Abstract
BACKGROUND—There is increasing evidence that reflux of bile plays a part in the pathogenesis of Barrett's oesophagus. Bile injury to the gastric mucosa results in a "chemical" gastritis in which oedema and intestinal metaplasia are prominent. AIM—To determine if patients with Barrett's oesophagus have more bile related changes in antral mucosa than patients with uncomplicated gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) or non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD). PATIENTS AND METHODS—Patients were identified by a retrospective search of pathology records and those with a clinically confirmed diagnosis of either Barrett's oesophagus or reflux oesophagitis who had oesophageal and gastric biopsies taken at the same endoscopy and had no evidence of Helicobacter pylori infection entered the study. Control biopsies were taken from H pylori negative NUD patients. Antral biopsies were examined "blind" to clinical group and graded for a series of histological features from which the "reflux gastritis score" (RGS) and "bile reflux index" (BRI) could be calculated. The reproducibility of these histological scores was tested by a second pathologist. RESULTS—There were 100 patients with Barrett's, 61 with GORD, and 50 with NUD. The RGSs did not differ between groups. BRI values in the Barrett's group were significantly higher than those in GORD subjects (p=0.014) which in turn were higher than those in NUD patients (p=0.037). Similarly, the frequency of high BRI values (>14) was significantly greater in the Barrett's group (29/100; 29%) than in the GORD (9/61; 14.8%) or NUD (4/50; 8%) group. However, agreement on BRI values was "poor", indicating limited applicability of this approach. CONCLUSION—Patients with Barrett's oesophagus have more evidence of bile related gastritis than subjects with uncomplicated GORD or NUD. The presence of bile in the refluxate could be a factor in both the development of "specialised" intestinal metaplasia and malignancy in the oesophagus. Keywords: Barrett's oesophagus; reflux gastritis; bile; duodenogastro-oesophageal reflux; intestinal metaplasia
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (157.9 KB).
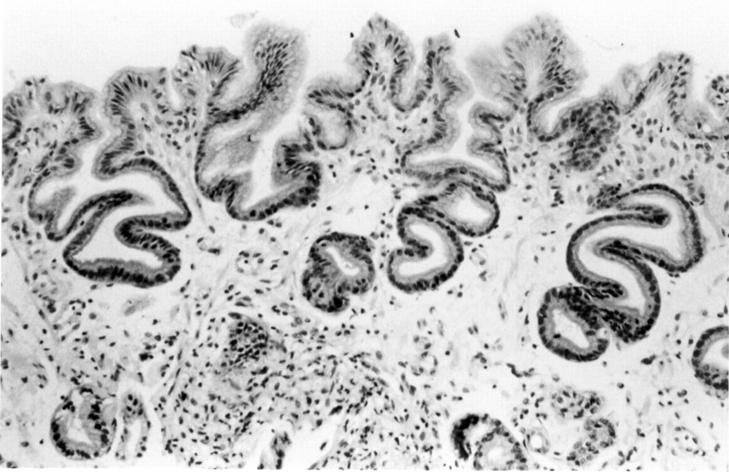
Figure 1 .
Antral biopsy from a patient with Barrett's oesophagus. This was graded as: foveolar hyperplasia=2;congestion=0; acute inflammation= 0; chronic inflammation=1; oedema=2; intestinal metaplasia=0. These grades give a reflux gastritis score of 9 and a bile reflux index of 18. An index >14 is taken as a strong predictor of a raised gastric juice bile acid content.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arul G. S., Moorghen M., Myerscough N., Alderson D. A., Spicer R. D., Corfield A. P. Mucin gene expression in Barrett's oesophagus: an in situ hybridisation and immunohistochemical study. Gut. 2000 Dec;47(6):753–761. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechi P., Amorosi A., Mazzanti R., Dei R., Bianchi S., Mugnai L., Masini E. Reflux-related gastric mucosal injury is associated with increased mucosal histamine content in humans. Gastroenterology. 1993 Apr;104(4):1057–1063. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90274-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechi P., Amorosi A., Mazzanti R., Romagnoli P., Tonelli L. Gastric histology and fasting bile reflux after partial gastrectomy. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowrey D. J., Clark G. W., Williams G. T. Patterns of gastritis in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut. 1999 Dec;45(6):798–803. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.6.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. F., Jr, Shuker D. E., Charnley G., Newberne P. M., Tannenbaum S. R., Wogan G. N. Carcinogenicity in rats of the nitrosated bile acid conjugates N-nitrosoglycocholic acid and N-nitrosotaurocholic acid. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1367–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion G., Richter J. E., Vaezi M. F., Singh S., Alexander R. Duodenogastroesophageal reflux: relationship to pH and importance in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1994 Sep;107(3):747–754. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasoma P. T., Lokuhetty D. M., Demeester T. R., Bremmer C. G., Peters J. H., Oberg S., Groshen S. Definition of histopathologic changes in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000 Mar;24(3):344–351. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200003000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craanen M. E., Dekker W., Blok P., Ferwerda J., Tytgat G. N. Intestinal metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori: an endoscopic bioptic study of the gastric antrum. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):16–20. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester S. R., DeMeester T. R. Columnar mucosa and intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus: fifty years of controversy. Ann Surg. 2000 Mar;231(3):303–321. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200003000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R. Antireflux surgery in the management of Barrett's esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Mar-Apr;4(2):124–128. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(00)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. F., O'Connor H. J., Axon A. T., King R. F., Johnston D. Reflux gastritis: distinct histopathological entity? J Clin Pathol. 1986 May;39(5):524–530. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.5.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidt S., Stolte M. Antral intestinal metaplasia in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Digestion. 1994;55(1):13–18. doi: 10.1159/000201116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipe M. I., Muñoz N., Matko I., Kato I., Pompe-Kirn V., Jutersek A., Teuchmann S., Benz M., Prijon T. Intestinal metaplasia types and the risk of gastric cancer: a cohort study in Slovenia. Int J Cancer. 1994 May 1;57(3):324–329. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber M. M., Lopez I. Reflux gastritis in gastroesophageal reflux disease: A histopathological study. Ann Diagn Pathol. 1999 Oct;3(5):281–286. doi: 10.1016/s1092-9134(99)80023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Anggiansah A., Manifold D. K., Owen W. A., Owen W. J. Effect of omeprazole 20 mg twice daily on duodenogastric and gastro-oesophageal bile reflux in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 1998 Nov;43(5):603–606. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.5.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Anggiansah A., Owen W. A., Owen W. J. The temporal relationship between oesophageal bile reflux and pH in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 May;10(5):385–392. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199805000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Anggiansah A., Owen W. J. Bile in the oesophagus: clinical relevance and ambulatory detection. Br J Surg. 1997 Jan;84(1):21–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Bremner C. G. Gastritis in Barrett's esophagus. World J Surg. 1995 Jan-Feb;19(1):96–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00316987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moayyedi P., Wason C., Peacock R., Walan A., Bardhan K., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Changing patterns of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in long-standing acid suppression. Helicobacter. 2000 Dec;5(4):206–214. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5378.2000.00032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth D. G., Godwin P. G., Dixon M. F., Williams N. S., Johnston D. Ileal ecology after pouch-anal anastomosis or ileostomy. A study of mucosal morphology, fecal bacteriology, fecal volatile fatty acids, and their interrelationship. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):817–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehra D., Howell P., Williams C. P., Pye J. K., Beynon J. Toxic bile acids in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: influence of gastric acidity. Gut. 1999 May;44(5):598–602. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.5.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor H. J., Wyatt J. I., Dixon M. F., Axon A. T. Campylobacter like organisms and reflux gastritis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 May;39(5):531–534. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offerhaus G. J., Rieu P. N., Jansen J. B., Joosten H. J., Lamers C. B. Prospective comparative study of the influence of postoperative bile reflux on gastric mucosal histology and Campylobacter pylori infection. Gut. 1989 Nov;30(11):1552–1557. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.11.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothery G. A., Patterson J. E., Stoddard C. J., Day D. W. Histological and histochemical changes in the columnar lined (Barrett's) oesophagus. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):1062–1068. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silcocks P. B. Measuring repeatability and validity of histological diagnosis--a brief review with some practical examples. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;36(11):1269–1275. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.11.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Epithelial metaplasia and the second anatomy. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):268–271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Stem cells in epithelial tissues. Science. 2000 Feb 25;287(5457):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5457.1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobala G. M., King R. F., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Reflux gastritis in the intact stomach. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;43(4):303–306. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.4.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobala G. M., O'Connor H. J., Dewar E. P., King R. F., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Bile reflux and intestinal metaplasia in gastric mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Mar;46(3):235–240. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.3.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Kauer W. K., Feussner H., Siewert J. R. Bile reflux in benign and malignant Barrett's esophagus: effect of medical acid suppression and nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 1998 Jul-Aug;2(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(98)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Smyrk T. C., DeMeester T. R., Rouse J., Hinder R. A. Clinical value of endoscopy and histology in the diagnosis of duodenogastric reflux disease. Surgery. 1992 Oct;112(4):796–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanholm H., Starklint H., Gundersen H. J., Fabricius J., Barlebo H., Olsen S. Reproducibility of histomorphologic diagnoses with special reference to the kappa statistic. APMIS. 1989 Aug;97(8):689–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen J., Nehra D., Citron D., Johansson J., Hagen J. A., Crookes P. F., DeMeester S. R., Bremner C. G., DeMeester T. R., Peters J. H. Suppression of gastric acid secretion in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease results in gastric bacterial overgrowth and deconjugation of bile acids. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Jan-Feb;4(1):50–54. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(00)80032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G. Proton pump inhibitors for Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2000 Feb;46(2):144–146. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi M. F., Richter J. E. Role of acid and duodenogastroesophageal reflux in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1996 Nov;111(5):1192–1199. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8898632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen M., Färkkilä M., Juhola M., Mecklin J. P., Sipponen P. Complete and incomplete intestinal metaplasia at the oesophagogastric junction: prevalences and associations with endoscopic erosive oesophagitis and gastritis. Gut. 1999 Nov;45(5):644–648. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.5.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. S., Shun C. T., Lee W. C., Chen C. J., Wang H. P., Lee W. J., Lin J. T. Gastric cancer risk in relation to Helicobacter pylori infection and subtypes of intestinal metaplasia. Br J Cancer. 1998 Jul;78(1):125–128. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Dixon M. F., Heatley R. V. Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;40(8):841–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]