Abstract
BACKGROUND—There is considerable evidence indicating that the severity of hepatic damage in individuals with cholestatic liver disease is causally associated with the extent of intrahepatic oxidative stress. Increased levels or accelerated generation of reactive oxygen species and toxic degradative products of lipid peroxidation have been reported in the plasma of individuals with chronic liver disease and animal models of liver disease. Hence, by virtue of their increased presence in the circulation, it is not unreasonable to suppose that they may account for extrahepatic tissue damage in chronic liver disease. MATERIALS AND METHODS—This hypothesis was tested by determining plasma levels of the ubiquitous antioxidant glutathione (GSH) and lipid peroxides (LP), together with assessment of the extent of lipid peroxidation in the kidney, brain, and heart, in 24 day chronically bile duct ligated (CBDL) rats. The extent of lipid peroxidation in tissues was based on measurement of conjugated dienes, lipid peroxides, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Data were compared with identical data collected from unoperated control, pair fed, 24 day bile duct manipulated (sham operated), and pair fed sham operated rats. RESULTS—In CBDL rats, total and reduced plasma GSH levels were almost half those determined in all control rats. Plasma, kidney, and heart LP levels were significantly increased in CBDL rats compared with controls. MDA levels were significantly higher in the kidney, brain, and heart homogenates prepared from CBDL rats compared with MDA content measured in tissue homogenates prepared from the four groups of control rats. CONCLUSIONS—Our data show that experimental cholestatic liver disease is associated with increased lipid peroxidation in the kidney, brain, and heart. Hence we have concluded that the oxidative stress in cholestatic liver disease is a systemic phenomenon probably encompassing all tissues and organs, even those separated by the blood-brain barrier. Keywords: cirrhosis; oxidative stress; lipid peroxidation; lipid peroxides; conjugated dienes; malondialdehyde; glutathione
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (129.4 KB).
Figure 1 .
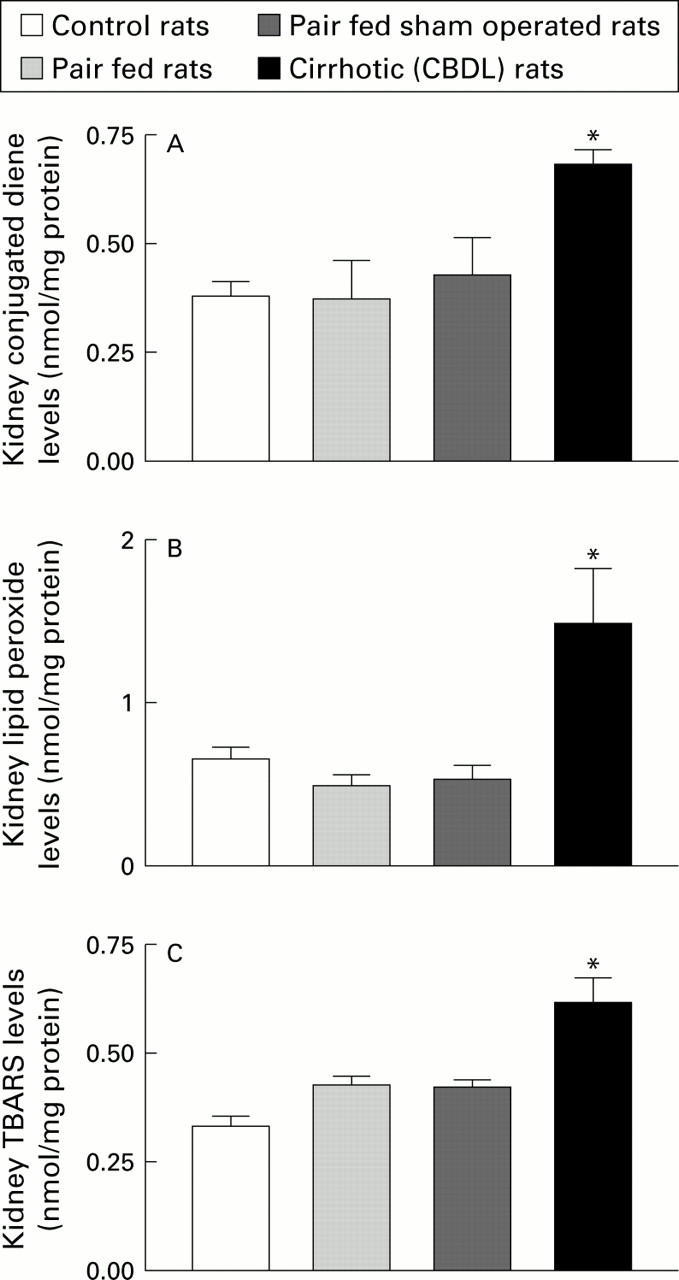
Extent of lipid peroxidation, measured as content of conjugated dienes (A), lipid peroxides (B), and malondialdehyde (TBARS) (C) in kidney homogenates prepared from control, pair fed, pair fed sham operated, and chronic bile duct ligated (CBDL) rats (n=7-17). (There were no data on sham operated rats (see text for details).) *p<0.05 compared with the three control groups..
Figure 2 .
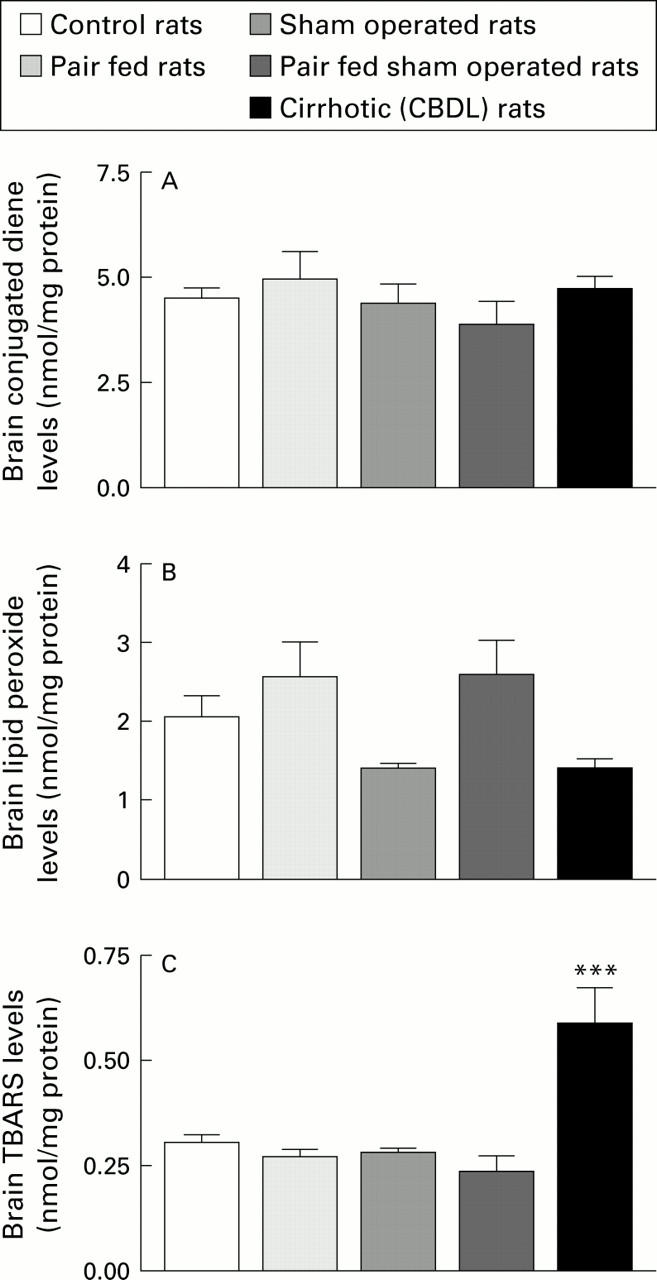
Extent of lipid peroxidation, measured as content of conjugated dienes (A), lipid peroxides (B), and malondialdehyde (TBARS) (C) in brain homogenates prepared from control, pair fed, sham operated, pair fed sham operated, and chronic bile duct ligated (CBDL) rats (n=7-17). ***p<0.001 compared with the four control groups.
Figure 3 .
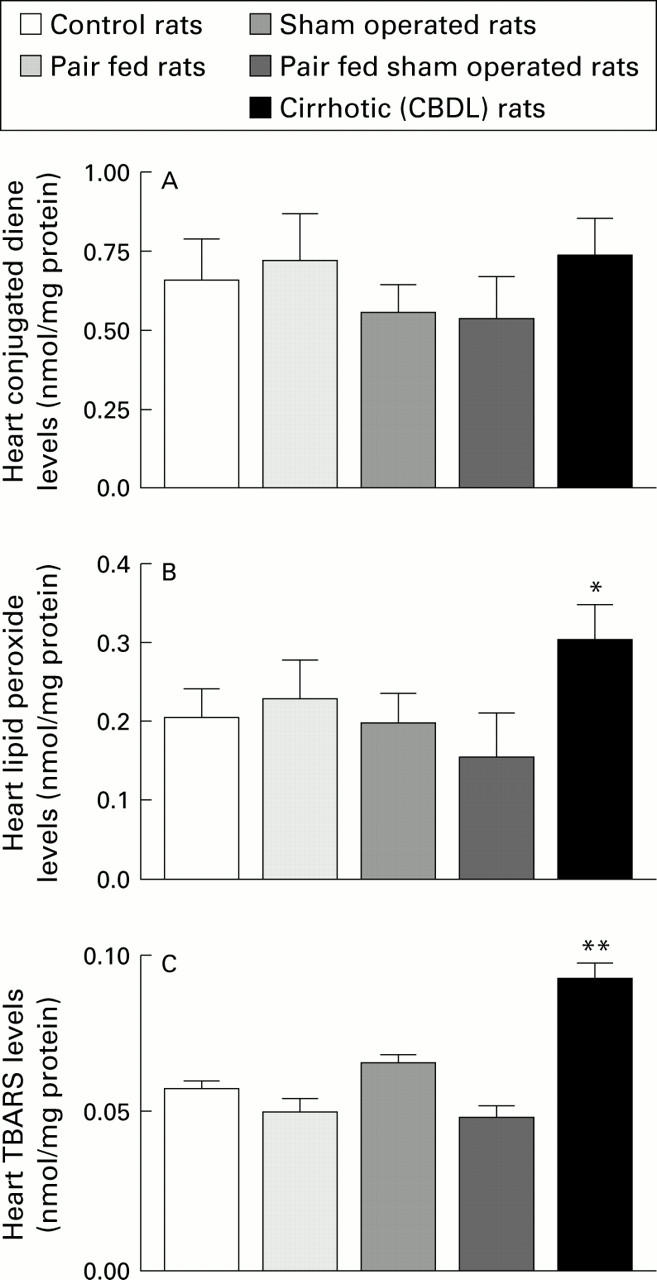
Extent of lipid peroxidation, measured as content of conjugated dienes (A), lipid peroxides (B), and malondialdehyde (TBARS) (C) in heart homogenates prepared from control, pair fed, sham operated, pair fed sham operated, and chronic bile duct ligated (CBDL) rats (n=7-17). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared with the four control groups.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. D., Jr, Lauterburg B. H., Mitchell J. R. Plasma glutathione and glutathione disulfide in the rat: regulation and response to oxidative stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Dec;227(3):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asayama K., Hayashibe H., Dobashi K., Niitsu T., Miyao A., Kato K. Antioxidant enzyme status and lipid peroxidation in various tissues of diabetic and starved rats. Diabetes Res. 1989 Oct;12(2):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M. E. Endotoxin, bile salts and renal function in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1976 Oct;63(10):774–778. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800631011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basile A. S., Jones E. A. Ammonia and GABA-ergic neurotransmission: interrelated factors in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 1997 Jun;25(6):1303–1305. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlett B. S., Stadtman E. R. Protein oxidation in aging, disease, and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 15;272(33):20313–20316. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.33.20313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Bugianesi E., Ronchi M., Fabbri A., Zoli M., Marchesini G. Glutathione kinetics in normal man and in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1997 Mar;26(3):606–613. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80426-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomzon A., Holt S., Moore K. Bile acids, oxidative stress, and renal function in biliary obstruction. Semin Nephrol. 1997 Nov;17(6):549–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomzon A., Jacob G., Lee S. S., Meddings J. In vitro vascular responsiveness to norepinephrine in experimental portal hypertension. Clin Invest Med. 1991 Feb;14(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceryak S., Bouscarel B., Fromm H. Comparative binding of bile acids to serum lipoproteins and albumin. J Lipid Res. 1993 Oct;34(10):1661–1674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman K. H., Slater T. F. An introduction to free radical biochemistry. Br Med Bull. 1993 Jul;49(3):481–493. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. F., Mo L. R., Lin R. C., Kuo J. Y., Chang K. K., Liao C., Lu F. J. Increase of resting levels of superoxide anion in the whole blood of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23(4):672–679. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(97)00057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper H. H., Hadley M. Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:421–431. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabris C., Pirisi M., Panozzo M. P., Soardo G., Toniutto P., Hocza V., Bartoli E. Intensity of inflammatory damage and serum lipid peroxide concentrations in liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Apr;46(4):364–367. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.4.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando B., Marley R., Holt S., Anand R., Harry D., Sanderson P., Smith R., Hamilton G., Moore K. N-acetylcysteine prevents development of the hyperdynamic circulation in the portal hypertensive rat. Hepatology. 1998 Sep;28(3):689–694. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman B., Oiknine J., Aviram M. Iron induces lipid peroxidation in cultured macrophages, increases their ability to oxidatively modify LDL, and affects their secretory properties. Atherosclerosis. 1994 Nov;111(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouma D. J., Roughneen P. T., Kumar S., Moody F. G., Rowlands B. J. Changes in nutritional status associated with obstructive jaundice and biliary drainage in rats. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Sep;44(3):362–369. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/44.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin Chem. 1995 Dec;41(12 Pt 2):1819–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Reactive oxygen species in living systems: source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am J Med. 1991 Sep 30;91(3C):14S–22S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen J. H., Ring-Larsen H., Christensen N. J. Sympathetic nervous activity in cirrhosis. A survey of plasma catecholamine studies. J Hepatol. 1985;1(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley A. E., Cheeseman K. H. Measuring free radical reactions in vivo. Br Med Bull. 1993 Jul;49(3):494–505. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob G., Bishara B., Lee S. S., Hilzenart N., Bomzon A. Cardiovascular responses to serotonin in experimental liver disease. Hepatology. 1991 Dec;14(6):1235–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata S., Chitranukroh A., Owen J. S., McIntyre N. Membrane lipid changes in erythrocytes, liver and kidney in acute and chronic experimental liver disease in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 9;896(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinugasa T., Uchida K., Kadowaki M., Takase H., Nomura Y., Saito Y. Effect of bile duct ligation on bile acid metabolism in rats. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krähenbühl S., Talos C., Lauterburg B. H., Reichen J. Reduced antioxidative capacity in liver mitochondria from bile duct ligated rats. Hepatology. 1995 Aug;22(2):607–612. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840220234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen J. B., Rajagopalan S., Galis Z., Tarpey M., Freeman B. A., Harrison D. G. Role of superoxide in angiotensin II-induced but not catecholamine-induced hypertension. Circulation. 1997 Feb 4;95(3):588–593. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.3.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljubuncic P., Fuhrman B., Oiknine J., Aviram M., Bomzon A. Effect of deoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid on lipid peroxidation in cultured macrophages. Gut. 1996 Sep;39(3):475–478. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Z., Lee S. S. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy: getting to the heart of the matter. Hepatology. 1996 Aug;24(2):451–459. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak A., Rose C., Buu P. N., Butterworth R. F. Evidence for altered central noradrenergic function in experimental acute liver failure in the rat. Hepatology. 1998 Feb;27(2):362–368. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. D., Moore K. P., Awad J. A., Ravenscraft M. D., Marini G., Badr K. F., Williams R., Roberts L. J., 2nd Marked overproduction of non-cyclooxygenase derived prostanoids (F2-isoprostanes) in the hepatorenal syndrome. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):417–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriel P., Suarez O. R. Role of lipid peroxidation in biliary obstruction in the rat. J Appl Toxicol. 1994 Nov-Dec;14(6):423–426. doi: 10.1002/jat.2550140607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Sekiya C., Ohhira M., Ohhira M., Namiki M., Endo Y., Suzuki K., Matsuda Y., Taniguchi N. Elevated level of serum Mn-superoxide dismutase in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: possible involvement of free radicals in the pathogenesis in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Nov;118(5):476–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis V., Kollinger M., Fabre M., Holstege A., Poynard T., Bedossa P. In situ detection of lipid peroxidation by-products in chronic liver diseases. Hepatology. 1997 Jul;26(1):135–142. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1997.v26.pm0009214462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parola M., Leonarduzzi G., Robino G., Albano E., Poli G., Dianzani M. U. On the role of lipid peroxidation in the pathogenesis of liver damage induced by long-standing cholestasis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;20(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(96)02055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen H. E., Ranek L., Andreasen P. B. The hepatic glutathione content in liver diseases. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1981 Oct;41(6):573–576. doi: 10.3109/00365518109090500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratico D., Iuliano L., Basili S., Ferro D., Camastra C., Cordova C., FitzGerald G. A., Violi F. Enhanced lipid peroxidation in hepatic cirrhosis. J Investig Med. 1998 Feb;46(2):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said O., Bomzon A. The effect of bile duct manipulation and pair-feeding on peripheral vascular neuroeffector mechanisms: in vitro studies. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1995 Aug;33(4):205–212. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(95)00017-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder E. T., Finn A. F., Jr, Hueber P. Suppression of vascular prostacyclin generation by jaundiced serum: relation to lipid peroxides. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Dec;112(6):784–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen A. A., Abd El-Fattah A., Gad M. Z. Effect of various stressors on the level of lipid peroxide, antioxidants and Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity in rat brain. Experientia. 1996 Apr 15;52(4):336–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01919536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singal P. K., Beamish R. E., Dhalla N. S. Potential oxidative pathways of catecholamines in the formation of lipid peroxides and genesis of heart disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;161:391–401. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4472-8_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Dhalla A. K., Seneviratne C., Singal P. K. Oxidative stress and heart failure. Mol Cell Biochem. 1995 Jun 7;147(1-2):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00944786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Shackleton G., Ah-Sing E., Chakraborty J., Bailey M. E. Antioxidant defenses in the bile duct-ligated rat. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1625–1629. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol R. J., Devereaux M., Khandwala R. A. Effect of dietary lipid and vitamin E on mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and hepatic injury in the bile duct-ligated rat. J Lipid Res. 1991 Aug;32(8):1349–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol R. J., Devereaux M., Khandwala R., O'Brien K. Evidence for involvement of oxygen free radicals in bile acid toxicity to isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1993 May;17(5):869–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol R. J., Winklhofer-Roob B. M., Devereaux M. W., McKim J. M., Jr Generation of hydroperoxides in isolated rat hepatocytes and hepatic mitochondria exposed to hydrophobic bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1995 Oct;109(4):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90585-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. Y., Lee K. T., Liu T. Z. Evidence for accelerated generation of hydroxyl radicals in experimental obstructive jaundice of rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998 Mar 15;24(5):732–737. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(97)00330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. Y., Lee K. T., Tsai S. M., Lee S. C., Yu H. S. Changes of lipid peroxide levels in blood and liver tissue of patients with obstructive jaundice. Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Apr 16;215(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(93)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Yamashita S., Fujisawa A., Kokura S., Yoshikawa T. Oxidative stress in patients with hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatoma evaluated by plasma antioxidants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jun 9;247(1):166–170. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Saadani M., Esterbauer H., el-Sayed M., Goher M., Nassar A. Y., Jürgens G. A spectrophotometric assay for lipid peroxides in serum lipoproteins using a commercially available reagent. J Lipid Res. 1989 Apr;30(4):627–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


