Abstract
INTRODUCTION—Erythromycin, a motilin agonist, is a potent prokinetic. ABT-229 is a specific motilin agonist that dose dependently accelerates gastric emptying. Dyspepsia and gastroparesis are common problems in type 1 diabetes mellitus. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of ABT-229 in symptomatic diabetic patients with and without delayed gastric emptying. METHODS—Patients with type 1 diabetes and postprandial symptoms were randomised (n=270). Based on a validated C13 octanoic acid breath test, patients were assigned to either the delayed or normal gastric emptying strata. Patients received one of four doses of ABT-229 (1.25, 2.5, 5, or 10 mg twice daily before breakfast and dinner) or placebo for four weeks following a two week baseline. A self report questionnaire measured symptoms on visual analogue scales; the primary outcome was assessment of change in the total upper abdominal symptom severity score (range 0-800 mm) from baseline to the final visit. RESULTS—The treatment arms were similar regarding baseline characteristics. There was symptom improvement on placebo and a similar level of improvement on active therapy for the upper abdominal discomfort severity score (mean change from baseline −169, −101, −155, −143, and −138 mm for placebo, and 1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg ABT-229, respectively, at four weeks by intent to treat). The results were not significantly different in those with and without delayed gastric emptying. The severity of bloating, postprandial nausea, epigastric discomfort, heartburn, and acid regurgitation worsened dose dependently in a greater number of patients receiving ABT-229 than placebo. Overall, 63% of patients on placebo reported a good or excellent global response, and this was not different from the active treatment arms. CONCLUSIONS—The motilin agonist ABT-229 was not efficacious in the relief of postprandial symptoms in diabetes mellitus in the presence or absence of delayed gastric emptying. Keywords: prokinetic; motilin; dyspepsia; gastric motility; type 1 diabetes; controlled trial; postprandial
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (139.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
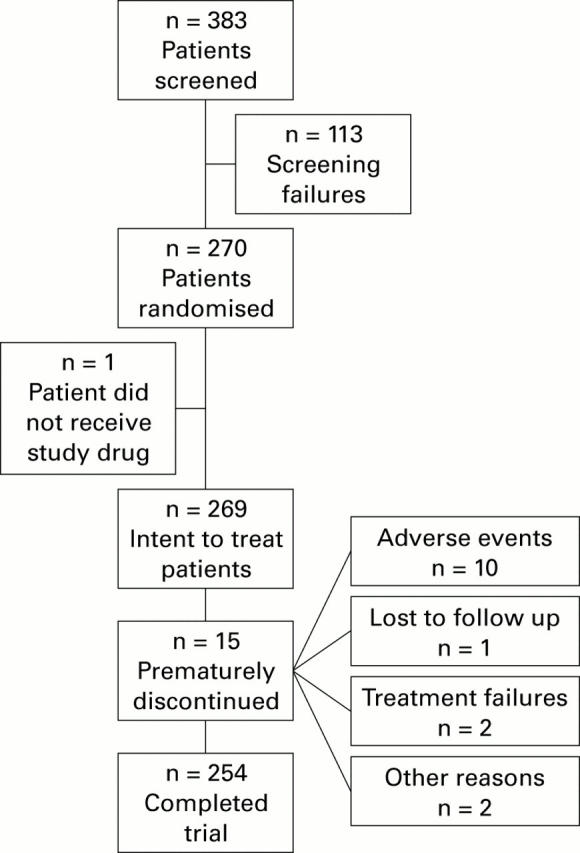
Patient flow chart.
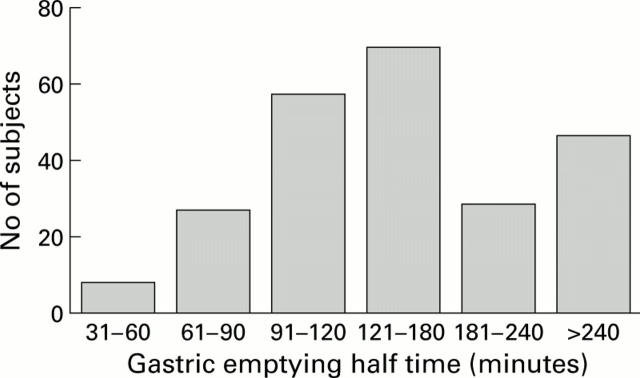
Figure 2 .
Distribution of gastric emptying half times (t1/2) in the study population.
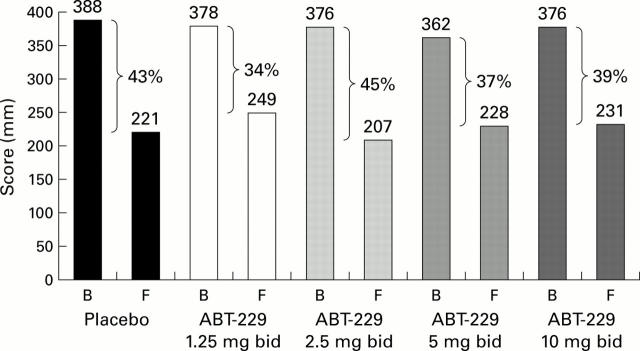
Figure 3 .
Mean upper abdominal discomfort score on combined visual analogue scales (mm) at baseline (B) and at the four week (final (F)) visit in each treatment arm.
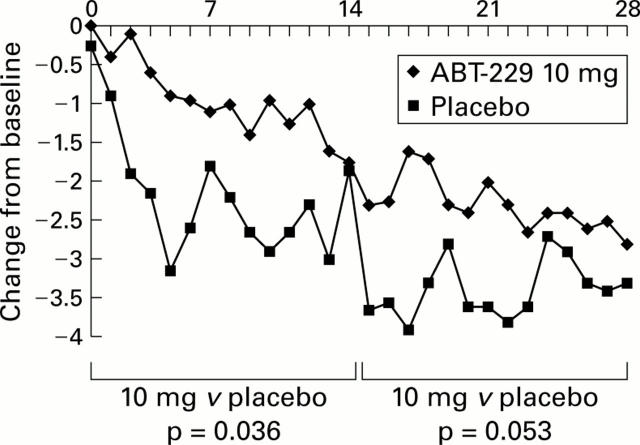
Figure 4 .
Change from baseline for the sum of daily severity scores for fullness, bloating, epigastric discomfort, and postprandial nausea from the patient diary in the placebo and ABT-229 10 mg groups.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achem-Karam S. R., Funakoshi A., Vinik A. I., Owyang C. Plasma motilin concentration and interdigestive migrating motor complex in diabetic gastroparesis: effect of metoclopramide. Gastroenterology. 1985 Feb;88(2):492–499. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90512-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annese V., Lombardi G., Frusciante V., Germani U., Andriulli A., Bassotti G. Cisapride and erythromycin prokinetic effects in gastroparesis due to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Jun;11(3):599–603. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi M. G., Camilleri M., Burton D. D., Zinsmeister A. R., Forstrom L. A., Nair K. S. [13C]octanoic acid breath test for gastric emptying of solids: accuracy, reproducibility, and comparison with scintigraphy. Gastroenterology. 1997 Apr;112(4):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. J., Wright T., Bertrand P. P., Bornstein J. C., Jenkinson K. M., Verlinden M., Furness J. B. Erythromycin derivatives ABT 229 and GM 611 act on motilin receptors in the rabbit duodenum. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1999 Mar;26(3):242–245. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.1999.03022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Clarke B. F. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 2;285(6346):916–918. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6346.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighner S. D., Tan C. P., McKee K. K., Palyha O. C., Hreniuk D. L., Pong S. S., Austin C. P., Figueroa D., MacNeil D., Cascieri M. A. Receptor for motilin identified in the human gastrointestinal system. Science. 1999 Jun 25;284(5423):2184–2188. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5423.2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M., Schiller L. R. Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):378–384. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney J. S., Kinnersley N., Hughes M., O'Bryan-Tear C. G., Lothian J. Meta-analysis of antisecretory and gastrokinetic compounds in functional dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998 Jun;26(4):312–320. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199806000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galmiche J. P., Delbende B., Perri F., Andriulli A. 13C octanoic acid breath test. Gut. 1998 Nov;43 (Suppl 3):S28–S30. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.2008.s28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoos Y. F., Maes B. D., Geypens B. J., Mys G., Hiele M. I., Rutgeerts P. J., Vantrappen G. Measurement of gastric emptying rate of solids by means of a carbon-labeled octanoic acid breath test. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1640–1647. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbard G. S., Samsom M., Sun W. M., Dent J., Horowitz M. Hyperglycemia affects proximal gastric motor and sensory function during small intestinal triglyceride infusion. Am J Physiol. 1996 Nov;271(5 Pt 1):G814–G819. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.271.5.G814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Edelbroek M., Fraser R., Maddox A., Wishart J. Disordered gastric motor function in diabetes mellitus. Recent insights into prevalence, pathophysiology, clinical relevance, and treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jul;26(7):673–684. doi: 10.3109/00365529108998583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii M., Nakamura T., Kasai F., Baba T., Takebe K. Erythromycin derivative improves gastric emptying and insulin requirement in diabetic patients with gastroparesis. Diabetes Care. 1997 Jul;20(7):1134–1137. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.7.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L., Berry M., Kong M. F., Kwiatek M. A., Samsom M., Horowitz M. Hyperglycemia attenuates the gastrokinetic effect of erythromycin and affects the perception of postprandial hunger in normal subjects. Diabetes Care. 1999 Feb;22(2):339–344. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall B. J., Chakravarti A., Kendall E., Soykan I., McCallum R. W. The effect of intravenous erythromycin on solid meal gastric emptying in patients with chronic symptomatic post-vagotomy-antrectomy gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Apr;11(2):381–385. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.148324000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall B. J., Kendall E. T., Soykan I., McCallum R. W. Cisapride in the long-term treatment of chronic gastroparesis: a 2-year open-label study. J Int Med Res. 1997 Jul-Aug;25(4):182–189. doi: 10.1177/030006059702500402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzian A., Iber F. L., Vaeth J. Gastric emptying in patients with insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Jan;82(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong M. F., Horowitz M. Gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus: relationship to blood-glucose control. Clin Geriatr Med. 1999 May;15(2):321–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong M. F., Horowitz M., Jones K. L., Wishart J. M., Harding P. E. Natural history of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes Care. 1999 Mar;22(3):503–507. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.3.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyrenås E. B., Olsson E. H., Arvidsson U. C., Orn T. J., Spjuth J. H. Prevalence and determinants of solid and liquid gastric emptying in unstable type I diabetes. Relationship to postprandial blood glucose concentrations. Diabetes Care. 1997 Mar;20(3):413–418. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor I. L., Gueller R., Watts H. D., Meyer J. H. The effect of acute hyperglycemia on gastric emptying in man. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):190–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R. Diabetic gastroparesis. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 1995 Oct;6(4):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyrén O., Adami H. O., Bates S., Bergström R., Gustavsson S., Löf L., Sjödén P. O. Self-rating of pain in nonulcer dyspepsia. A methodological study comparing a new fixed-point scale and the visual analogue scale. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;9(4):408–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Abell T., Rothstein R., Koch K., Barnett J. A double-blind multicenter comparison of domperidone and metoclopramide in the treatment of diabetic patients with symptoms of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 May;94(5):1230–1234. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters T. L. Erythromycin and other macrolides as prokinetic agents. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1886–1899. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91089-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrakis I. E., Vrachassotakis N., Sciacca V., Vassilakis S. I., Chalkiadakis G. Hyperglycaemia attenuates erythromycin-induced acceleration of solid-phase gastric emptying in idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999 Apr;34(4):396–403. doi: 10.1080/003655299750026416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner C. K., Verhagen M. A., Hebbard G. S., DiMatteo A. C., Doran S. M., Horowitz M. Proximal gastric compliance and perception of distension in type 1 diabetes mellitus: effects of hyperglycemia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 May;95(5):1175–1183. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacher G., Schernthaner G., Francesconi M., Kopp H. P., Bergmann H., Stacher-Janotta G., Weber U. Cisapride versus placebo for 8 weeks on glycemic control and gastric emptying in insulin-dependent diabetes: a double blind cross-over trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Jul;84(7):2357–2362. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.7.5859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm A., Holtmann G., Goebell H., Gerken G. Prokinetics in patients with gastroparesis: a systematic analysis. Digestion. 1999 Sep-Oct;60(5):422–427. doi: 10.1159/000007687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack J., Piessevaux H., Coulie B., Caenepeel P., Janssens J. Role of impaired gastric accommodation to a meal in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1998 Dec;115(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Verlinden M., Snape W., Beker J. A., Ducrotte P., Dettmer A., Brinkhoff H., Eaker E., Ohning G., Miner P. B. Failure of a motilin receptor agonist (ABT-229) to relieve the symptoms of functional dyspepsia in patients with and without delayed gastric emptying: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Dec;14(12):1653–1661. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troncon L. E., Rosa-e-Silva L., Oliveira R. B., Iazigi N., Gallo L., Jr, Foss M. C. Abnormal intragastric distribution of a liquid nutrient meal in patients with diabetes mellitus. Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Jul;43(7):1421–1429. doi: 10.1023/a:1018834025351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno N., Inui A., Asakawa A., Takao F., Tani S., Komatsu Y., Itoh Z., Kasuga M. Erythromycin improves glycaemic control in patients with Type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2000 Apr;43(4):411–415. doi: 10.1007/s001250051323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undeland K. A., Hausken T., Gilja O. H., Aanderud S., Berstad A. Gastric meal accommodation studied by ultrasound in diabetes. Relation to vagal tone. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Mar;33(3):236–241. doi: 10.1080/00365529850170784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undeland K. A., Hausken T., Svebak S., Aanderud S., Berstad A. Wide gastric antrum and low vagal tone in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 compared to patients with functional dyspepsia and healthy individuals. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02208577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen M. A., Samsom M., Maes B., Geypens B. J., Ghoos Y. F., Smout A. J. Effects of a new motilide, ABT-229, on gastric emptying and postprandial antroduodenal motility in healthy volunteers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Dec;11(6):1077–1086. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D., Schadewaldt P., Pour Mirza A., Piolot R., Schommartz B., Reinhardt M., Vosberg H., Brösicke H., Gries F. A. [13C]octanoic acid breath test for non-invasive assessment of gastric emptying in diabetic patients: validation and relationship to gastric symptoms and cardiovascular autonomic function. Diabetologia. 1996 Jul;39(7):823–830. doi: 10.1007/s001250050516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]