Abstract
BACKGROUND—Platelet activating factor (PAF) is believed to amplify the activity of key mediators of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in acute pancreatitis, resulting in multiorgan dysfunction syndrome. We tested the hypothesis that a potent PAF antagonist, lexipafant, could dampen SIRS and reduce organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. METHODS—We conducted a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, multicentre trial of lexipafant (100 mg/24 hours intravenously for seven days commenced within 72 hours of the onset of symptoms) involving 290 patients with an APACHE II score >6. Power calculations assumed that complications would be reduced from 40% to 24%. Secondary end points studied included severity of organ failure, markers of the inflammatory response, and mortality rate. FINDINGS—Overall, 80/138 (58%) patients in the placebo group and 85/148 (57%) in the lexipafant group developed one or more organ failures. The primary hypothesis was invalidated by the unexpected finding that 44% of patients had organ failure on entry into the study; only 39 (14%) developed new organ failure. Organ failure scores were reduced in the lexipafant group only on day 3: median change −1 (range −4 to +8) versus 0 (−4 to +10) in the placebo group (p=0.04). Systemic sepsis affected fewer patients in the lexipafant group (13/138 v 4/148; p=0.023). Local complications occurred in 41/138 (30%) patients in the placebo group and in 30/148 (20%) in the lexipafant group (20%; p=0.065); pseudocysts developed in 19 (14%) and eight (5%) patients, respectively (p=0.025). Deaths attributable to acute pancreatitis were not significantly different. Interleukin 8, a marker of neutrophil activation, and E-selectin, a marker of endothelial damage, decreased more rapidly in the lexipafant group (both p<0.05); however, absolute values were not different between the two groups. INTERPRETATION—The high incidence of organ failure within 72 hours of the onset of symptoms undermined the primary hypothesis, and power calculations for future studies in severe acute pancreatitis will need to allow for this. Lexipafant had no effect on new organ failure during treatment. This adequately powered study has shown that antagonism of PAF activity on its own is not sufficient to ameliorate SIRS in severe acute pancreatitis Keywords: platelet activating factor; organ failure; systemic inflammatory response syndrome; lexipafant; acute pancreatitis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (182.0 KB).
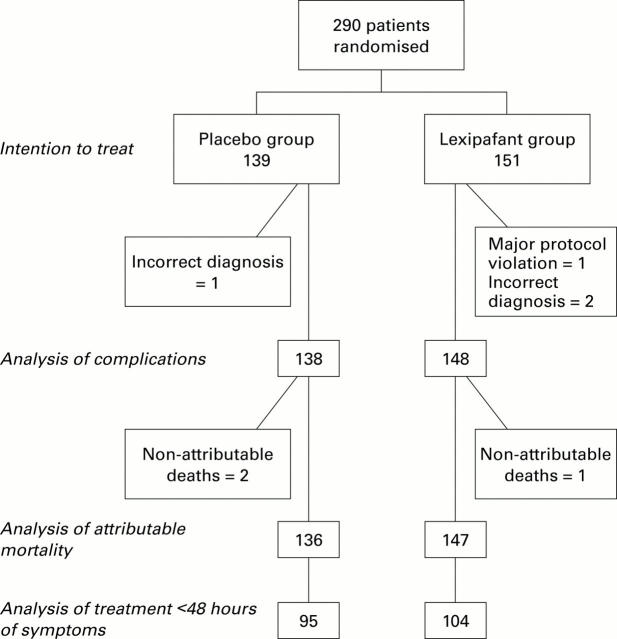
Figure 1 .
Summary of patients treated. A total of 2340 patients were screened; 379 were eligible and 291 were randomised. One patient withdrew after randomisation. Treatment allocations, exclusions, and non-attributable deaths showing the basis for analysis of outcome by intention to treat, complications, and attributable mortality.
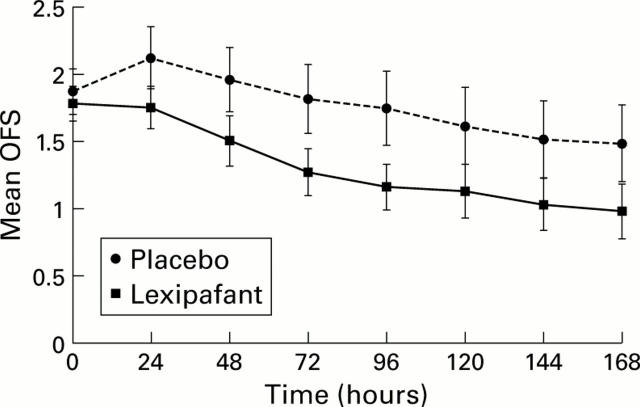
Figure 2 .
Mean organ failure scores (OFS) in the placebo and lexipafant groups (mean (SEM)). Values observed on day 3 were significantly different in the placebo and treatment groups (p=0.039).
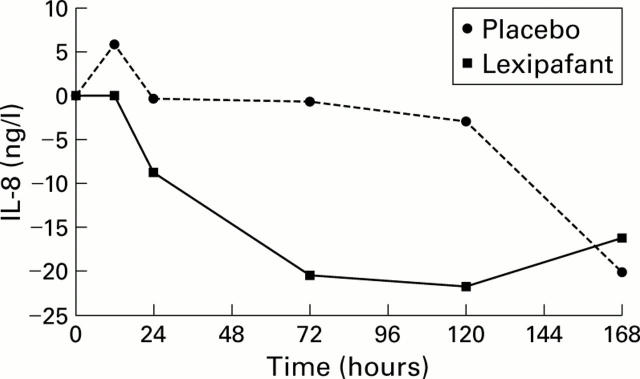
Figure 3 .
Median (interquartile range) changes in interleukin 8 (IL-8) levels from baseline values given in the text. Values observed 12 hours after the start of therapy were significantly different (p=0.006, Wilcoxon rank sum test). Median area under the curve (AUC) for placebo was 0 (−499 to 9820) and for lexipafant -1.53 (−3890 to 1190) (p=0.003).
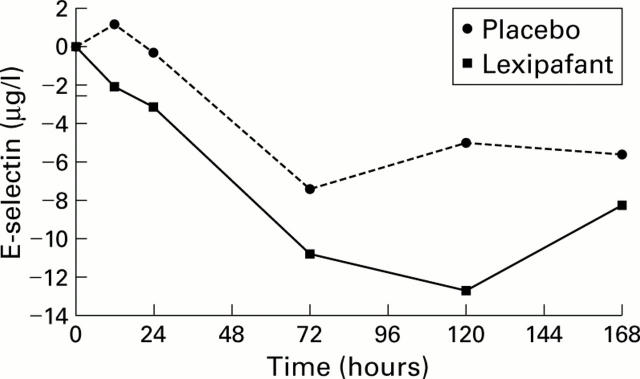
Figure 4 .
Median (interquartile range) changes in E-selectin levels from the baseline values given in the text. Values observed 12 hours after the start of therapy were significantly different (p=0.005, Wilcoxon rank sum test). Median area under the curve (AUC) for placebo was −0.0 (−24 to 130) and for lexipafant −1.3 (−95 to 77) (p=0.03).
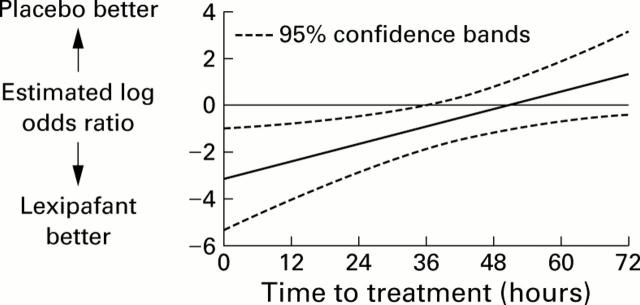
Figure 5 .
Relationship between duration of symptoms before treatment and risk of death, expressed as log odds ratio of death in the lexipafant group compared with the placebo group. Solid line, estimated ratio; broken lines, 95% confidence intervals.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert D. H., Conway R. G., Magoc T. J., Tapang P., Rhein D. A., Luo G., Holms J. H., Davidsen S. K., Summers J. B., Carter G. W. Properties of ABT-299, a prodrug of A-85783, a highly potent platelet activating factor receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Jun;277(3):1595–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Balk R. A., Cerra F. B., Dellinger R. P., Fein A. M., Knaus W. A., Schein R. M., Sibbald W. J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992 Jun;101(6):1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Toward a theory regarding the pathogenesis of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: what we do and do not know about cytokine regulation. Crit Care Med. 1996 Jan;24(1):163–172. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199601000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., 3rd A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg. 1993 May;128(5):586–590. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420170122019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelli G., Montrucchio G., Gaia E., Dughera L., Corvetti G., Gubetta L. Experimental acute pancreatitis induced by platelet activating factor in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan S. T., Lai E. C., Mok F. P., Lo C. M., Zheng S. S., Wong J. Early treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis by endoscopic papillotomy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 28;328(4):228–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formela L. J., Galloway S. W., Kingsnorth A. N. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1995 Jan;82(1):6–13. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formela L. J., Wood L. M., Whittaker M., Kingsnorth A. N. Amelioration of experimental acute pancreatitis with a potent platelet-activating factor antagonist. Br J Surg. 1994 Dec;81(12):1783–1785. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800811224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsmark C. E., Toskes P. P. Acute pancreatitis. Medical management. Crit Care Clin. 1995 Apr;11(2):295–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fölsch U. R., Nitsche R., Lüdtke R., Hilgers R. A., Creutzfeldt W. Early ERCP and papillotomy compared with conservative treatment for acute biliary pancreatitis. The German Study Group on Acute Biliary Pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jan 23;336(4):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199701233360401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal H. P., Mohey el Din A., Gaber L., Kotb M., Gaber A. O. Amelioration of the physiologic and biochemical changes of acute pancreatitis using an anti-TNF-alpha polyclonal antibody. Am J Surg. 1994 Jan;167(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross V., Leser H. G., Heinisch A., Schölmerich J. Inflammatory mediators and cytokines--new aspects of the pathophysiology and assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis? Hepatogastroenterology. 1993 Dec;40(6):522–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsnorth A. N., Galloway S. W., Formela L. J. Randomized, double-blind phase II trial of Lexipafant, a platelet-activating factor antagonist, in human acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1995 Oct;82(10):1414–1420. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800821039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Dembinski A., Konturek P. J., Warzecha Z., Jaworek J., Gustaw P., Tomaszewska R., Stachura J. Role of platelet activating factor in pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis in rats. Gut. 1992 Sep;33(9):1268–1274. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.9.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larvin M., McMahon M. J. APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach S. D., Gorelick F. S., Modlin I. M. New perspectives on acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;192:29–38. doi: 10.3109/00365529209095976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt U., Fayyazzi A., Seidensticker F., Stöckmann F., Söling H. D., Creutzfeldt W. Influence of a platelet-activating factor antagonist on severe pancreatitis in two experimental models. Int J Pancreatol. 1992 Oct;12(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF02924640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luiten E. J., Hop W. C., Lange J. F., Bruining H. A. Controlled clinical trial of selective decontamination for the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1995 Jul;222(1):57–65. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199507000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay C. J., Curran F., Sharples C., Baxter J. N., Imrie C. W. Prospective placebo-controlled randomized trial of lexipafant in predicted severe acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1997 Sep;84(9):1239–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay C. J., Evans S., Sinclair M., Carter C. R., Imrie C. W. High early mortality rate from acute pancreatitis in Scotland, 1984-1995. Br J Surg. 1999 Oct;86(10):1302–1305. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoptolemos J. P., Carr-Locke D. L., London N. J., Bailey I. A., James D., Fossard D. P. Controlled trial of urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment for acute pancreatitis due to gallstones. Lancet. 1988 Oct 29;2(8618):979–983. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Schulz H. U. Current conservative treatment of acute pancreatitis: evidence from animal and human studies. Hepatogastroenterology. 1993 Dec;40(6):538–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H. Fatal pancreatitis, a consequence of excessive leukocyte stimulation? Int J Pancreatol. 1988 Mar;3(2-3):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02798921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainio V., Kemppainen E., Puolakkainen P., Taavitsainen M., Kivisaari L., Valtonen V., Haapiainen R., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E. Early antibiotic treatment in acute necrotising pancreatitis. Lancet. 1995 Sep 9;346(8976):663–667. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Murata A., Uda K., Toda H., Kato T., Hayashida H., Matsuura N., Mori T. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist modifies the changes in vital organs induced by acute necrotizing pancreatitis in a rat experimental model. Crit Care Med. 1995 May;23(5):901–908. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199505000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner S., Sica G., Hughes M., Noordhoek E., Feng S., Zinner M., Banks P. A. Relationship of necrosis to organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1997 Sep;113(3):899–903. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl W., Isenmann R., Curti G., Vogel R., Beger H. G., Büchler M. W. Influence of etiology on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1996 Nov;13(4):335–343. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199611000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Laethem J. L., Marchant A., Delvaux A., Goldman M., Robberecht P., Velu T., Devière J. Interleukin 10 prevents necrosis in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jun;108(6):1917–1922. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable M. E., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Platelet-activating factor: a phospholipid autacoid with diverse actions. J Lipid Res. 1993 May;34(5):691–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Heath D. I., Imrie C. W. Prediction of outcome in acute pancreatitis: a comparative study of APACHE II, clinical assessment and multiple factor scoring systems. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1260–1264. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. G., Manji M., Neoptolemos J. P. Acute pancreatitis as a model of sepsis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998 Jan;41 (Suppl A):51–63. doi: 10.1093/jac/41.suppl_1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]