Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (169.5 KB).
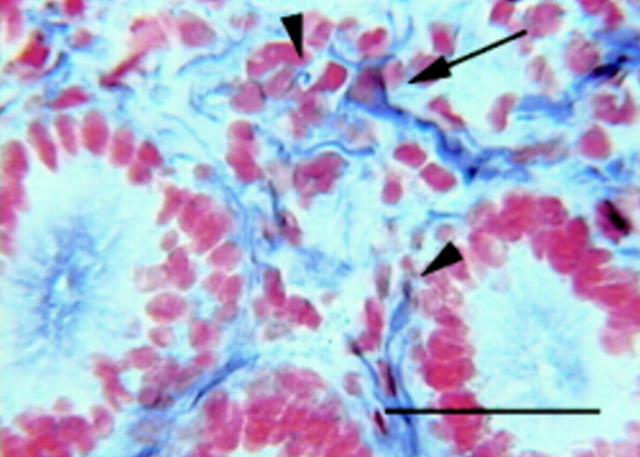
Figure 1 .
Human small intestinal mucosa. Arrowheads show apposition of the PrPc positive nerve fibres to lymphoid and epithelial cells; arrow indicates a cell showing the characteristics of an enteroglial cell. 3F4 monoclonal antibody immunohistochemistry, avidin:biotinylated enzyme complex/alkaline phosphatase with nitroblue tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate as substrate. Nuclei were stained with neutral red. Scale bar represents 50 µm (originally published in Nat Med 2000;6:840-1).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper T., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. The exceptionally small size of the scrapie agent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekes M., McBride P. A. Early accumulation of pathological PrP in the enteric nervous system and gut-associated lymphoid tissue of hamsters orally infected with scrapie. Neurosci Lett. 2000 Jan 14;278(3):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00934-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekes M., McBride P. A. Early accumulation of pathological PrP in the enteric nervous system and gut-associated lymphoid tissue of hamsters orally infected with scrapie. Neurosci Lett. 2000 Jan 14;278(3):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00934-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Brown H. R., Rudelli R. D., Scala L. J., Goller N. L., Wen G. Y., Kascsak R. J., Cashman N. R., Bolton D. C. Nearly ubiquitous tissue distribution of the scrapie agent precursor protein. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):149–156. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blättler T., Brandner S., Raeber A. J., Klein M. A., Voigtländer T., Weissmann C., Aguzzi A. PrP-expressing tissue required for transfer of scrapie infectivity from spleen to brain. Nature. 1997 Sep 4;389(6646):69–73. doi: 10.1038/37981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonn D. Future uncertain for reliable vCJD screening tests. Lancet. 2000 Jul 15;356(9225):228–228. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)74481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bons N., Mestre-Frances N., Belli P., Cathala F., Gajdusek D. C., Brown P. Natural and experimental oral infection of nonhuman primates by bovine spongiform encephalopathy agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):4046–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandner S., Raeber A., Sailer A., Blättler T., Fischer M., Weissmann C., Aguzzi A. Normal host prion protein (PrPC) is required for scrapie spread within the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 12;93(23):13148–13151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.23.13148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Qin K., Herms J. W., Madlung A., Manson J., Strome R., Fraser P. E., Kruck T., von Bohlen A., Schulz-Schaeffer W. The cellular prion protein binds copper in vivo. Nature. 1997 Dec 18;390(6661):684–687. doi: 10.1038/37783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. L., Stewart K., Ritchie D. L., Mabbott N. A., Williams A., Fraser H., Morrison W. I., Bruce M. E. Scrapie replication in lymphoid tissues depends on prion protein-expressing follicular dendritic cells. Nat Med. 1999 Nov;5(11):1308–1312. doi: 10.1038/15264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B. BSE and prions: uncertainties about the agent. Science. 1998 Jan 2;279(5347):42–43. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5347.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collee J. G., Bradley R. BSE: a decade on--Part 2. Lancet. 1997 Mar 8;349(9053):715–721. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)08496-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1999 Jul 24;354(9175):317–323. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)05128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornes J. S. Number, size, and distribution of Peyer's patches in the human small intestine: Part I The development of Peyer's patches. Gut. 1965 Jun;6(3):225–229. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjeux J. F. The molecular and genetic base of congenital transport defects. Gut. 2000 May;46(5):585–587. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsen J. M., Amigues Y., Schelcher F., Ducrocq V., Andreoletti O., Eychenne F., Khang J. V., Poivey J. P., Lantier F., Laplanche J. L. Genetic susceptibility and transmission factors in scrapie: detailed analysis of an epidemic in a closed flock of Romanov. Arch Virol. 1999;144(3):431–445. doi: 10.1007/s007050050516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar C. F., Somerville R. A., Bruce M. E. Straining the prion hypothesis. Nature. 1998 Jan 22;391(6665):345–346. doi: 10.1038/34818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. G., Escaig-Haye F., Billette de Villemeur T., Robain O., Lasmézas C. I., Deslys J. P., Dormont D., Brown P. Distribution and submicroscopic immunogold localization of cellular prion protein (PrPc) in extracerebral tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1998 Apr;292(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/s004410051036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y. Evidence of M cells as portals of entry for antigens in the nasopharyngeal lymphoid tissue of humans. Virchows Arch. 2000 Jun;436(6):560–566. doi: 10.1007/s004289900177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggebø R., Press C. M., Gunnes G., Lie K. I., Tranulis M. A., Ulvund M., Groschup M. H., Landsverk T. Distribution of prion protein in the ileal Peyer's patch of scrapie-free lambs and lambs naturally and experimentally exposed to the scrapie agent. J Gen Virol. 2000 Sep;81(Pt 9):2327–2337. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-81-9-2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herms J. W., Korte S., Gall S., Schneider I., Dunker S., Kretzschmar H. A. Altered intracellular calcium homeostasis in cerebellar granule cells of prion protein-deficient mice. J Neurochem. 2000 Oct;75(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberg R. M., Mayer L. F. Antigen processing and presentation by intestinal epithelial cells - polarity and complexity. Immunol Today. 2000 Mar;21(3):123–128. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. F., Antoniou M., Collinge J. Protease-resistant prion protein produced in vitro lacks detectable infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1999 Jan;80(Pt 1):11–14. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. F., Butterworth R. J., Joiner S., Jackson G., Rossor M. N., Thomas D. J., Frosh A., Tolley N., Bell J. E., Spencer M. Investigation of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other human prion diseases with tonsil biopsy samples. Lancet. 1999 Jan 16;353(9148):183–189. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)12075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. A., Fathers E., Edwards P., Ironside J. W., Zajicek J. Prion immunoreactivity in appendix before clinical onset of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1998 Aug 29;352(9129):703–704. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)24035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Caughey B. Specific binding of normal prion protein to the scrapie form via a localized domain initiates its conversion to the protease-resistant state. EMBO J. 1999 Jun 15;18(12):3193–3203. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.12.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ironside J. W., Hilton D. A., Ghani A., Johnston N. J., Conyers L., McCardle L. M., Best D. Retrospective study of prion-protein accumulation in tonsil and appendix tissues. Lancet. 2000 May 13;355(9216):1693–1694. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Millson G. C., Hunter G. D. An experimental examination of the scrapie agent in cell membrane mixtures. 3. Studies of the operational size. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Jul;81(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Walker C. A. Pathogenesis of scrapie in mice after intragastric infection. Virus Res. 1989 Mar;12(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucharzik T., Lügering N., Schmid K. W., Schmidt M. A., Stoll R., Domschke W. Human intestinal M cells exhibit enterocyte-like intermediate filaments. Gut. 1998 Jan;42(1):54–62. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasmézas C. I., Deslys J. P., Robain O., Jaegly A., Beringue V., Peyrin J. M., Fournier J. G., Hauw J. J., Rossier J., Dormont D. Transmission of the BSE agent to mice in the absence of detectable abnormal prion protein. Science. 1997 Jan 17;275(5298):402–405. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5298.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabbott N. A., Mackay F., Minns F., Bruce M. E. Temporary inactivation of follicular dendritic cells delays neuroinvasion of scrapie. Nat Med. 2000 Jul;6(7):719–720. doi: 10.1038/77401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maignien T., Lasmézas C. I., Beringue V., Dormont D., Deslys J. P. Pathogenesis of the oral route of infection of mice with scrapie and bovine spongiform encephalopathy agents. J Gen Virol. 1999 Nov;80(Pt 11):3035–3042. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-11-3035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride P. A., Eikelenboom P., Kraal G., Fraser H., Bruce M. E. PrP protein is associated with follicular dendritic cells of spleens and lymph nodes in uninfected and scrapie-infected mice. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):413–418. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. M., Baird A. W. Cytokine regulation of epithelial permeability and ion transport. Gut. 1999 Feb;44(2):283–289. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKie A. T., Zammit P. S., Naftalin R. J. Comparison of cattle and sheep colonic permeabilities to horseradish peroxidase and hamster scrapie prion protein in vitro. Gut. 1999 Dec;45(6):879–888. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillet-Richard S., Ermonval M., Chebassier C., Laplanche J. L., Lehmann S., Launay J. M., Kellermann O. Signal transduction through prion protein. Science. 2000 Sep 15;289(5486):1925–1928. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5486.1925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti C. Unsolved mysteries of intestinal M cells. Gut. 2000 Nov;47(5):735–739. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pammer J., Cross H. S., Frobert Y., Tschachler E., Oberhuber G. The pattern of prion-related protein expression in the gastrointestinal tract. Virchows Arch. 2000 May;436(5):466–472. doi: 10.1007/s004280050474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protopopova E. V., Konavalova S. N., Loktev V. B. Vydelenie kletochnogo retseptora dlia virusa kleshchevogo éntsefalita pri pomoshchi antiidiotipicheskikh antitel. Vopr Virusol. 1997 Nov-Dec;42(6):264–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Cochran S. P., Alpers M. P. Transmission of scrapie in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):971–978. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Nov 10;95(23):13363–13383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R., Oldstone M., Chesebro B. Entry versus blockade of brain infection following oral or intraperitoneal scrapie administration: role of prion protein expression in peripheral nerves and spleen. J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(2):828–833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.2.828-833.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeber A. J., Brandner S., Klein M. A., Benninger Y., Musahl C., Frigg R., Roeckl C., Fischer M. B., Weissmann C., Aguzzi A. Transgenic and knockout mice in research on prion diseases. Brain Pathol. 1998 Oct;8(4):715–733. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1998.tb00197.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger R., Edenhofer F., Lasmézas C. I., Weiss S. The human 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor interacts with the prion protein in eukaryotic cells. Nat Med. 1997 Dec;3(12):1383–1388. doi: 10.1038/nm1297-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaked G. M., Fridlander G., Meiner Z., Taraboulos A., Gabizon R. Protease-resistant and detergent-insoluble prion protein is not necessarily associated with prion infectivity. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 18;274(25):17981–17986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.25.17981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu S., Hoshi K., Muramoto T., Homma M., Ironside J. W., Kuzuhara S., Sato T., Yamamoto T., Kitamoto T. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with florid-type plaques after cadaveric dura mater grafting. Arch Neurol. 1999 Mar;56(3):357–362. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmakov A. N., Bode J., Kilshaw P. J., Ghosh S. Diverse patterns of expression of the 67-kD laminin receptor in human small intestinal mucosa: potential binding sites for prion proteins? J Pathol. 2000 Jul;191(3):318–322. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH640>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmakov A. N., McLennan N. F., McBride P., Farquhar C. F., Bode J., Rennison K. A., Ghosh S. Cellular prion protein is expressed in the human enteric nervous system. Nat Med. 2000 Aug;6(8):840–841. doi: 10.1038/78558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderholm J. D., Olaison G., Lindberg E., Hannestad U., Vindels A., Tysk C., Järnerot G., Sjödahl R. Different intestinal permeability patterns in relatives and spouses of patients with Crohn's disease: an inherited defect in mucosal defence? Gut. 1999 Jan;44(1):96–100. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Koga M., Mori R. Experimental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1981 Nov;31(6):943–951. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1981.tb02008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thellung S., Florio T., Villa V., Corsaro A., Arena S., Amico C., Robello M., Salmona M., Forloni G., Bugiani O. Apoptotic cell death and impairment of L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel activity in rat cerebellar granule cells treated with the prion protein fragment 106-126. Neurobiol Dis. 2000 Aug;7(4):299–309. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2000.0301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Gray-Owen S. D., Knorre A., Meyer T. F., Dehio C. Opa binding to cellular CD66 receptors mediates the transcellular traversal of Neisseria gonorrhoeae across polarized T84 epithelial cell monolayers. Mol Microbiol. 1998 Nov;30(3):657–671. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. S., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Ou S., Strauss J. H. High-affinity laminin receptor is a receptor for Sindbis virus in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4992–5001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4992-5001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Taraboletti G., Sobel M. E., Albrechtsen R., Liotta L. A. Role of laminin receptor in tumor cell migration. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5691–5698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will R. G., Ironside J. W. Oral infection by the bovine spongiform encephalopathy prion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Apr 27;96(9):4738–4739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.9.4738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Pan T., Liu T., Li R., Petersen R. B., Jones I. M., Gambetti P., Brown D. R., Sy M. S. Prion disease: A loss of antioxidant function? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Aug 28;275(2):249–252. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerr I., Brandel J. P., Masullo C., Wientjens D., de Silva R., Zeidler M., Granieri E., Sampaolo S., van Duijn C., Delasnerie-Lauprêtre N. European surveillance on Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a case-control study for medical risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000 Jul;53(7):747–754. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(99)00207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]