Abstract
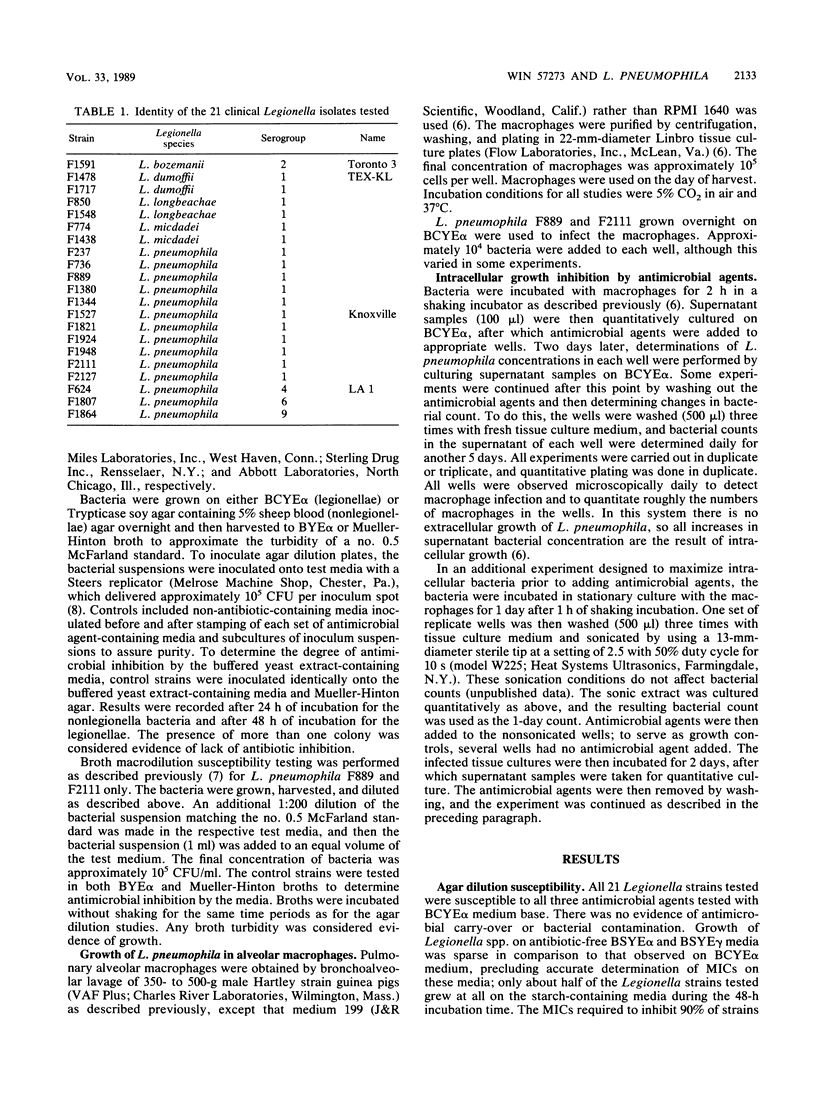
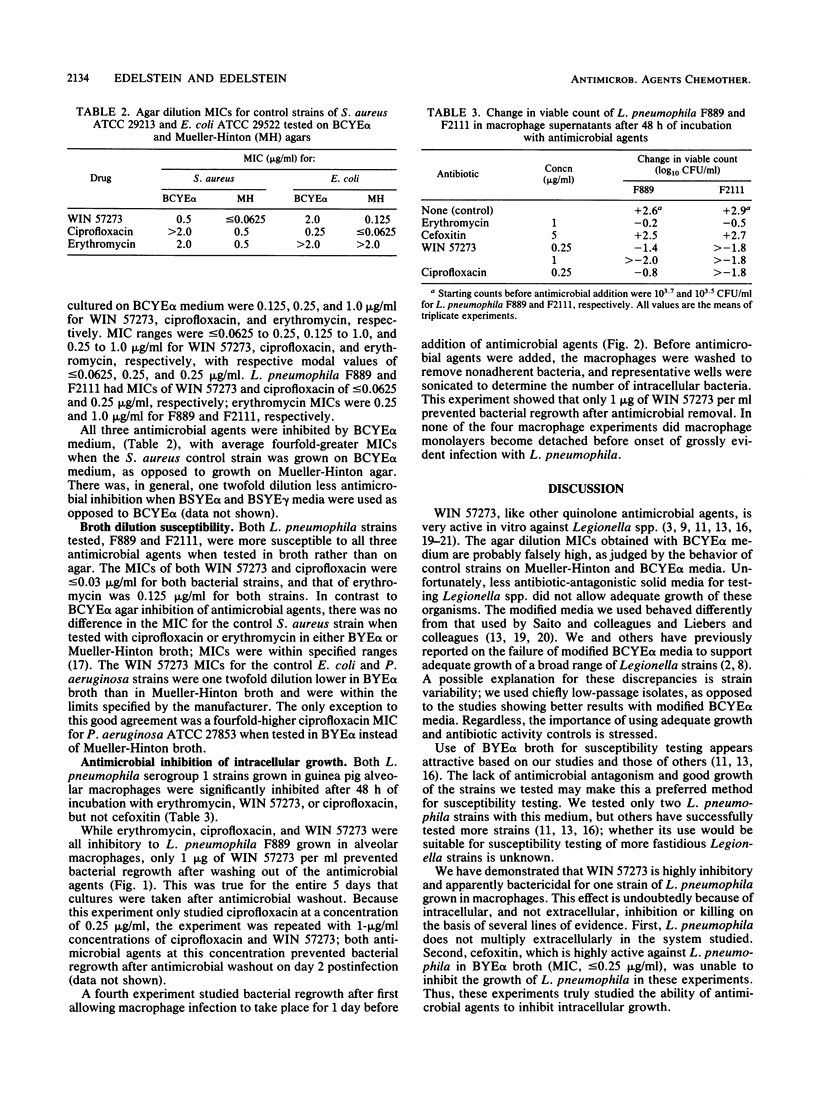
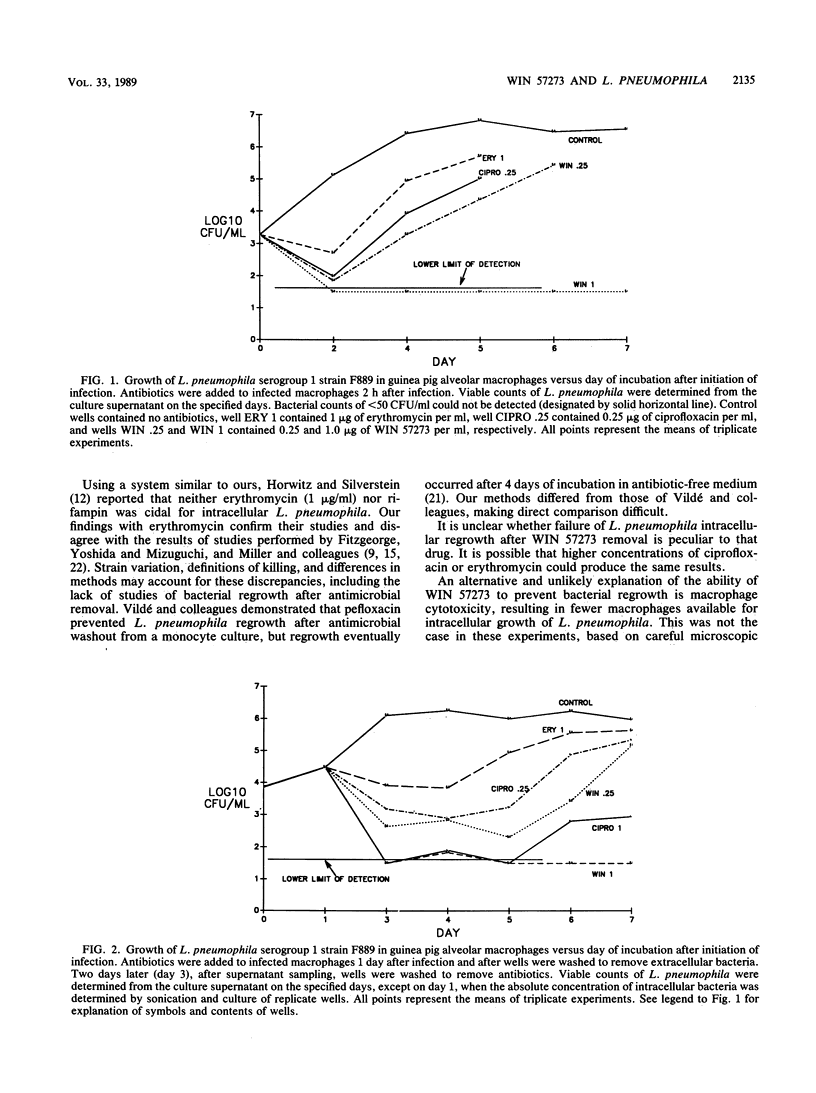
The in vitro antimicrobial activity of WIN 57273, a new quinolone antimicrobial agent, was determined for 21 Legionella strains, using broth macrodilution and agar dilution testing methods; ciprofloxacin and erythromycin were tested as well. Three different buffered yeast extract media were used for the agar dilution studies, two of which were made with starch rather than charcoal. Broth macrodilution susceptibility testing was performed with buffered yeast extract broth and two Legionella pneumophila strains. Antimicrobial inhibition of L. pneumophila growth in guinea pig alveolar macrophages was also studied, using a method able to detect bacterial killing. The MICs for 90% of the 21 strains of Legionella spp. grown on buffered charcoal yeast extract medium were 0.125 microgram/ml for WIN 57273, 0.25 microgram/ml for ciprofloxacin, and 1.0 micrograms/ml for erythromycin. These MICs were falsely high, because of inhibition of drug activity by the medium used. Use of less drug-antagonistic, starch-containing media did not support good growth of the test strains. The broth macrodilution MICs for two strains of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 were less than or equal to 0.03 microgram/ml for WIN 57273 and ciprofloxacin and 0.125 microgram/ml for erythromycin. WIN 57273, ciprofloxacin, and erythromycin all inhibited growth of L. pneumophila in guinea pig alveolar macrophages at concentrations of 1 microgram/ml, but only WIN 57273 prevented regrowth or killed L. pneumophila after removal of extracellular antimicrobial agent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacheson M. A., Friedman H. M., Benson C. E. Antimicrobial susceptibility of intracellular Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):691–692. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Roudier C., Fleurette J. Determination of the activity on Legionella of eight macrolides and related agents by comparative testing on three media. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15(1):17–22. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournon E., Rajagopalan P., Vilde J. L., Pocidalo J. J. Efficacy of pefloxacin in comparison with erythromycin in the treatment of experimental guinea pig legionellosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):41–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Beer K. B., DeBoynton E. D. Influence of growth temperature on virulence of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2701–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2701-2705.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Calarco K., Yasui V. K. Antimicrobial therapy of experimentally induced Legionnaires' disease in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):849–856. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Pasiecznik K. A., Yasui V. K., Meyer R. D. Susceptibility of Legionella spp. to mycinamicin I and II and other macrolide antibiotics: effects of media composition and origin of organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):90–93. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Gibson D. H., Jepras R., Baskerville A. Studies on ciprofloxacin therapy of experimental Legionnaires' disease. J Infect. 1985 May;10(3):194–203. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B. The effect of antibiotics on the growth of Legionella pneumophila in guinea-pig alveolar phagocytes infected in vivo by an aerosol. J Infect. 1985 May;10(3):189–193. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlichek D., Saravolatz L., Pohlod D. Effect of quinolones and other antimicrobial agents on cell-associated Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1529–1534. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):15–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI110744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebers D. M., Baltch A. L., Smith R. P., Hammer M. C., Conroy J. V. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to eight antimicrobial agents including four macrolides under different assay conditions. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Jan;23(1):37–41. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Legionella infections: a review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):258–278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Martin J. R., Johnson P., Ulrich J. T., Rdzok E. J., Billing P. Erythromycin uptake and accumulation by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and efficacy of erythromycin in killing ingested Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):714–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffie B. G., Mouton R. P. Sensitivity and resistance of Legionella pneumophila to some antibiotics and combinations of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22(4):457–462. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki M., Paucod J. C., Bornstein N., Meugnier H., Isoard P., Fleurette J. Comparative efficacy of five antibiotics on experimental airborne legionellosis in guinea-pigs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22(4):513–519. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Koga H., Shigeno H., Watanabe K., Mori K., Kohno S., Shigeno Y., Suzuyama Y., Yamaguchi K., Hirota M. The antimicrobial activity of ciprofloxacin against Legionella species and the treatment of experimental Legionella pneumonia in guinea pigs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Aug;18(2):251–260. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Sawatari K., Fukuda Y., Nagasawa M., Koga H., Tomonaga A., Nakazato H., Fujita K., Shigeno Y., Suzuyama Y. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to ofloxacin in vitro and in experimental Legionella pneumonia in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vildé J. L., Dournon E., Rajagopalan P. Inhibition of Legionella pneumophila multiplication within human macrophages by antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):743–748. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Mizuguchi Y. Antibiotic susceptibility of Legionella pneumophia Philadelphia-1 in cultured guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):901–906. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



