Abstract
BACKGROUND—Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) is assumed to preserve sphincter of Oddi function because it causes little trauma to the papilla. However, few studies have addressed this issue specifically. In this study, we investigated whether EPBD can preserve sphincter function, and evaluated whether or not such preservation has clinical significance. METHODS—Seventy patients with common bile duct (CBD) stones were randomly assigned to EPBD or endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST). Sphincter of Oddi (SO) function was measured by endoscopic manometry before, one week after, and one year after treatment. Incidence of pneumobilia and later complications were compared between the two groups at one year. Series manometric data were compared within each group and between the two groups. For a more detailed analysis of the cumulative incidence of later complications, retrospective cohorts were added to the study groups, giving a total number of 235 patients in the EPBD group and 126 in the EST group. RESULTS—Baseline characteristics did not differ significantly between the 35 EPBD and 35 EST patients. CBD stones were discharged successfully in all cases. CBD pressure, SO basal and peak pressures, and contraction frequency decreased significantly at one week in both groups. The damage was more severe in the EST group, and SO contraction completely disappeared in 23 patients in this group. The incidence of pneumobilia was significantly lower in the EPBD group than in the EST group (p<0.01) whereas CBD stones recurred and cholecystitis appeared at a similar rate in both groups at one year. A complete series of manometric data up to one year was obtained in 55 patients; 28 in the post-EPBD and 27 in post-EST groups. In the post-EPBD group, SO basal and peak pressures significantly recovered at one year compared with data at one week but these measures still remained significantly lower than those before EPBD (p< 0.01). In the post-EST group, SO contraction did not recover even after one year. A Kaplan-Meier analysis of 235 EPBD and 126 EST patients for a median follow up of 37 months revealed significantly lower incidences of biliary complications such as recurrent CBD stones and cholangitis, and cholecystitis in the EPBD group than in the EST group (p<0.05). The risk of pneumobilia was also significantly lower in the EPBD group (p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS—Preservation of papillary function after EPBD was not complete but remained somewhat reduced. However, preservation was more successful with EPBD than with EST. Such preservation may be clinically beneficial for the prevention of later complications. Keywords: endoscopic papillary balloon dilation; endoscopic manometry; sphincter of Oddi; common bile duct stone
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (117.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
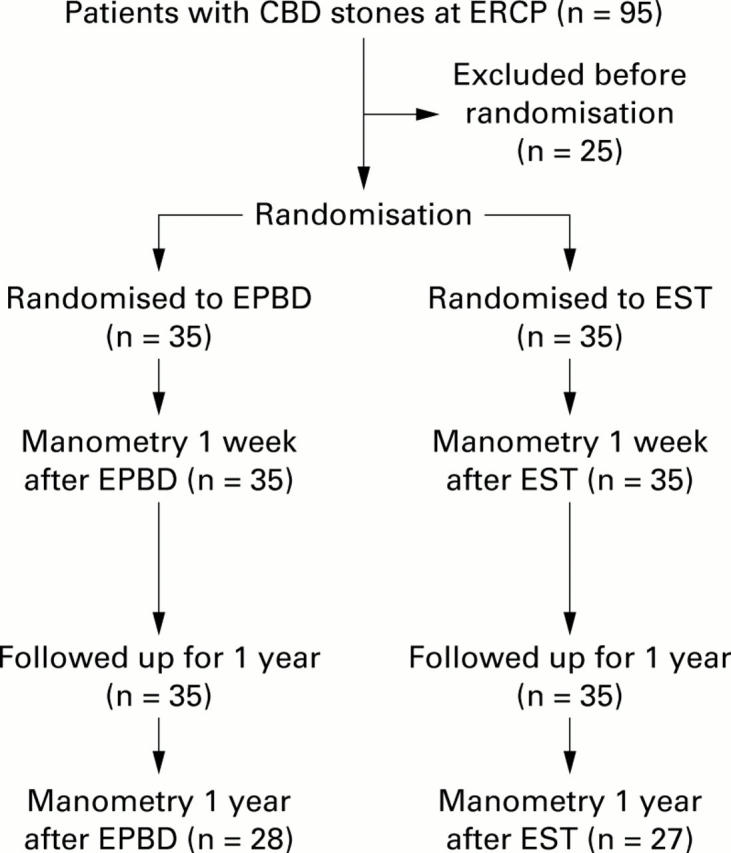
Trial profile. EPBD, endoscopic papillary balloon dilation; CBD, common bile duct; EST, endoscopic sphincterotomy; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
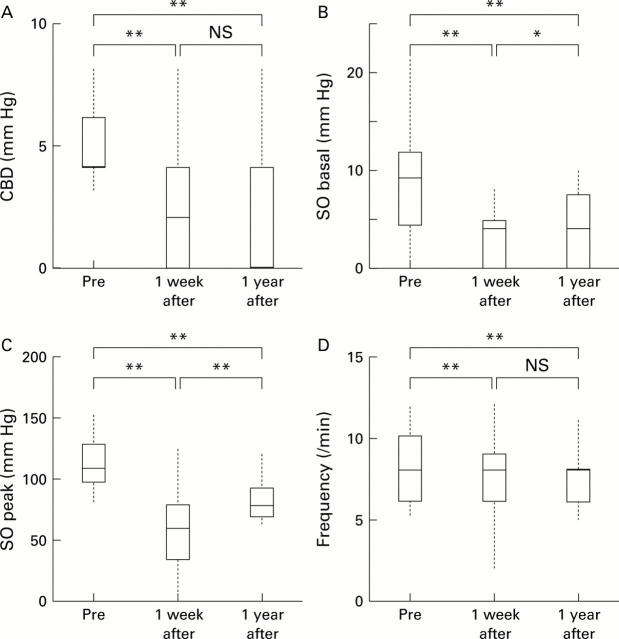
Figure 2 .
Common bile duct (CBD) pressure (A), sphincter of Oddi (SO) basal and peak pressures (B, C), and SO contraction frequency (D) before (Pre), one week after, and one year after endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) in patients with CBD stones. Data are expressed by the outlier box plot generated by JMP v. 4 software. The box represents the 25th and 75th quantiles (quartiles), with the line in the middle of the box identifying the median; the broken lines indicate the upper quartile +1.5× (interquartile range) and the lower quartile −1.5× (interquartile range), respectively. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Figure 3 .
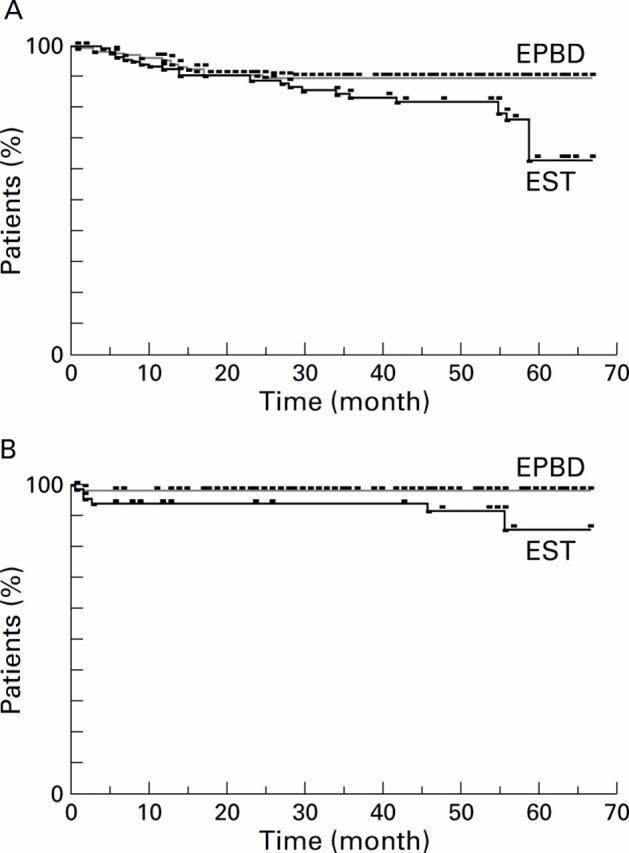
Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients without biliary complications (A) in the post-endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) (n=235) and post-endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) patients (n=126) (p<0.05) or cholecystitis (B) in the post-EPBD (n=150) and post-EST patients (n=68) (p<0.05).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman J. J., Rauws E. A., Fockens P., van Berkel A. M., Bossuyt P. M., Tijssen J. G., Tytgat G. N., Huibregtse K. Randomised trial of endoscopic balloon dilation versus endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bileduct stones. Lancet. 1997 Apr 19;349(9059):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)11026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman J. J., van Berkel A. M., Groen A. K., Schoeman M. N., Offerhaus J., Tytgat G. N., Huibregtse K. Biliary manometry, bacterial characteristics, bile composition, and histologic changes fifteen to seventeen years after endoscopic sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997 May;45(5):400–405. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakamada K., Sasaki M., Endoh M., Itoh T., Morita T., Konn M. Late development of bile duct cancer after sphincteroplasty: a ten- to twenty-two-year follow-up study. Surgery. 1997 May;121(5):488–492. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(97)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Tanaka M., Matsumoto S., Yoshimoto H., Itoh H. Endoscopic sphincterotomy: long-term results in 408 patients with complete follow-up. Endoscopy. 1988 Jan;20(1):13–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Komatsu Y., Tada M., Toda N., Ohashi M., Shiratori Y., Omata M. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation in cirrhotic patients: removal of common bile duct stones without sphincterotomy. Endoscopy. 1996 Oct;28(8):694–698. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Kawabe T., Toda N., Ohashi M., Isayama M., Tateishi K., Sato S., Koike Y., Yamagata M., Tada M. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation for the management of common bile duct stones: experience of 226 cases. Endoscopy. 1998 Jan;30(1):12–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-993721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurumado K., Nagai T., Kondo Y., Abe H. Long-term observations on morphological changes of choledochal epithelium after choledochoenterostomy in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Apr;39(4):809–820. doi: 10.1007/BF02087428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mac Mathuna P., Siegenberg D., Gibbons D., Gorin D., O'Brien M., Afdhal N. A., Chuttani R. The acute and long-term effect of balloon sphincteroplasty on papillary structure in pigs. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Dec;44(6):650–655. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mac Mathuna P., White P., Clarke E., Lennon J., Crowe J. Endoscopic sphincteroplasty: a novel and safe alternative to papillotomy in the management of bile duct stones. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):127–129. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathuna P. M., White P., Clarke E., Merriman R., Lennon J. R., Crowe J. Endoscopic balloon sphincteroplasty (papillary dilation) for bile duct stones: efficacy, safety, and follow-up in 100 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995 Nov;42(5):468–474. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. R., Cotton P. B., Edmunds S. E., Chong W. Removal of stones from the bile duct at ERCP without sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993 Nov-Dec;39(6):749–754. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(93)70258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami A., Nakatsu T., Uchida N., Hirabayashi S., Fukuma H., Morshed S. A., Nishioka M. Papillary dilation vs sphincterotomy in endoscopic removal of bile duct stones. A randomized trial with manometric function. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Dec;40(12):2550–2554. doi: 10.1007/BF02220440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi Y., Mukawa K., Kiyosawa K., Akamatsu T. Comparing the treatment outcomes of endoscopic papillary dilation and endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bile duct stones. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999 Jan;14(1):90–96. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Kodama T., Takaaki J., Tatsumi Y., Maeda T., Fujita S., Fukui Y., Ogasawara H., Mitsufuji S. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation may preserve sphincter of Oddi function after common bile duct stone management: evaluation from the viewpoint of endoscopic manometry. Gut. 1997 Oct;41(4):541–544. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.4.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert E. Long-term follow-up after endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST). Endoscopy. 1988 Aug;20 (Suppl 1):232–235. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staritz M., Ewe K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Endoscopic papillary dilation (EPD) for the treatment of common bile duct stones and papillary stenosis. Endoscopy. 1983 May;15 (Suppl 1):197–198. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno N., Ozawa Y. Endoscopic sphincter dilation in patients with bile duct stones: immediate and medium-term results. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999 Aug;14(8):822–826. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda I., Tomita E., Moriwaki H., Kato T., Wakahara T., Sugihara J., Nagura K., Nishigaki Y., Sugiyama A., Enya M. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation for common bile duct stones: efficacy of combination with extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy for large stones. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Dec;10(12):1045–1050. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199812000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]