Abstract
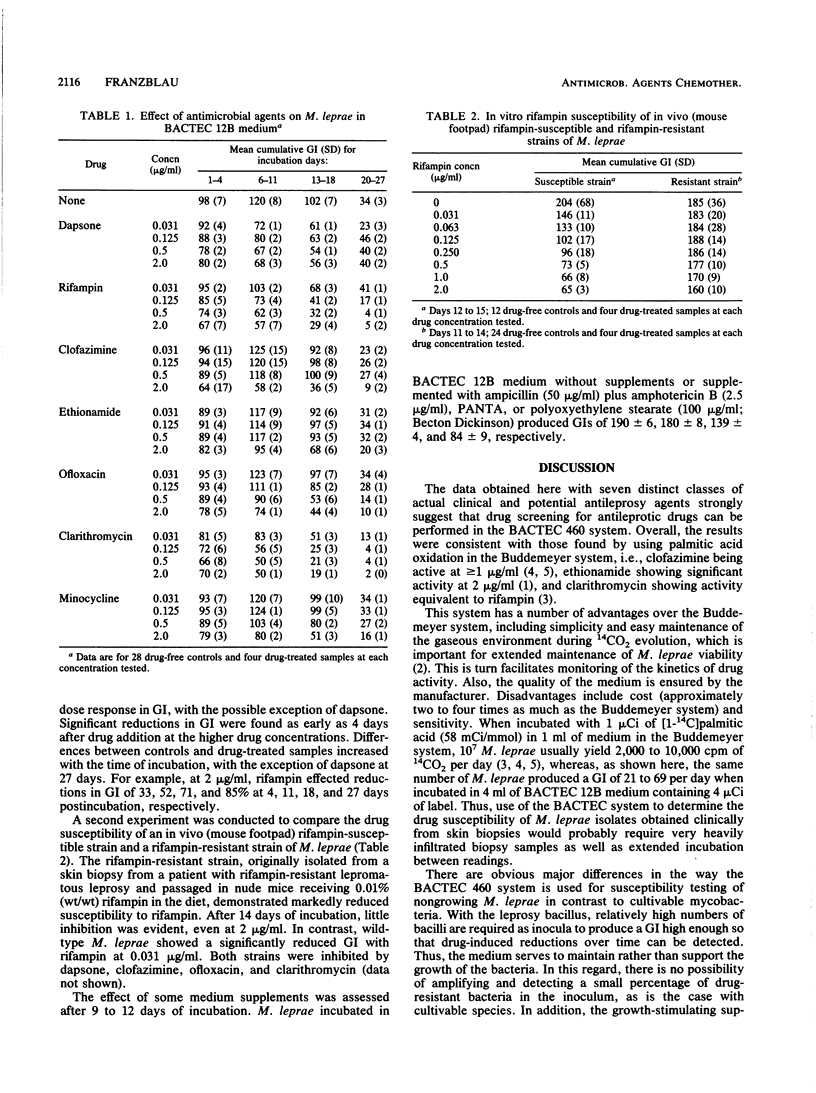
The susceptibility of Mycobacterium leprae to clinical and experimental antileprosy agents was assessed in the BACTEC 460 system. Nude-mouse-derived M. leprae (10(7) cells), incubated in BACTEC 12B medium at 33 degrees C under reduced oxygen, maintained a fairly constant growth index (14CO2 evolution) for 2 to 3 weeks. At concentrations ranging from 0.031 to 2.0 micrograms/ml, dapsone, rifampin, clofazimine, ethionamide, ofloxacin, clarithromycin, and minocycline all effected reductions in the growth index within 1 to 2 weeks, the extent of inhibition increasing with the incubation time. An in vivo rifampin-resistant isolate displayed markedly reduced susceptibility to rifampin compared with an in vivo-susceptible strain. This system appears to be highly suitable for in vitro drug susceptibility testing of M. leprae.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franzblau S. G., Harris E. B. Biophysical optima for metabolism of Mycobacterium leprae. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1124-1129.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., Hastings R. C. In vitro and in vivo activities of macrolides against Mycobacterium leprae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1758–1762. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., O'Sullivan J. F. Structure-activity relationships of selected phenazines against Mycobacterium leprae in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1583–1585. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G. Oxidation of palmitic acid by Mycobacterium leprae in an axenic medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):18–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.18-21.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., White K. E., O'Sullivan J. F. Structure-activity relationships of tetramethylpiperidine-substituted phenazines against Mycobacterium leprae in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):2004–2005. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. B., Franzblau S. G., Hastings R. C. Inhibition of phenolic glycolipid-I synthesis in extracellular Mycobacterium leprae as an indicator of antimicrobial activity. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1988 Dec;56(4):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings R. C., Franzblau S. G. Chemotherapy of leprosy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:231–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings R. C., Gillis T. P., Krahenbuhl J. L., Franzblau S. G. Leprosy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jul;1(3):330–348. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.3.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Lindholm-Levy P. J. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle. 1987 Dec;68(4):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(87)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasesh N., Krahenbuhl J. L., Hastings R. C. In vitro effects of antimicrobial agents on Mycobacterium leprae in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):657–662. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler P. R. Measurement of hypoxanthine incorporation in purified suspensions of Mycobacterium leprae: a suitable method to screen for anti-leprosy agents in vitro. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Mar;25(3):167–174. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-3-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


