Abstract
BACKGROUND—Little information is available on the pathogenesis of cholesterol microlithiasis, and it is not clear if biliary lipid composition in these patients is similar to changes seen in cholesterol gall stone patients. AIMS—To measure biliary lipid composition in patients with cholesterol microlithiasis. PATIENTS—Eleven patients with cholesterol microlithiasis, 20 cholesterol gall stone patients, and 17 healthy controls. METHODS—Duodenal bile was collected in the fasting state during ceruletide infusion. Biliary cholesterol, phospholipids, and total bile acids were analysed by enzymatic assays, and conjugated bile acids by high pressure liquid chromatography. RESULTS—Patients with microlithiasis had a cholesterol saturation index significantly higher than controls (mean value 1.30 (95% confidence interval 1.05-1.54) v 0.90 (0.72-1.08)) but similar to gall stone patients (1.51 (1.40-1.63)). This was due to a significant decrease in per cent phospholipid (10.0% (7.1-12.8)) compared with controls (21.4% (18.1-24.6)) and gall stone patients (24.9% (20.5-29.3)). Per cent cholesterol was similar in patients with microlithiasis and controls (5.3% (4.5-6.1) and 5.6 % (4.3-6.8), respectively) but was significantly increased in gall stone patients (10.9% (9.3-12.4)). Bile acid composition in patients with microlithiasis was similar to controls whereas in gall stone patients deoxycholic acid was significantly increased: 27.3% (24.8-29.7) v 19.0% (15.7-22.2) in controls and 20.6% (14.9-26.2) in patients with microlithiasis. CONCLUSION—Patients with cholesterol microlithiasis have biliary cholesterol supersaturation, similarly to cholesterol gall stone patients. Whereas in the latter this is due to increased per cent cholesterol, in patients with microlithiasis this is caused by phospholipid deficiency, with normal per cent cholesterol and normal biliary bile acid composition. Keywords: cholesterol microlithiasis; biliary sludge; biliary lipid composition; bile acids; phospholipid; deoxycholic acid
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (124.5 KB).
Figure 1 .
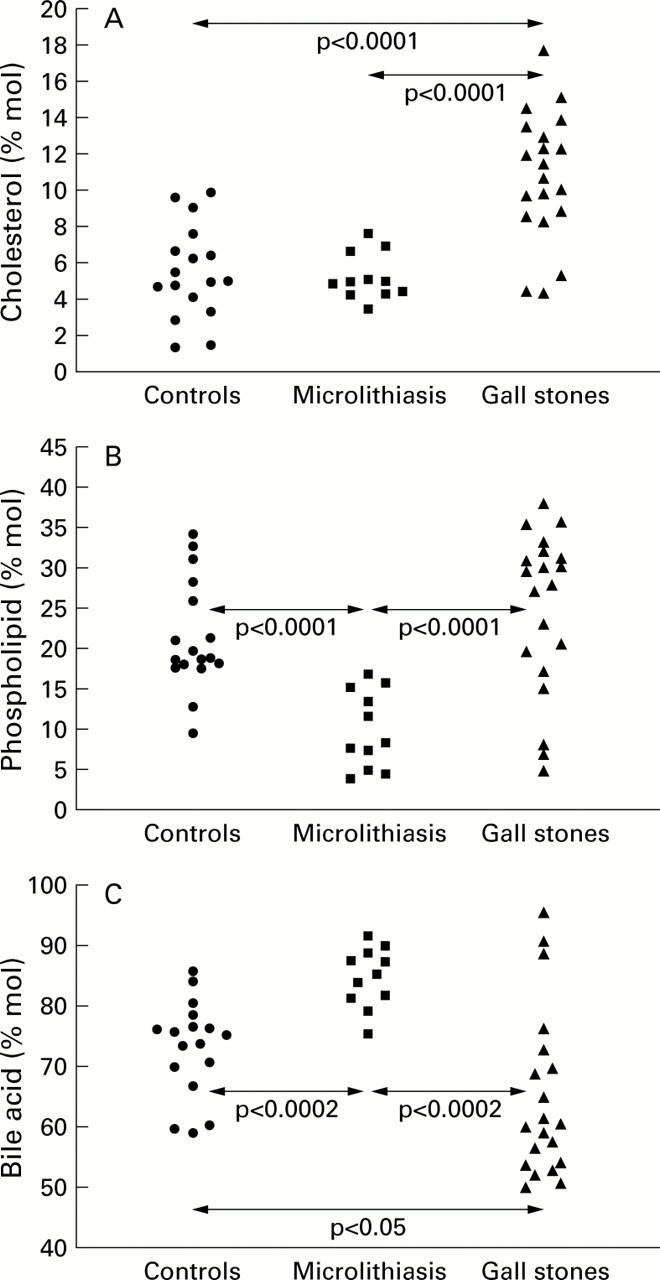
Individual data for per cent molar concentration of biliary lipids in healthy control subjects, in patients with cholesterol microlithiasis, and in cholesterol gall stone patients. Arrows indicate statistical differences between groups. (A) % molar cholesterol; (B) % molar phospholipids; and (C) % molar bile acids.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apstein M. D., Carey M. C. Pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones: a parsimonious hypothesis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1996 May;26(5):343–352. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1996.148287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Lamont J. T. Cholesterol gallstone formation. 1. Physical-chemistry of bile and biliary lipid secretion. Prog Liver Dis. 1992;10:139–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Amaral J., Biancani P., Behar J. Excess membrane cholesterol alters human gallbladder muscle contractility and membrane fluidity. Gastroenterology. 1999 Mar;116(3):678–685. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Goldfischer S. Perinatal hemochromatosis: one disease, several diseases or a spectrum? Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):176–177. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filly R. A., Allen B., Minton M. J., Bernhoft R., Way L. W. In vitro investigation of the origin of echoes with biliary sludge. J Clin Ultrasound. 1980 Jun;8(3):193–200. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fracchia M., Pellegrino S., Secreto P., Pera A., Galatola G. Biliary lipid composition in idiopathic bile acid malabsorption. Gut. 1998 Dec;43(6):812–816. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.6.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginanni Corradini S., Ripani C., Della Guardia P., Giovannelli L., Elisei W., Cantafora A., Codacci Pisanelli M., Tebala G. D., Nuzzo G., Corsi A. The human gallbladder increases cholesterol solubility in bile by differential lipid absorption: a study using a new in vitro model of isolated intra-arterially perfused gallbladder. Hepatology. 1998 Aug;28(2):314–322. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Z., Moshkowitz M., Laufer H., Peled Y., Gilat T. Effect of phospholipids and their molecular species on cholesterol solubility and nucleation in human and model biles. Gut. 1993 Jan;34(1):110–115. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegardt F. G., Dam H. The solubility of cholesterol in aqueous solutions of bile salts and lecithin. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1971 Apr;10(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02020933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Grundy S. M., Lachin J. M., Lan S. P., Baum R. A., Hanson R. F., Hersh T., Hightower N. C., Jr, Marks J. W., Mekhjian H. Pretreatment biliary lipid composition in white patients with radiolucent gallstones in the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):738–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko C. W., Sekijima J. H., Lee S. P. Biliary sludge. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Feb 16;130(4 Pt 1):301–311. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-4-199902160-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Hayashi A., Kim Y. S. Biliary sludge: curiosity or culprit? Hepatology. 1994 Aug;20(2):523–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Maher K., Nicholls J. F. Origin and fate of biliary sludge. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90626-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Nicholls J. F. Nature and composition of biliary sludge. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):677–686. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Nicholls J. F., Park H. Z. Biliary sludge as a cause of acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Feb 27;326(9):589–593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199202273260902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. N., Heaton K. W. Deoxycholic acid and the pathogenesis of gall stones. Gut. 1988 Apr;29(4):522–533. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.4.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuhara M., Yasunaga M., Tanigawa K., Tamura F., Yamashita S., Sakaida I., Okita K. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta 1 messenger RNA in various human liver diseases and correlation with hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatology. 1996 Aug;24(2):323–329. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1996.v24.pm0008690400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazer N. A., Carey M. C. Mathematical model of biliary lipid secretion: a quantitative analysis of physiological and biochemical data from man and other species. J Lipid Res. 1984 Sep;25(9):932–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama F., Nakagaki M. Quantitative determination of bile acids in bile with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Sep 12;183(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81708-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsell K., Angelin B., Liljeqvist L., Einarsson K. Biliary lipid output and bile acid kinetics in cholesterol gallstone disease. Evidence for an increased hepatic secretion of cholesterol in Swedish patients. Gastroenterology. 1985 Aug;89(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., Hofmann A. F. Biliary lipid output during three meals and an overnight fast. I. Relationship to bile acid pool size and cholesterol saturation of bile in gallstone and control subjects. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oude Elferink R. P., Ottenhoff R., van Wijland M., Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Groen A. K. Regulation of biliary lipid secretion by mdr2 P-glycoprotein in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI117658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi M. Y., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. The enzymatic determination of total phospholipids in bile and bile-rich duodenal aspirates. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Aug 19;105(3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Festi D., Sama C., Mazzella G., Alini R., Roda E., Barbara L. Enzymatic determination of cholesterol in bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Nov 3;64(3):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros E., Navarro S., Bru C., Garcia-Pugés A., Valderrama R. Occult microlithiasis in 'idiopathic' acute pancreatitis: prevention of relapses by cholecystectomy or ursodeoxycholic acid therapy. Gastroenterology. 1991 Dec;101(6):1701–1709. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90410-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. C., Agarwal D. K., Dhiman R. K., Baijal S. S., Choudhuri G., Saraswat V. A. Bile lithogenicity and gallbladder emptying in patients with microlithiasis: effect of bile acid therapy. Gastroenterology. 1998 Jul;115(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoda J., He B. F., Tanaka N., Matsuzaki Y., Osuga T., Yamamori S., Miyazaki H., Sjövall J. Increase of deoxycholate in supersaturated bile of patients with cholesterol gallstone disease and its correlation with de novo syntheses of cholesterol and bile acids in liver, gallbladder emptying, and small intestinal transit. Hepatology. 1995 May;21(5):1291–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Groen A. K., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Ottenhoff R., van der Lugt N. M., van Roon M. A. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sömjen G. J., Gilat T. Contribution of vesicular and micellar carriers to cholesterol transport in human bile. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jun;26(6):699–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Letter: A simple calculation of the lithogenic index of bile: expressing biliary lipid composition on rectangular coordinates. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vree J. M., Jacquemin E., Sturm E., Cresteil D., Bosma P. J., Aten J., Deleuze J. F., Desrochers M., Burdelski M., Bernard O. Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):282–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


