Abstract
BACKGROUND AND AIM—An oral glutamine load in cirrhotic patients awaiting liver transplantation was shown to cause a rise in blood ammonia and psychometric abnormalities which were reversed by hepatic transplantation. L-Ornithine-L-aspartate (LOLA) has been shown to reduce ammonia and improve psychometric function in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of LOLA in healthy patients with cirrhosis and no evidence of clinical encephalopathy after challenging the central nervous system by administration of oral glutamine. PATIENTS AND METHODS—Eight cirrhotics (Child's B or C) without transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS) and seven with TIPS underwent two oral glutamine (20 g) challenges, receiving LOLA (5 g intravenously) on one occasion and placebo on the other in random order. Psychometric tests, including choice reaction time (CRT) and number connection test, were performed before and after glutamine, together with electroencephalography and blood ammonia. RESULTS—Mean basal ammonia was 27 (SEM 5) µmol/l in non-TIPS and 76 (10) µmol/l in TIPS patients (p<0.05). Basal CRT 2 was 0.643 (0.033) s in non-TIPS and 0.825 (0.076) s in TIPS patients (p<0.02). In non-TIPS patients, ammonia increased to 36 (10) µmol/l when LOLA was administered and to 62 (13) µmol/l with placebo (p<0.02). There was no alteration in psychometric function in non-TIPS patients after glutamine when LOLA was given but when placebo was given, glutamine caused prolongation of CRT (p=0.02). Glutamine did not affect psychometric function in TIPS patients with or without LOLA. CONCLUSION—This study showed that LOLA ameliorated the deleterious psychometric effects of glutamine in Child's grade B and C patients with cirrhosis without TIPS and supports its use in clinical practice in hepatic encephalopathy. Keywords: hepatic encephalopathy; portosystemic encephalopathy; transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; L-ornithine-L-aspartate
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (101.7 KB).
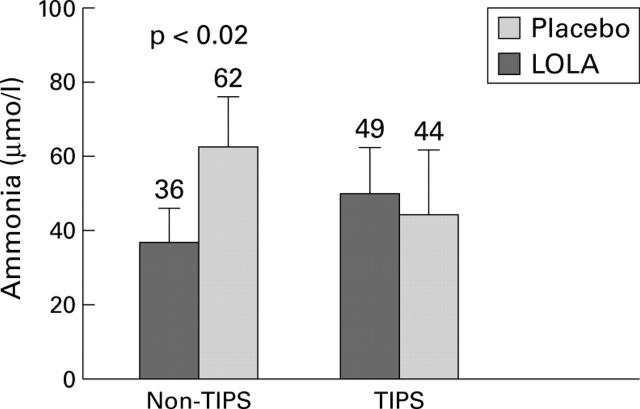
Figure 1 .
Increase in venous ammonia following glutamine challenge in TIPS and non-TIPS patients after administration of L-ornithine-L-aspartate (LOLA) or placebo (mean (SEM)).
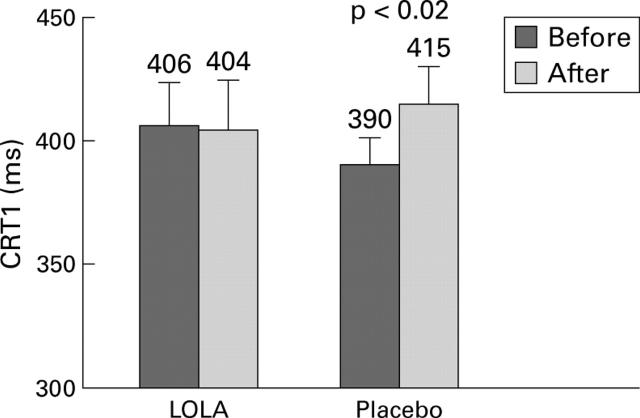
Figure 2 .
Change in choice reaction time 1 (CRT1) in non-TIPS patients before and after glutamine challenge in the L-ornithine-L-aspartate (LOLA) and placebo groups (mean (SEM)).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Henglein-Ottermann D. Der Einfluss von Ornithin-aspartat auf die experimentell erzeugte Hyperammoniämie. Klinisch-experimentelle Studie. Ther Ggw. 1976 Sep;115(9):1504–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizenga J. R., Tangerman A., Gips C. H. A rapid method for blood ammonia determination using the new blood ammonia checker (BAC) II. Clin Chim Acta. 1992 Sep 15;210(1-2):153–155. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(92)90054-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalan R., Seery J. P., Taylor-Robinson S. D. Review article: pathogenesis and treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Oct;10(5):681–697. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1996.58200000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kircheis G., Nilius R., Held C., Berndt H., Buchner M., Görtelmeyer R., Hendricks R., Krüger B., Kuklinski B., Meister H. Therapeutic efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hepatology. 1997 Jun;25(6):1351–1360. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte W., Wiltfang J., Schindler C., Münke H., Unterberg K., Zumhasch U., Figulla H. R., Werner G., Hartmann H., Ramadori G. Portosystemic hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with cirrhosis: clinical, laboratory, psychometric, and electroencephalographic investigations. Hepatology. 1998 Nov;28(5):1215–1225. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppong K. N., Al-Mardini H., Thick M., Record C. O. Oral glutamine challenge in cirrhotics pre- and post-liver transplantation: a psychometric and analyzed EEG study. Hepatology. 1997 Oct;26(4):870–876. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record C. O. Neurochemistry of hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1991 Nov;32(11):1261–1263. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.11.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees C. J., Hudson M., Record C. O. Therapeutic modalities in portal hypertension. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997 Jan;9(1):9–11. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199701000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C., Michalak A., Pannunzio P., Therrien G., Quack G., Kircheis G., Butterworth R. F. L-ornithine-L-aspartate in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy: therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of action. Metab Brain Dis. 1998 Jun;13(2):147–157. doi: 10.1023/a:1020613314572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staedt U., Leweling H., Gladisch R., Kortsik C., Hagmüller E., Holm E. Effects of ornithine aspartate on plasma ammonia and plasma amino acids in patients with cirrhosis. A double-blind, randomized study using a four-fold crossover design. J Hepatol. 1993 Nov;19(3):424–430. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauch S., Kircheis G., Adler G., Beckh K., Ditschuneit H., Görtelmeyer R., Hendricks R., Heuser A., Karoff C., Malfertheiner P. Oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate therapy of chronic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Hepatol. 1998 May;28(5):856–864. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]