestinal villous atrophy (p<0.0001; relative risk 86.17). After a GFD, AAA became undetectable within five months. CONCLUSIONS—Apart from the immune reaction against the extracellular matrix, we have described an immune reaction against the cytoskeleton in both children and adults with CD. As AAA are strongly associated with more severe degrees of villous atrophy, they may represent a useful serological marker of severe intestinal atrophy in CD. Keywords: coeliac disease; autoantibody; intestinal villous atrophy; cytoskeleton; actin; smooth muscle
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (176.4 KB).
Figure 1 .
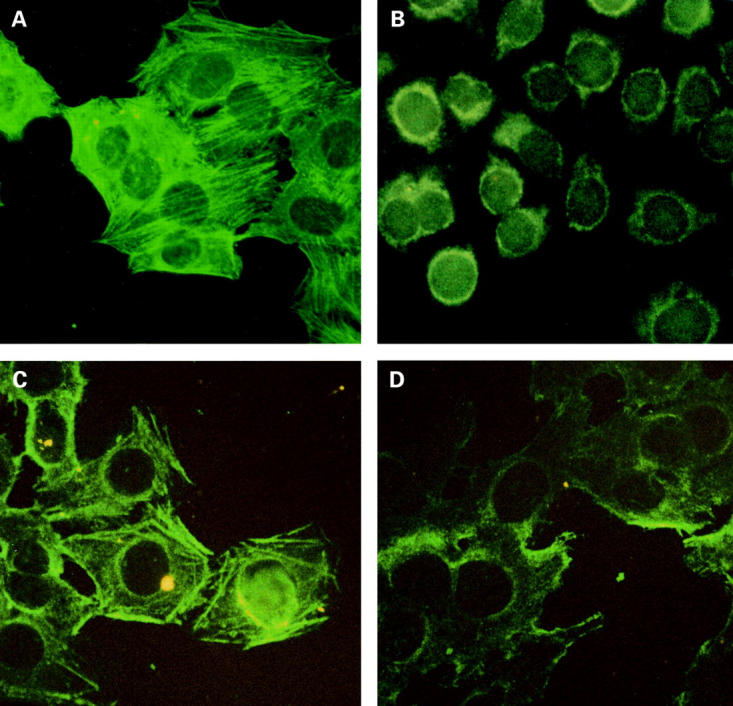
Actin stress fibre immunostaining pattern in indirect immunofluorescence of HEp-2 cells using serum from patient No 21 (see table 1), at a screening dilution of 1:40, and the FITC conjugate antihuman IgA (photomicrograph images, ×50; (A)). Typical actin stress fibres appear as long cytoplasmic parallel filaments. (B) Negative immunostaining image obtained using monoclonal antitransglutaminase antibody on HEp-2 cells (photomicrograph images, ×50). The results of actin absorption experiments using 1:1000 diluted serum are shown in (C) (before absorption) and (D) (after absorption).
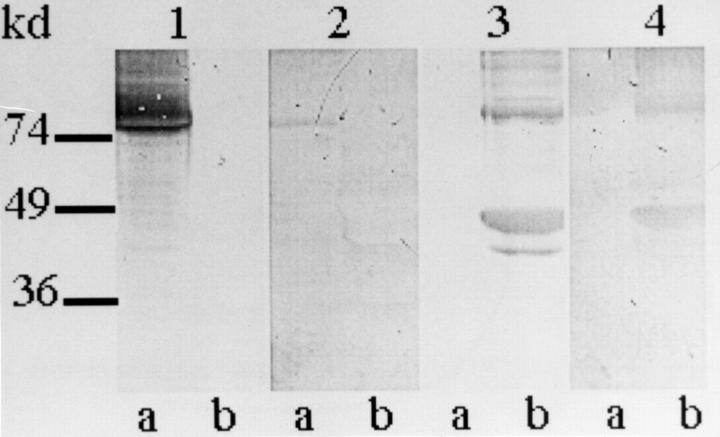
Figure 2 .
Western blotting with guinea pig liver tissue transglutaminase (tTG) (lines a) and bovine muscle actin (lines b). No 1: monoclonal anti-tTG antibody; No 2: serum from coeliac patient No 13 (see table 3); No 3: antiactin affinity antibody; No. 4: serum from coeliac patient No 2 (see table 2). Molecular mass is shown on the left.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey D. S., Freedman A. R., Price S. C., Chescoe D., Ciclitira P. J. Early biochemical responses of the small intestine of coeliac patients to wheat gluten. Gut. 1989 Jan;30(1):78–85. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Fairfax A., Swana G., Doniach D., Groeschel-Stewart U. Classification of smooth muscle autoantibodies detected by immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):403–410. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cançado E. L., Vilas-Boas L. S., Abrantes-Lemos C. P., Novo N. F., Porta G., Da Silva L. C., Laudanna A. A. Heat serum inactivation as a mandatory procedure for antiactin antibody detection in cell culture. Hepatology. 1996 May;23(5):1098–1104. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury Z. A., Barsigian C., Chalupowicz G. D., Bach T. L., Garcia-Manero G., Martinez J. Colocalization of tissue transglutaminase and stress fibers in human vascular smooth muscle cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1997 Feb 25;231(1):38–49. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.3448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente M. G., Meloni A., Obermayer-Straub P., Frau F., Manns M. P., De Virgiliis S. Two cytochromes P450 are major hepatocellular autoantigens in autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1. Gastroenterology. 1998 Feb;114(2):324–328. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja A. J., Cassani F., Cataleta M., Valentini P., Bianchi F. B. Frequency and significance of antibodies to actin in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 1996 Nov;24(5):1068–1073. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J., Gerber M., Hoofnagle J. H., Manns M., Scheuer P. J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994 Jun;19(6):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich W., Ehnis T., Bauer M., Donner P., Volta U., Riecken E. O., Schuppan D. Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med. 1997 Jul;3(7):797–801. doi: 10.1038/nm0797-797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Not T., Wang W., Uzzau S., Berti I., Tommasini A., Goldblum S. E. Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. Lancet. 2000 Apr 29;355(9214):1518–1519. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagander B., Berg N. O., Brandt L., Nordén A., Sjölund K., Stenstam M. Hepatic injury in adult coeliac disease. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):270–272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90954-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren Peterson K., Magnusson K. E., Stenhammar L., Fälth-Magnusson K. Confocal laser scanning microscopy of small-intestinal mucosa in celiac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Mar;30(3):228–234. doi: 10.3109/00365529509093269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karská K., Tucková L., Steiner L., Tlaskalová-Hogenová H., Michalak M. Calreticulin--the potential autoantigen in celiac disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 17;209(2):597–605. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayalar C., Ord T., Testa M. P., Zhong L. T., Bredesen D. E. Cleavage of actin by interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme to reverse DNase I inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 5;93(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Linder E., Miettinen A., Alfthan O. Smooth muscle antibodies of actin and "non-actin" specificity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Apr;9(4):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levee M. G., Dabrowska M. I., Lelli J. L., Jr, Hinshaw D. B. Actin polymerization and depolymerization during apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Am J Physiol. 1996 Dec;271(6 Pt 1):C1981–C1992. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.6.C1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Transglutaminase, gluten and celiac disease: food for thought. Transglutaminase is identified as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med. 1997 Jul;3(7):725–726. doi: 10.1038/nm0797-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays R. W., Beck K. A., Nelson W. J. Organization and function of the cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells: a component of the protein sorting machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molberg O., Mcadam S. N., Körner R., Quarsten H., Kristiansen C., Madsen L., Fugger L., Scott H., Norén O., Roepstorff P. Tissue transglutaminase selectively modifies gliadin peptides that are recognized by gut-derived T cells in celiac disease. Nat Med. 1998 Jun;4(6):713–717. doi: 10.1038/nm0698-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Collin P. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 1997 Jun 14;349(9067):1755–1759. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)70237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pender S. L., Tickle S. P., Docherty A. J., Howie D., Wathen N. C., MacDonald T. T. A major role for matrix metalloproteinases in T cell injury in the gut. J Immunol. 1997 Feb 15;158(4):1582–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revised criteria for diagnosis of coeliac disease. Report of Working Group of European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Aug;65(8):909–911. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.8.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D., Dieterich W., Riecken E. O. Exposing gliadin as a tasty food for lymphocytes. Nat Med. 1998 Jun;4(6):666–667. doi: 10.1038/nm0698-666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölander A., Magnusson K. E. Effects of wheat germ agglutinin on the cellular content of filamentous actin in Intestine 407 cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;47(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollid L. M., Markussen G., Ek J., Gjerde H., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Evidence for a primary association of celiac disease to a particular HLA-DQ alpha/beta heterodimer. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):345–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkanen S., Halttunen T., Laurila K., Kolho K. L., Korponay-Szabó I. R., Sarnesto A., Savilahti E., Collin P., Mäki M. Tissue transglutaminase autoantibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in detecting celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1998 Dec;115(6):1322–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terjung B., Herzog V., Worman H. J., Gestmann I., Bauer C., Sauerbruch T., Spengler U. Atypical antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies with perinuclear fluorescence in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and hepatobiliary disorders colocalize with nuclear lamina proteins. Hepatology. 1998 Aug;28(2):332–340. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek J. J., Halliday N. L., Updike D. L., Ahern-Moore J. S., Vu T. K., Liu R. W., Howard E. W. Gelatinase A activation is regulated by the organization of the polymerized actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 14;272(11):7482–7487. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.11.7482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S. Diagnosis of celiac sprue. Gastroenterology. 1998 Jul;115(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Holborow E. J. Gliadin and reticulin antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Apr 16;1(8329):874–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vajro P., Fontanella A., Mayer M., De Vincenzo A., Terracciano L. M., D'Armiento M., Vecchione R. Elevated serum aminotransferase activity as an early manifestation of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J Pediatr. 1993 Mar;122(3):416–419. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varedi M., Ghahary A., Scott P. G., Tredget E. E. Cytoskeleton regulates expression of genes for transforming growth factor-beta 1 and extracellular matrix proteins in dermal fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1997 Aug;172(2):192–199. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199708)172:2<192::AID-JCP6>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura A., Magazzù G., Greco L. Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. SIGEP Study Group for Autoimmune Disorders in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology. 1999 Aug;117(2):297–303. doi: 10.1053/gast.1999.0029900297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volta U., De Franceschi L., Lari F., Molinaro N., Zoli M., Bianchi F. B. Coeliac disease hidden by cryptogenic hypertransaminasaemia. Lancet. 1998 Jul 4;352(9121):26–29. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(97)11222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]