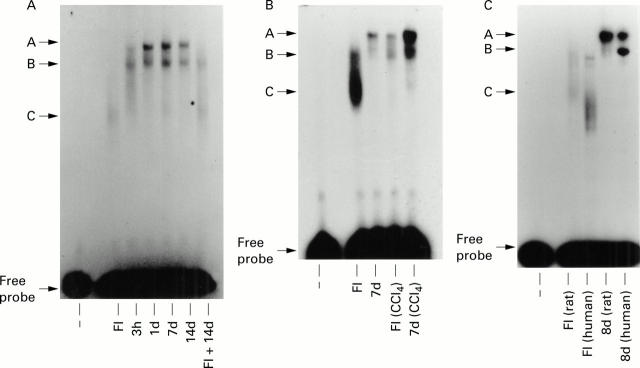
Figure 1 .
Analysis of E-box DNA binding activities in primary rat and human hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). (A) Modulation of E-box DNA binding in cultured rat HSCs. Nuclear extracts (10 µg) prepared from freshly isolated (FI) and cultured (three hours to 14 days) rat HSCs were used to detect E-box DNA binding activities by EMSA. A control track (−) lacking nuclear extract was included on the far left hand side of the gel. FI+14 days shows the effects of adding equal quantities (10 µg of each) of nuclear extract into the same EMSA reaction mixture. A, B, and C denote retarded E-box DNA:protein binding complexes. (B) Modulation of E-box DNA binding during in vivo activation of rat HSCs. Control and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) treated rats (48 hours) were used to prepare HSCs which were either harvested (FI and FI (CCl4)) or cultured for seven days (7d and 7d (CCl4)) prior to preparation of nuclear extracts; 10 µg of each extract were used for electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). (C) Comparison of rat and human HSC E-box DNA binding activities: 10 µg of nuclear extract prepared from freshly isolated (FI) or eight day cultured (8d) rat and human HSCs were used in EMSA assays. All gels are representative of at least three independent experiments.