Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (182.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
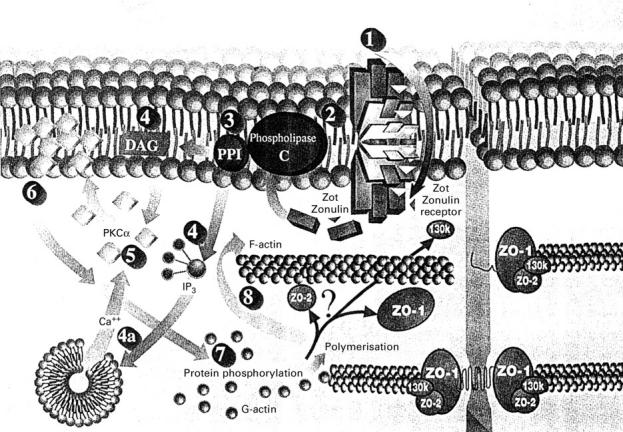
Proposed zonulin/zonula occludens toxin (Zot) intracellular signalling leading to the opening of intestinal tight junctions. Zonulin and Zot interact with the same specific surface receptor (1) whose distribution within the intestine varies. The proteins are then internalised and activate phospholipase C (2) that hydrolyses phosphatidyl inositol (3) to release inositol 1,4,5-tris phosphate (PPI-3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) (4). Protein kinase C (PKC)α is then activated (5), either directly (via DAG) (4) or through release of intracellular Ca++ (via PPI- 3) (4a). PKCα catalyses the phosphorylation of target protein(s) with subsequent polymerisation of soluble G-actin to F-actin (7). This polymerisation causes the rearrangement of the filaments of actin and the subsequent displacement of proteins (including ZO-1) from the junctional complex (8). As a result, intestinal tight junctions become looser (from Fasano32 with permission, modified).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry B., Fasano A., Ketley J., Kaper J. B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.428-434.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Baudry B., Pumplin D. W., Wasserman S. S., Tall B. D., Ketley J. M., Kaper J. B. Vibrio cholerae produces a second enterotoxin, which affects intestinal tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5242–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A. Cellular microbiology: can we learn cell physiology from microorganisms? Am J Physiol. 1999 Apr;276(4 Pt 1):C765–C776. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1999.276.4.C765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Fiorentini C., Donelli G., Uzzau S., Kaper J. B., Margaretten K., Ding X., Guandalini S., Comstock L., Goldblum S. E. Zonula occludens toxin modulates tight junctions through protein kinase C-dependent actin reorganization, in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):710–720. doi: 10.1172/JCI118114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A. Innovative strategies for the oral delivery of drugs and peptides. Trends Biotechnol. 1998 Apr;16(4):152–157. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(97)01170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Not T., Wang W., Uzzau S., Berti I., Tommasini A., Goldblum S. E. Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. Lancet. 2000 Apr 29;355(9214):1518–1519. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A. Regulation of intercellular tight junctions by zonula occludens toxin and its eukaryotic analogue zonulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;915:214–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Uzzau S., Fiore C., Margaretten K. The enterotoxic effect of zonula occludens toxin on rabbit small intestine involves the paracellular pathway. Gastroenterology. 1997 Mar;112(3):839–846. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9041245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Uzzau S. Modulation of intestinal tight junctions by Zonula occludens toxin permits enteral administration of insulin and other macromolecules in an animal model. J Clin Invest. 1997 Mar 15;99(6):1158–1164. doi: 10.1172/JCI119271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Fawcett D. W., Aoki A. The Sertoli cell occluding junctions and gap junctions in mature and developing mammalian testis. Dev Biol. 1976 May;50(1):142–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Kaila M., Arvola T., Majamaa H., Rantala I., Virtanen E., Arvilommi H. Diet during rotavirus enteritis affects jejunal permeability to macromolecules in suckling rats. Pediatr Res. 1993 Jun;33(6):548–553. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199306000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Loosening tight junctions. Lessons from the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI113987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Pappenheimer J. R. Structural basis for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02209147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson T., Jacobson J. B., Stackpole C. W. Relationship between intercellular permeability and junction organization in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):214–224. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcial M. A., Carlson S. L., Madara J. L. Partitioning of paracellular conductance along the ileal crypt-villus axis: a hypothesis based on structural analysis with detailed consideration of tight junction structure-function relationships. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(1):59–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01868690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazariegos M. R., Tice L. W., Hand A. R. Alteration of tight junctional permeability in the rat parotid gland after isoproterenol stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1865–1877. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meddings J. B., Jarand J., Urbanski S. J., Hardin J., Gall D. G. Increased gastrointestinal permeability is an early lesion in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Am J Physiol. 1999 Apr;276(4 Pt 1):G951–G957. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1999.276.4.G951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milks L. C., Conyers G. P., Cramer E. B. The effect of neutrophil migration on epithelial permeability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2729–2738. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Stafford J., Madara J. L. The selective and superoxide-independent disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junctions during leukocyte transmigration. Lab Invest. 1988 Oct;59(4):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Brown S. S. Cell junctions in development, with particular reference to the neural tube. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:443–455. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Pisam M., Maetz J. The surface epithelium of teleostean fish gills. Cellular and junctional adaptations of the chloride cell in relation to salt adaptation. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):96–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Walters D. V., Olver R. E. Development of intercellular junctions in the pulmonary epithelium of the foetal lamb. J Cell Sci. 1978 Aug;32:307–324. doi: 10.1242/jcs.32.1.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Winter M., Shasby S. S. Oxidants and conductance of cultured epithelial cell monolayers: inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C781–C788. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzzau S., Cappuccinelli P., Fasano A. Expression of Vibrio cholerae zonula occludens toxin and analysis of its subcellular localization. Microb Pathog. 1999 Dec;27(6):377–385. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1999.0312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzzau S., Lu R., Wang W., Fiore C., Fasano A. Purification and preliminary characterization of the zonula occludens toxin receptor from human (CaCo2) and murine (IEC6) intestinal cell lines. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Jan 1;194(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb09437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura A., Magazzù G., Greco L. Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. SIGEP Study Group for Autoimmune Disorders in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology. 1999 Aug;117(2):297–303. doi: 10.1053/gast.1999.0029900297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Uzzau S., Goldblum S. E., Fasano A. Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J Cell Sci. 2000 Dec;113(Pt 24):4435–4440. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.24.4435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


