Abstract
BACKGROUND AND AIMS—Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, both of which are multifactorial diseases involving the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. A region on chromosome 12 centred around the marker locus D12S83 has previously been associated with IBD predisposition. The aim of the study was to investigate this genetic region in an independent panel of European families affected by Crohn's disease. METHODS—A sample of 95 families with two or more affected relatives and 75 simplex nuclear families were genotyped for 19 microsatellite loci located on chromosome 12. A search for linkage and linkage disequilibrium was performed using non-parametric two point and multipoint analyses with the Analyze and Genehunter packages. RESULTS—No evidence of linkage or linkage disequilibrium was observed for any of the marker loci, including D12S83 (p=0.35 for the two point linkage test). Multipoint linkage analysis also failed to reveal positive linkage on chromosome 12. Power calculations allowed us to reject the hypothesis that the genetic region of chromosome 12 centred on D12S83 contains a susceptibility locus with a relative risk (λs) equal to or greater than 2.0 in these families. CONCLUSION—Failure to detect linkage or linkage disequilibrium in these families suggests that the chromosome 12 locus previously reported to be associated with genetic predisposition to IBD does not play a role in all European family samples. This observation is compatible with heterogeneity in the genetic basis of susceptibility to the disease and/or exposure to various environmental factors among Caucasian families. Keywords: chromosome 12; inflammatory bowel disease; Crohn's disease; linkage analyses; replication study
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (173.4 KB).
Figure 1 .

Linkage map of chromosome 12 markers. The genetic map was derived from genotyping data of 170 families with Crohn's disease and generated by the Crimap program. The markers used were selected from the ABI Prism linkage mapping set version 1.0 and from the Genethon database (http://www.genethon.fr).
Figure 2 .
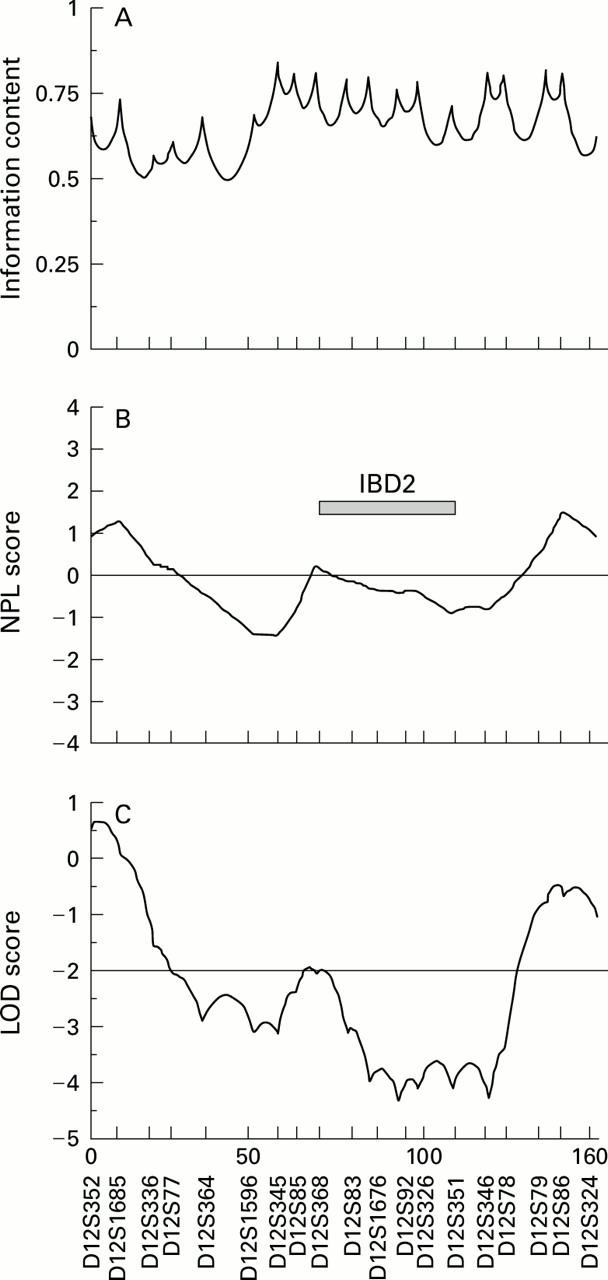
Multipoint linkage analyses of chromosome 12 in 95 multiplex families with Crohn's disease (CD) using the Genehunter package. (A) Information content; (B) multipoint non-parametric linkage (NPL) statistics. The region implicated by Satsangi et al9 containing the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) susceptibility locus is indicated by a shaded box. (C) Exclusion map calculated for a hypothetical locus with a relative risk λs=2. The exclusion threshold of LOD score (−2) is indicated.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brant S. R., Fu Y., Fields C. T., Baltazar R., Ravenhill G., Pickles M. R., Rohal P. M., Mann J., Kirschner B. S., Jabs E. W. American families with Crohn's disease have strong evidence for linkage to chromosome 16 but not chromosome 12. Gastroenterology. 1998 Nov;115(5):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh J. A., Callen D. F., Wilson S. R., Stanford P. M., Sraml M. E., Gorska M., Crawford J., Whitmore S. A., Shlegel C., Foote S. Analysis of Australian Crohn's disease pedigrees refines the localization for susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16. Ann Hum Genet. 1998 Jul;62(Pt 4):291–298. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-1809.1998.6240291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho J. H., Nicolae D. L., Gold L. H., Fields C. T., LaBuda M. C., Rohal P. M., Pickles M. R., Qin L., Fu Y., Mann J. S. Identification of novel susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosomes 1p, 3q, and 4q: evidence for epistasis between 1p and IBD1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 23;95(13):7502–7507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr R. H., Barmada M. M., Zhang L., Davis S., Preston R. A., Chensny L. J., Brown J. L., Ehrlich G. D., Weeks D. E., Aston C. E. Linkage and association between inflammatory bowel disease and a locus on chromosome 12. Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Jul;63(1):95–100. doi: 10.1086/301929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugot J. P., Laurent-Puig P., Gower-Rousseau C., Olson J. M., Lee J. C., Beaugerie L., Naom I., Dupas J. L., Van Gossum A., Orholm M. Mapping of a susceptibility locus for Crohn's disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1996 Feb 29;379(6568):821–823. doi: 10.1038/379821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Reeve-Daly M. P., Lander E. S. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1347–1363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. Faster multipoint linkage analysis using Fourier transforms. J Comput Biol. 1998 Spring;5(1):1–7. doi: 10.1089/cmb.1998.5.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard-Jones J. E. Classification of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;170:2–19. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirza M. M., Lee J., Teare D., Hugot J. P., Laurent-Puig P., Colombel J. F., Hodgson S. V., Thomas G., Easton D. F., Lennard-Jones J. E. Evidence of linkage of the inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility locus on chromosome 16 (IBD1) to ulcerative colitis. J Med Genet. 1998 Mar;35(3):218–221. doi: 10.1136/jmg.35.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Yang H. Y., Yamamoto K. K., Zhao H. Y., Ma Y., Bentley L. G., Huang Z., Gerwehr S., Pressman S., McElree C. Susceptibility locus for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16 has a role in Crohn's disease, but not in ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Oct;5(10):1679–1683. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.10.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes M., Satsangi J., Lathrop G. M., Bell J. I., Jewell D. P. Susceptibility loci in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1996 Dec 7;348(9041):1588–1588. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux J. D., Daly M. J., Green T., Stone V., Lander E. S., Hudson T. J., Steinhart A. H., Bull S., Cohen Z., Greenberg G. Absence of linkage between inflammatory bowel disease and selected loci on chromosomes 3, 7, 12, and 16. Gastroenterology. 1998 Nov;115(5):1062–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satsangi J., Parkes M., Louis E., Hashimoto L., Kato N., Welsh K., Terwilliger J. D., Lathrop G. M., Bell J. I., Jewell D. P. Two stage genome-wide search in inflammatory bowel disease provides evidence for susceptibility loci on chromosomes 3, 7 and 12. Nat Genet. 1996 Oct;14(2):199–202. doi: 10.1038/ng1096-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


