Abstract
BACKGROUND—Circulating antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) are often detected in patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) but little is known about the causes of their formation. AIMS—We have evaluated whether ethanol mediated oxidative injury might promote the development of aPL in ALD. PATIENTS AND METHODS—IgG against β2 glycoprotein 1 (β2-GP1), cardiolipin, and human serum albumin (HSA) complexed with either oxidised arachidonic acid (HSA-APP) or malondialdehyde (HSA-MDA) were assayed by ELISA in heavy drinkers with or without ALD and in healthy subjects. RESULTS—Circulating IgG recognising cardiolipin were significantly higher in ALD patients than in controls. However, anticardiolipin reactivity of ALD sera was only evident using, as the antigen, oxidised cardiolipin but not oxidation protected cardiolipin. In ALD patients, individual values of IgG antioxidised cardiolipin were associated with the titres of antibodies against HSA-MDA and HSA-APP (r=0.68 and 0.72, respectively; p<0.0001) used as markers of oxidative stress. ALD patients also displayed increased levels of antibodies against phospholipid binding protein β2-GP1, and individual reactivity towards oxidised cardiolipin and β2-GP1 were highly correlated (r=0.85; p<0.0001). IgG binding to oxidised cardiolipin, HSA-MDA, and HSA-APP was also significantly higher in β2-GP1 positive than in β2-GP1 negative sera. However, preadsorption of β2-GP1 positive sera on β2-GP1 coated ELISA plates reduced reactivity to oxidised cardiolipin by 80%, without affecting that to HSA-APP or HSA-MDA. CONCLUSIONS—Ethanol induced oxidative injury is associated with the development of antibodies targeting complexes between oxidised cardiolipin and β2-GP1. These antibodies might account for high aPL titres observed in patients with severe ALD. Keywords: oxidative stress; lipid peroxidation; β2 glycoprotein 1; ethanol; autoantibodies
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (179.7 KB).
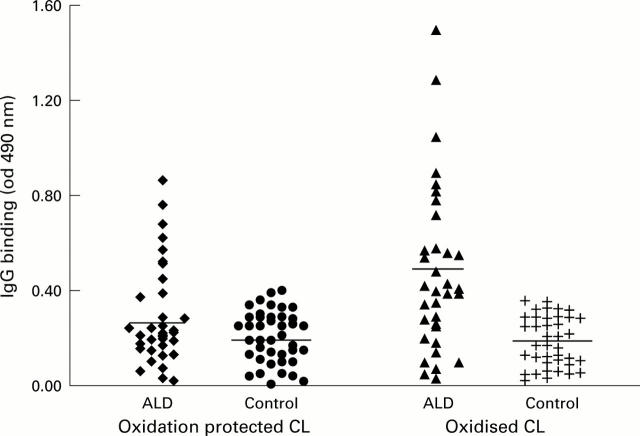
Figure 1 .
Immune reactivity against native or oxidised cardiolipin (CL) of sera from 36 patients with alcoholic cirrhosis with or without alcoholic hepatitis (ALD) and from 42 healthy control subjects. IgG binding to ELISA plates coated with CL allowed to auto-oxidise in air or oxidation protected CL was evaluated, as reported in the patients and methods section. The horizontal bars represent median values in each group. Values in each group were normally distributed, as evaluated by the Komolgorov-Smirnov test.
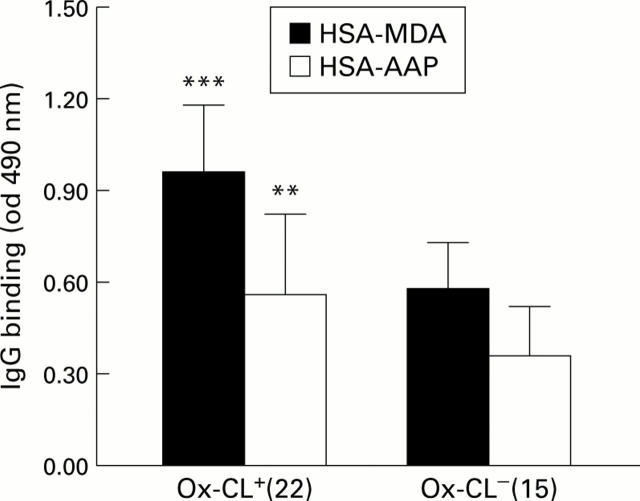
Figure 2 .
Reactivity with antigens derived from the reaction of proteins with lipid peroxidation products of sera from patients with alcoholic liver disease positive (Ox-CL+) or negative (Ox-CL ) for the presence of antibodies against oxidised cardiolipin. Human serum albumin (HSA) modified by the reaction with either malondialdehyde (HSA-MDA) or products from arachidonic acid peroxidation (HSA-APP) were used as antigens, as reported in the patients and methods section. Results are mean (SD) ELISA values. **p<0.01, ***p<0.0001 versus Ox-CL subjects.
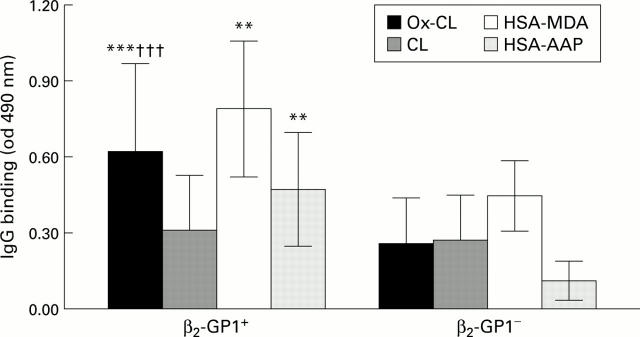
Figure 3 .
Reactivity with oxidised cardiolipin or with antigens derived from the reaction of proteins with lipid peroxidation products of sera from patients with alcoholic liver disease positive (β2-GP1+; n=23) or negative (β2-GP1 ; n=13) for the presence of antibodies against β2-glycoprotein 1. ELISA plates coated with oxidation protected (CL) or oxidised (Ox-CL) cardiolipin, or with malondialdehyde (HSA-MDA) or products from arachidonic acid peroxidation (HSA-APP) were used to evaluate IgG binding. Results are mean (SD) ELISA values. **p<0.005, ***p<0.001 versus β2-GP1 negative subjects; †††p<0.001 versus native cardiolipin.
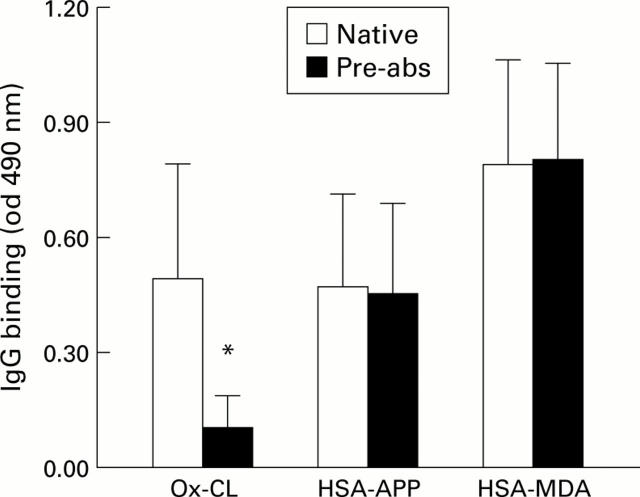
Figure 4 .
Reactivity with oxidised cardiolipin or human serum albumin (HSA) complexed with lipid peroxidation products following preabsorption with the β2 glycoprotein 1 (β2-GP1) of sera from alcoholic patients. Fifteen sera from patients with alcoholic liver disease displaying high titres of IgG against both cardiolipin and β2-GP1 were incubated overnight at 4°C on irradiated ELISA plates coated with β2-GP1 and tested for IgG binding to oxidised cardiolipin (Ox-CL) or HSA modified by reaction with malondialdehyde (HSA-MDA) or products of arachidonic acid peroxidation (HSA-APP). Results are mean (SD) ELISA values obtained with native sera or β2-GP1 preabsorbed sera. *p<0.0001 versus non-pre-absorbed sera.
Figure 5 .
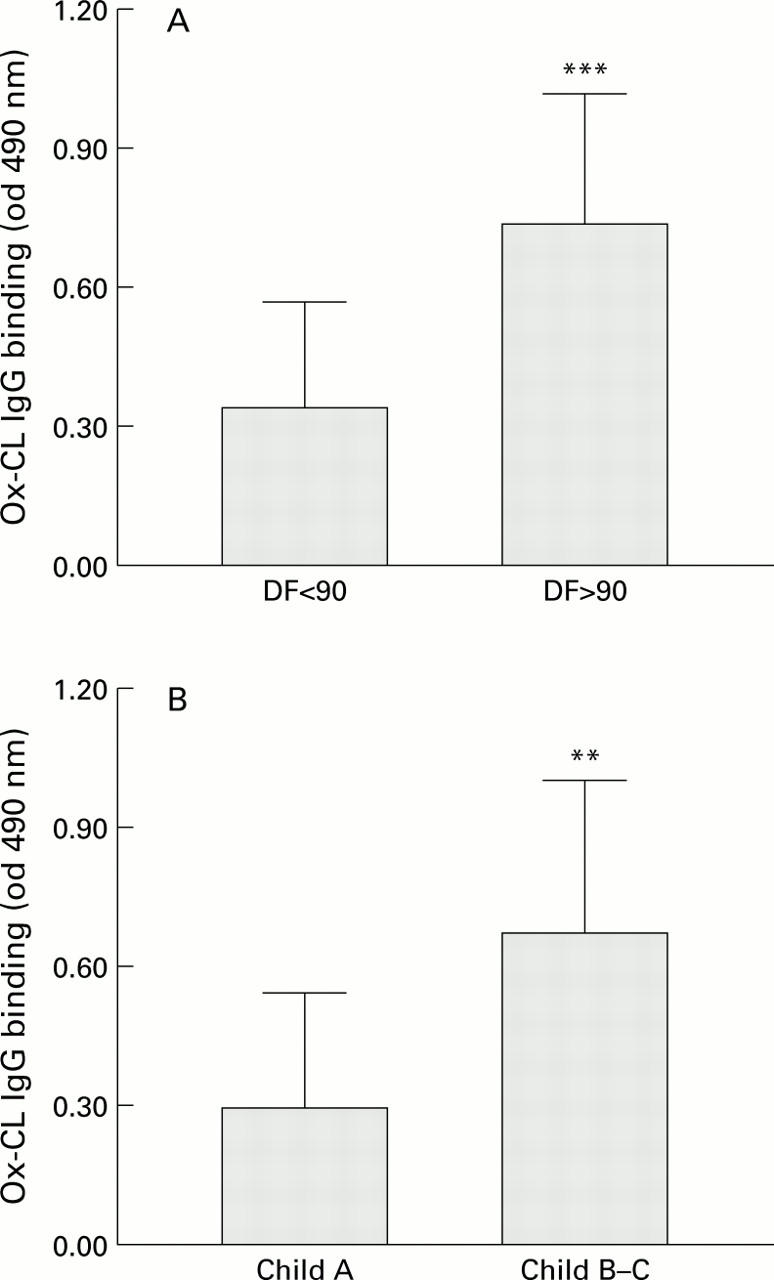
Reactivity against oxidised cardiolipin (Ox-CL) in relation to the severity of alcohol liver injury. The clinical severity of hepatic damage was estimated according to Maddrey's DF classification23 (A) or Child-Turcotte classification (B). Patients with DF values less than 90 (n=26) were considered to have mild or moderate hepatic injury and patients with DF values greater than 90 (n=10) represented the group with severe damage. Child A group consisted of 15 patients, while 21 subjects belonged to Child B-C groups. The optical density (od) values in each group were normally distributed, as evaluated by the Komolgorov-Smirnov test. ***p<0.0002 versus DF <90; **p<0.01 versus Child A group.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleynik S. I., Leo M. A., Aleynik M. K., Lieber C. S. Increased circulating products of lipid peroxidation in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998 Feb;22(1):192–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G., Mills P., Smith D., Runcie J. Antibodies to phospholipid in alcoholic liver disease. BMJ. 1994 Oct 29;309(6962):1161–1161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6962.1161b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C., Andréani H., Blanc P., Ramos J., Ducos J., Guigue N., Michel H., Larrey D., Schved J. F. Prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with chronic liver disease related to alcohol or hepatitis C virus: correlation with liver injury. J Lab Clin Med. 1998 Mar;131(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(98)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C., Lalloyer N., Tonnelot J. L., Larget D., Gris J. C., Schved J. F. Anticardiolipin antibodies and acute alcoholic intoxication. Lupus. 1995 Dec;4(6):486–490. doi: 10.1177/096120339500400612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley L. W., Duncalf A. M., Konarkowska B., Mitchell M. D., Johnson P. M. Conformationally altered beta 2-glycoprotein I is the antigen for anti-cardiolipin autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Mar;115(3):571–576. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. K., Bergmark C., Laurila A., Hörkkö S., Han K. H., Friedman P., Dennis E. A., Witztum J. L. Monoclonal antibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein bind to apoptotic cells and inhibit their phagocytosis by elicited macrophages: evidence that oxidation-specific epitopes mediate macrophage recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 May 25;96(11):6353–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid A., Chadalawada K. R., Morgan T. R., Moritz T. E., Mendenhall C. L., Hammond J. B., Emblad P. W., Cifuentes D. C., Kwak J. W., Gilman-Sachs A. Phospholipid antibodies in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1994 Dec;20(6):1465–1471. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840200614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clot P., Bellomo G., Tabone M., Aricò S., Albano E. Detection of antibodies against proteins modified by hydroxyethyl free radicals in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clot P., Tabone M., Aricò S., Albano E. Monitoring oxidative damage in patients with liver cirrhosis and different daily alcohol intake. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1637–1643. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cominacini L., Garbin U., Davoli A., Micciolo R., Bosello O., Gaviraghi G., Scuro L. A., Pastorino A. M. A simple test for predisposition to LDL oxidation based on the fluorescence development during copper-catalyzed oxidative modification. J Lipid Res. 1991 Feb;32(2):349–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. A peek at the Child-Turcotte classification. Hepatology. 1981 Nov-Dec;1(6):673–676. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont I., Lucas D., Clot P., Ménez C., Albano E. Cytochrome P4502E1 inducibility and hydroxyethyl radical formation among alcoholics. J Hepatol. 1998 Apr;28(4):564–571. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Maassen C., Hemker H. C., de Baets M. H., van Breda-Vriesman P. J., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) directed not to cardiolipin but to a plasma protein cofactor. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1544–1547. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91374-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattagliano I., Vendemiale G., Sabbà C., Buonamico P., Altomare E. Oxidation of circulating proteins in alcoholics: role of acetaldehyde and xanthine oxidase. J Hepatol. 1996 Jul;25(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80324-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N. Antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jan;74(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. B., Awad J. A. Increased urinary F2-isoprostane excretion in alcoholic liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999 Mar;26(5-6):656–660. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R. The antiphospholipid syndrome: ten years on. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörkkö S., Miller E., Branch D. W., Palinski W., Witztum J. L. The epitopes for some antiphospholipid antibodies are adducts of oxidized phospholipid and beta2 glycoprotein 1 (and other proteins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 16;94(19):10356–10361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörkkö S., Miller E., Dudl E., Reaven P., Curtiss L. K., Zvaifler N. J., Terkeltaub R., Pierangeli S. S., Branch D. W., Palinski W. Antiphospholipid antibodies are directed against epitopes of oxidized phospholipids. Recognition of cardiolipin by monoclonal antibodies to epitopes of oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1996 Aug 1;98(3):815–825. doi: 10.1172/JCI118854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itabe H., Yamamoto H., Suzuki M., Kawai Y., Nakagawa Y., Suzuki A., Imanaka T., Takano T. Oxidized phosphatidylcholines that modify proteins. Analysis by monoclonal antibody against oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 27;271(52):33208–33217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.52.33208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuliano L., Praticò D., Ferro D., Pittoni V., Valesini G., Lawson J., FitzGerald G. A., Violi F. Enhanced lipid peroxidation in patients positive for antiphospholipid antibodies. Blood. 1997 Nov 15;90(10):3931–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose I., Higuchi H., Miura S., Saito H., Watanabe N., Hokari R., Hirokawa M., Takaishi M., Zeki S., Nakamura T. Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis of hepatocytes exposed to acute ethanol intoxication. Hepatology. 1997 Feb;25(2):368–378. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1997.v25.pm0009021949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte E., Herbeth B., Pirollet P., Chancerelle Y., Arnaud J., Musse N., Paille F., Siest G., Artur Y. Effect of alcohol consumption on blood antioxidant nutrients and oxidative stress indicators. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Aug;60(2):255–261. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/60.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy V., Arvieux J., Jacob M. C., Maynard-Muet M., Baud M., Zarski J. P. Prevalence and significance of anticardiolipin, anti-beta2 glycoprotein I and anti-prothrombin antibodies in chronic hepatitis C. Br J Haematol. 1998 Jun;101(3):468–474. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddrey W. C., Boitnott J. K., Bedine M. S., Weber F. L., Jr, Mezey E., White R. I., Jr Corticosteroid therapy of alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):193–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangia A., Margaglione M., Cascavilla I., Gentile R., Cappucci G., Facciorusso D., Grandone E., Di Minno G., Rizzetto M., Andriulli A. Anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Oct;94(10):2983–2987. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Yasuda T., Triplett D. A., Koike T. Anticardiolipin antibodies recognize beta 2-glycoprotein I structure altered by interacting with an oxygen modified solid phase surface. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):457–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevorach D., Zhou J. L., Song X., Elkon K. B. Systemic exposure to irradiated apoptotic cells induces autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1998 Jul 20;188(2):387–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanji A. A. Apoptosis and alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 1998;18(2):187–190. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann R., Ribière C., Rouach H. Implication of free radical mechanisms in ethanol-induced cellular injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 1992;12(3):219–240. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(92)90030-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Hörkkö S., Miller E., Steinbrecher U. P., Powell H. C., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Cloning of monoclonal autoantibodies to epitopes of oxidized lipoproteins from apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Demonstration of epitopes of oxidized low density lipoprotein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1996 Aug 1;98(3):800–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI118853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Rosenfeld M. E., Butler S. W., Socher S. A., Parthasarathy S., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Antisera and monoclonal antibodies specific for epitopes generated during oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):325–335. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. E., Rauch J., Shia M. A., Walsh M. T., Lieberthal W., Gilligan H. M., O'Laughlin T., Koh J. S., Levine J. S. Anti-phospholipid autoantibodies bind to apoptotic, but not viable, thymocytes in a beta 2-glycoprotein I-dependent manner. J Immunol. 1996 Sep 1;157(5):2201–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto J., Yuste J. R., Beloqui O., Civeira M. P., Riezu J. I., Aguirre B., Sangro B. Anticardiolipin antibodies in chronic hepatitis C: implication of hepatitis C virus as the cause of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Hepatology. 1996 Feb;23(2):199–204. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolla R., Vay D., Mottaran E., Parodi M., Traverso N., Aricó S., Sartori M., Bellomo G., Klassen L. W., Thiele G. M. Detection of circulating antibodies against malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts in patients with alcohol-induced liver disease. Hepatology. 2000 Apr;31(4):878–884. doi: 10.1053/he.2000.5373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorice M., Circella A., Misasi R., Pittoni V., Garofalo T., Cirelli A., Pavan A., Pontieri G. M., Valesini G. Cardiolipin on the surface of apoptotic cells as a possible trigger for antiphospholipids antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Nov;122(2):277–284. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zima T., Fialová L., Mikulíková L., Malbohan I. M., Popov P., Nespor K. Antibodies against phospholipids and oxidized LDL in alcoholic patients. Physiol Res. 1998;47(5):351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]