Abstract
BACKGROUND—Hypersensitivity to distension of the stomach is a frequent finding in functional dyspepsia. During gastric distension studies both wall tension and elongation are increased. AIM—We wished to distinguish changes in wall tension from changes in elongation in the genesis of perception of mechanical stimuli originating from the proximal stomach in healthy subjects. SUBJECTS AND METHODS—Twenty six volunteers were studied using gastric barostat and antroduodenal manometry. In 14 subjects, stepwise isobaric and isovolumetric distensions were performed before and during erythromycin infusion. In all volunteers, on a separate occasion, phasic contractions of the proximal stomach were detected as intraballoon pressure increases during fixed volume inflation. These contractions were matched with perception changes during two 10 minute periods, before and during administration of erythromycin. RESULTS—Erythromycin significantly lowered the perception and discomfort thresholds during stepwise gastric distension. During fixed volume inflation, erythromycin increased the number and amplitude of fundic contractions and enhanced their perception from 51.1 (7.4)% to 64.0 (4.7)%. The proportion of perception score increases coinciding with fundic contractions increased from 47.3 (0.7)% to 81.5 (0.5)%. The amplitude of correctly identified isolated fundic pressure waves was higher compared with non-identified waves. CONCLUSIONS—These results support the hypothesis that changes in gastric wall tension may be involved in the genesis of symptoms originating from the stomach. Keywords: visceral hypersensitivity; stomach physiology; mechanoreceptors; wall tension; erythromycin; barostat
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (147.2 KB).
Figure 1 .
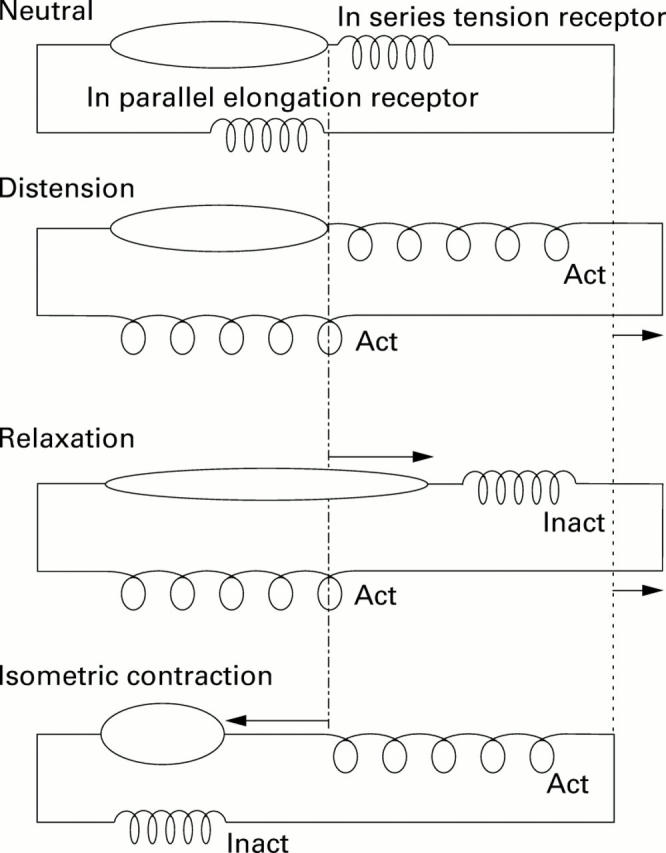
Schematic model of the proximal stomach wall with muscular component, in series tension receptor, and in parallel elongation receptor. The four panels represent the behaviour of the model in various experimental conditions. Top: Neutral condition; second panel: during distension both elongation and tension receptors are activated (Act). Muscular contraction status is unchanged; third panel: during relaxation, elongation but not tension receptors are activated. The muscular component is lengthened; bottom: during isometric contraction only tension receptors but not elongation receptors are activated. The muscular component is shortened. Inact, inactivated.
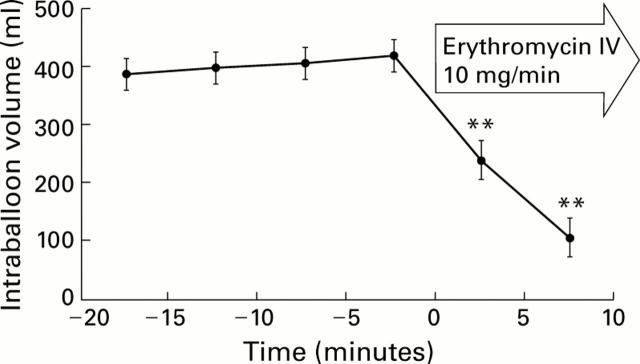
Figure 2 .
Influence of intravenous (IV) erythromycin on tone of the proximal stomach. Gastric tone is reflected by the volume of a barostat balloon in the proximal stomach. Intraballoon pressure is kept constant at a fixed pressure selected to obtain an initial volume of approximately 400 ml. Values are mean (SEM). Student's t test: **p<0.01 (n=14).
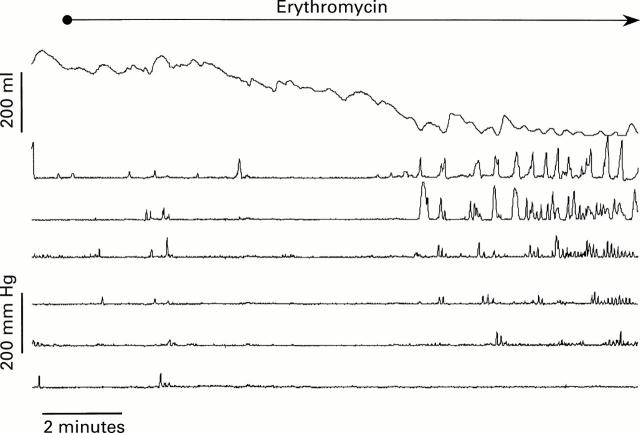
Figure 3 .
Influence of erythromycin 10 mg/min given intravenously on motor activity of the stomach and duodenum. Combined barostat of the proximal stomach and antroduodenal manometry in a healthy volunteer. The highest trace represents intraballoon volume. The second and third channels show antral pressure, and the four other channels duodenal pressure. Erythromycin induced enhancement of fundic tone (represented as a decrease in intraballoon volume) which preceded the appearance of antral phase III-like contractions.
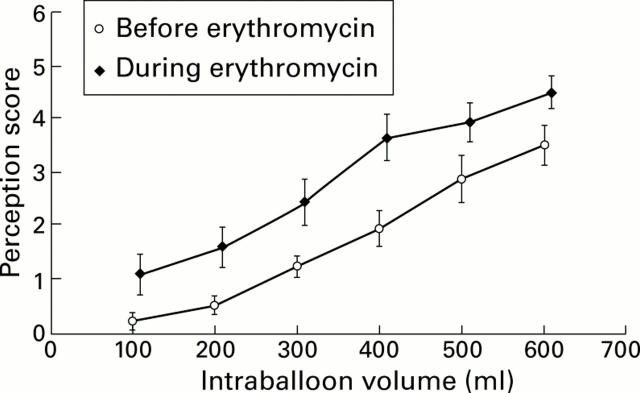
Figure 4 .
Distension-perception relation during isovolumetric distensions of the proximal stomach. A barostat balloon placed in the proximal stomach is inflated stepwise with increasing volumes (step increment 100 ml, step duration two minutes). Perception of abdominal discomfort is recorded at the end of each distension step on a scale ranging from 0 to 6, before and during intravenous infusion of erythromycin. Erythromycin (10 mg/min) significantly enhanced perception of gastric distension. Values are mean (SEM) perception scores (area under the curve; p<0.01) (n=14).
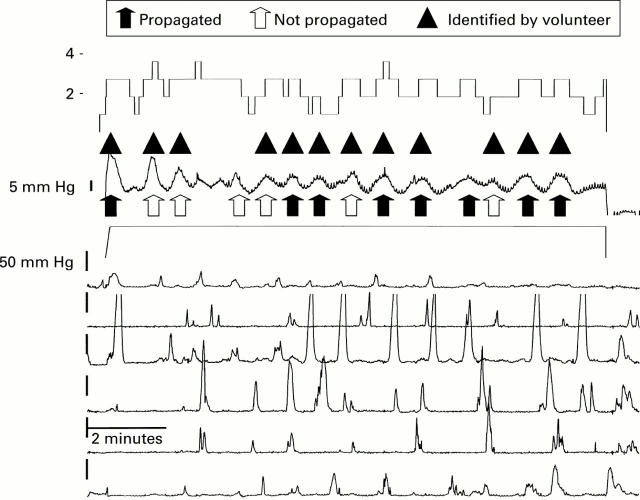
Figure 5 .
Perception of phasic activity of the proximal stomach. Combined barostat of the proximal stomach and antroduodenal manometry in a healthy volunteer. The highest trace represents perception score. The second and third traces shows intraballoon pressure and volume, respectively. The six other traces represent antroduodenal manometry. This tracing illustrates fundic pressure waves propagated or not to the antrum. Some of the fundic pressure waves were identified by the volunteer.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackshaw L. A., Grundy D., Scratcherd T. Vagal afferent discharge from gastric mechanoreceptors during contraction and relaxation of the ferret corpus. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Jan;18(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradette M., Pare P., Douville P., Morin A. Visceral perception in health and functional dyspepsia. Crossover study of gastric distension with placebo and domperidone. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jan;36(1):52–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01300087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin B., Azpiroz F., Guarner F., Malagelada J. R. Selective gastric hypersensitivity and reflex hyporeactivity in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1345–1351. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distrutti E., Azpiroz F., Soldevilla A., Malagelada J. R. Gastric wall tension determines perception of gastric distention. Gastroenterology. 1999 May;116(5):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart G. F. Visceral nociception: consequences, modulation and the future. Eur J Anaesthesiol Suppl. 1995 May;10:24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilja O. H., Hausken T., Wilhelmsen I., Berstad A. Impaired accommodation of proximal stomach to a meal in functional dyspepsia. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Apr;41(4):689–696. doi: 10.1007/BF02213124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen H., Kassab G. Biomechanics of the gastrointestinal tract. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1996 Dec;8(4):277–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.1996.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy D. Speculations on the structure/function relationship for vagal and splanchnic afferent endings supplying the gastrointestinal tract. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Apr;22(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. H., Talley N. J. Visceral perception in functional gastro-intestinal disorders: disease marker or epiphenomenon? Dig Dis. 1996 Sep-Oct;14(5):276–288. doi: 10.1159/000171559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lémann M., Dederding J. P., Flourié B., Franchisseur C., Rambaud J. C., Jian R. Abnormal perception of visceral pain in response to gastric distension in chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. The irritable stomach syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Sep;36(9):1249–1254. doi: 10.1007/BF01307517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R. Functional dyspepsia. Insights on mechanisms and management strategies. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1996 Mar;25(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearin F., Cucala M., Azpiroz F., Malagelada J. R. The origin of symptoms on the brain-gut axis in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1991 Oct;101(4):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90726-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notivol R., Coffin B., Azpiroz F., Mearin F., Serra J., Malagelada J. R. Gastric tone determines the sensitivity of the stomach to distention. Gastroenterology. 1995 Feb;108(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. A study of gastric stretch receptors; their role in the peripheral mechanism of satiation of hunger and thirst. J Physiol. 1954 Nov 29;126(2):255–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. S. Visceral hyperalgesia: the key for unrevealing functional gastrointestinal disorders. Dig Dis. 1996 Sep-Oct;14(5):271–275. doi: 10.1159/000171558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salet G. A., Samsom M., Roelofs J. M., van Berge Henegouwen G. P., Smout A. J., Akkermans L. M. Responses to gastric distension in functional dyspepsia. Gut. 1998 Jun;42(6):823–829. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.6.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack J., Coulie B., Wilmer A., Andrioli A., Janssens J. Influence of sumatriptan on gastric fundus tone and on the perception of gastric distension in man. Gut. 2000 Apr;46(4):468–473. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack J., Piessevaux H., Coulie B., Caenepeel P., Janssens J. Role of impaired gastric accommodation to a meal in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1998 Dec;115(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Stanghellini V., Heading R. C., Koch K. L., Malagelada J. R., Tytgat G. N. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut. 1999 Sep;45 (Suppl 2):II37–II42. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2008.ii37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Weaver A. L., Tesmer D. L., Zinsmeister A. R. Lack of discriminant value of dyspepsia subgroups in patients referred for upper endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 1993 Nov;105(5):1378–1386. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90142-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thumshirn M., Camilleri M., Choi M. G., Zinsmeister A. R. Modulation of gastric sensory and motor functions by nitrergic and alpha2-adrenergic agents in humans. Gastroenterology. 1999 Mar;116(3):573–585. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troncon L. E., Bennett R. J., Ahluwalia N. K., Thompson D. G. Abnormal intragastric distribution of food during gastric emptying in functional dyspepsia patients. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):327–332. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troncon L. E., Thompson D. G., Ahluwalia N. K., Barlow J., Heggie L. Relations between upper abdominal symptoms and gastric distension abnormalities in dysmotility like functional dyspepsia and after vagotomy. Gut. 1995 Jul;37(1):17–22. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]