Abstract
BACKGROUND AND AIMS—Various opinions have been expressed as to the long term prognosis of liver disease associated with Alagille syndrome (AGS). PATIENTS AND METHODS—We reviewed the outcome of 163 children with AGS and liver involvement, investigated from 1960 to 2000, the end point of the study (median age 10 years (range 2 months to 44 years)) being death, liver transplantation, or the last visit. RESULTS—At the study end point, of the 132 patients who presented with neonatal cholestatic jaundice, 102 remained jaundiced, 112 had poorly controlled pruritus, and 40 had xanthomas; cirrhosis was found in 35/76 livers, varices in 25/71 patients, and liver transplantation had been carried out in 44 patients (33%). Forty eight patients died, 17 related to complications of liver disease. Of 31 patients who did not present with neonatal cholestatic jaundice, five were jaundiced at the study end point, 17 had well controlled pruritus, and none had xanthomas; cirrhosis was found in 6/18 patients, varices in 4/11, and none underwent liver transplantation. Nine patients died, two of liver disease. In the whole series, actuarial survival rates with native liver were 51% and 38% at 10 and 20 years, respectively, and overall survival rates were 68% and 62%, respectively. Neonatal cholestatic jaundice was associated with poorer survival with native liver (p=0.0004). CONCLUSIONS—The prognosis of liver disease in AGS is worse in children who present with neonatal cholestatic jaundice. However, severe liver complications are possible even after late onset of liver disease, demanding follow up throughout life. Keywords: Alagille syndrome; cholestasis; end stage liver disease; liver transplantation
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (123.7 KB).
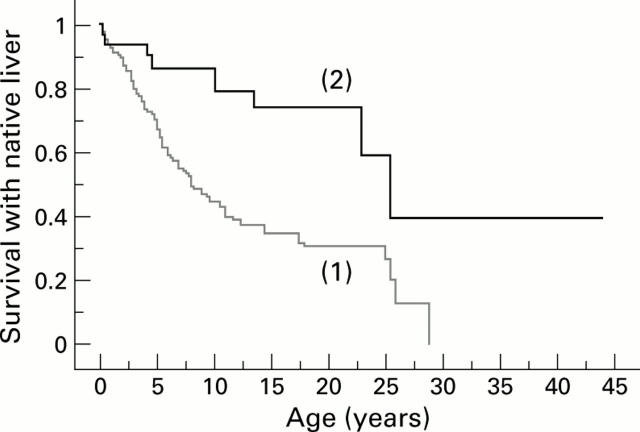
Figure 1 .
Survival with native liver in 163 patients with Alagille syndrome and chronic liver disease. 1, 132 patients with neonatal cholestatic jaundice; 2, 31 patients with late onset cholestasis (p=0.0004).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. C. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with arteriohepatic dysplasia. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Apr;31(4):438–442. doi: 10.1007/BF01311683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alagille D., Estrada A., Hadchouel M., Gautier M., Odièvre M., Dommergues J. P. Syndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts (Alagille syndrome or arteriohepatic dysplasia): review of 80 cases. J Pediatr. 1987 Feb;110(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alagille D., Odièvre M., Gautier M., Dommergues J. P. Hepatic ductular hypoplasia associated with characteristic facies, vertebral malformations, retarded physical, mental, and sexual development, and cardiac murmur. J Pediatr. 1975 Jan;86(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80706-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Békássy A. N., Garwicz S., Wiebe T., Hägerstrand I., Jensen O. A. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with arteriohepatic dysplasia in a 4-year-old girl. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1992;20(1):78–83. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950200118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardona J., Houssin D., Gauthier F., Devictor D., Losay J., Hadchouel M., Bernard O. Liver transplantation in children with Alagille syndrome--a study of twelve cases. Transplantation. 1995 Aug 27;60(4):339–342. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199508270-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deprettere A., Portmann B., Mowat A. P. Syndromic paucity of the intrahepatic bile ducts: diagnostic difficulty; severe morbidity throughout early childhood. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1987 Nov-Dec;6(6):865–871. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198711000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerick K. M., Rand E. B., Goldmuntz E., Krantz I. D., Spinner N. B., Piccoli D. A. Features of Alagille syndrome in 92 patients: frequency and relation to prognosis. Hepatology. 1999 Mar;29(3):822–829. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffenberg E. J., Narkewicz M. R., Sondheimer J. M., Smith D. J., Silverman A., Sokol R. J. Outcome of syndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts (Alagille syndrome) with onset of cholestasis in infancy. J Pediatr. 1995 Aug;127(2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. S., Wood R. P., Shaw B. W., Jr, Markin R. S., Gridelli B., Vanderhoof J. A. Hepatocarcinoma in a child with the Alagille syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Jun;141(6):698–700. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460060114050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz I. D., Piccoli D. A., Spinner N. B. Alagille syndrome. J Med Genet. 1997 Feb;34(2):152–157. doi: 10.1136/jmg.34.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Krantz I. D., Deng Y., Genin A., Banta A. B., Collins C. C., Qi M., Trask B. J., Kuo W. L., Cochran J. Alagille syndrome is caused by mutations in human Jagged1, which encodes a ligand for Notch1. Nat Genet. 1997 Jul;16(3):243–251. doi: 10.1038/ng0797-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan J. C., Shepherd R., Heritage M. Arteriohepatic dysplasia (Alagille syndrome; Watson-Alagille syndrome). Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1998 Jun;12(2):275–291. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3528(98)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda T., Elkahloun A. G., Pike B. L., Okajima K., Krantz I. D., Genin A., Piccoli D. A., Meltzer P. S., Spinner N. B., Collins F. S. Mutations in the human Jagged1 gene are responsible for Alagille syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997 Jul;16(3):235–242. doi: 10.1038/ng0797-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiros-Tejeira R. E., Ament M. E., Heyman M. B., Martin M. G., Rosenthal P., Hall T. R., McDiarmid S. V., Vargas J. H. Variable morbidity in alagille syndrome: a review of 43 cases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999 Oct;29(4):431–437. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199910000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riely C. A., Cotlier E., Jensen P. S., Klatskin G. Arteriohepatic dysplasia: a benign syndrome of intrahepatic cholestasis with multiple organ involvement. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):520–527. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenberg S. J., Grothe R. M., Sharp H. L., Snover D. C., Freese D. Long-term complications of arteriohepatic dysplasia. Am J Med. 1992 Aug;93(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90047-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzakis A. G., Reyes J., Tepetes K., Tzoracoleftherakis V., Todo S., Starzl T. E. Liver transplantation for Alagille's syndrome. Arch Surg. 1993 Mar;128(3):337–339. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420150093017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]