Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (73.6 KB).
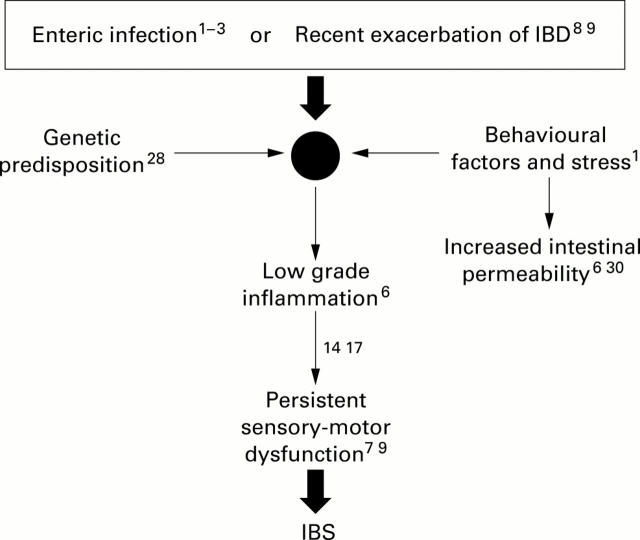
Figure 1 .
Schematic representation of the relationship between inflammation and the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Citations represent evidence, from basic or clinical research, that support the proposed model. IBD, inflammatory bowel disease.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbara G., De Giorgio R., Deng Y., Vallance B., Blennerhassett P., Collins S. M. Role of immunologic factors and cyclooxygenase 2 in persistent postinfective enteric muscle dysfunction in mice. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jun;120(7):1729–1736. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.24847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbara G., Vallance B. A., Collins S. M. Persistent intestinal neuromuscular dysfunction after acute nematode infection in mice. Gastroenterology. 1997 Oct;113(4):1224–1232. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9322517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. M. The immunomodulation of enteric neuromuscular function: implications for motility and inflammatory disorders. Gastroenterology. 1996 Dec;111(6):1683–1699. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(96)70034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der T., Bercik P., Donnelly G., Jackson T., Berezin I., Collins S. M., Huizinga J. D. Interstitial cells of cajal and inflammation-induced motor dysfunction in the mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology. 2000 Dec;119(6):1590–1599. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.20221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galeazzi F., Haapala E. M., van Rooijen N., Vallance B. A., Collins S. M. Inflammation-induced impairment of enteric nerve function in nematode-infected mice is macrophage dependent. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000 Feb;278(2):G259–G265. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2000.278.2.G259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwee K. A., Graham J. C., McKendrick M. W., Collins S. M., Marshall J. S., Walters S. J., Read N. W. Psychometric scores and persistence of irritable bowel after infectious diarrhoea. Lancet. 1996 Jan 20;347(8995):150–153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwee K. A., Leong Y. L., Graham C., McKendrick M. W., Collins S. M., Walters S. J., Underwood J. E., Read N. W. The role of psychological and biological factors in postinfective gut dysfunction. Gut. 1999 Mar;44(3):400–406. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.3.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIATT R. B., KATZ L. Mast cells in inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Gastroenterol. 1962 May;37:541–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isgar B., Harman M., Kaye M. D., Whorwell P. J. Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in ulcerative colitis in remission. Gut. 1983 Mar;24(3):190–192. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.3.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. A., McLaughlan P., Shorthouse M., Workman E., Hunter J. O. Food intolerance: a major factor in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet. 1982 Nov 20;2(8308):1115–1117. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiliaan A. J., Saunders P. R., Bijlsma P. B., Berin M. C., Taminiau J. A., Groot J. A., Perdue M. H. Stress stimulates transepithelial macromolecular uptake in rat jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1998 Nov;275(5 Pt 1):G1037–G1044. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.5.G1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening-Baucke V., Metcalf A. M., Shirazi S. Rectosigmoid motility in patients with quiescent and active ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Jan;84(1):34–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendrick M. W., Read N. W. Irritable bowel syndrome--post salmonella infection. J Infect. 1994 Jul;29(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(94)94871-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munzer D., Eyad C. Spastic colitis and irritable bowel syndrome: which expression is prevalent? (A review of 120 cases). Trop Gastroenterol. 1992 Jan-Mar;13(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal K. R., Hebden J., Spiller R. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms six months after bacterial gastroenteritis and risk factors for development of the irritable bowel syndrome: postal survey of patients. BMJ. 1997 Mar 15;314(7083):779–782. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7083.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M., Clayton N., Breslin N. P., Harman I., Bountra C., McLaren A., O'Morain C. A. Increased mast cells in the irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2000 Oct;12(5):449–457. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.2000.00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima S., Fujimura M., Fukimiya M. Changes in number of serotonin-containing cells and serotonin levels in the intestinal mucosa of rats with colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate. Histochem Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;112(4):257–263. doi: 10.1007/s004180050445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzmann J. L., Peltier-Koch F., Bloch F., Petite J. P., Camilleri J. P. Morphometric study of colonic biopsies: a new method of estimating inflammatory diseases. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):847–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller R. C., Jenkins D., Thornley J. P., Hebden J. M., Wright T., Skinner M., Neal K. R. Increased rectal mucosal enteroendocrine cells, T lymphocytes, and increased gut permeability following acute Campylobacter enteritis and in post-dysenteric irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2000 Dec;47(6):804–811. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.6.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance B. A., Galeazzi F., Collins S. M., Snider D. P. CD4 T cells and major histocompatibility complex class II expression influence worm expulsion and increased intestinal muscle contraction during Trichinella spiralis infection. Infect Immun. 1999 Nov;67(11):6090–6097. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.11.6090-6097.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Biddle W. L., Bhatia P. S., Miner P. B., Jr Terminal ileal mucosal mast cells in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Sep;38(9):1590–1595. doi: 10.1007/BF01303164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]