Abstract
A 20 year old man with severe chest pain was hospitalised for acute myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography revealed total obstruction of his right coronary artery, which was successfully recanalised by direct percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). There was also diffuse thrombi in the left coronary artery that was not recanalised by perfusion with 3000 U pro-urokinase. Anticoagulant therapy was performed after PTCA. Creatine kinase peaked one day after hospitalisation (4805 U/l). The activated partial thromboplastin time was 62.6 seconds (45%). Plasma anticardiolipin IgG antibodies were high (3.8 and 2.7) in repeated examinations. The PTCA site was patent after three months. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome should be considered as a cause of acute myocardial infarction in young adults, and PTCA with anticoagulant treatment is effective for initial treatment of the syndrome. Keywords: primary antiphospholipid syndrome; acute myocardial infarction; percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (84.2 KB).
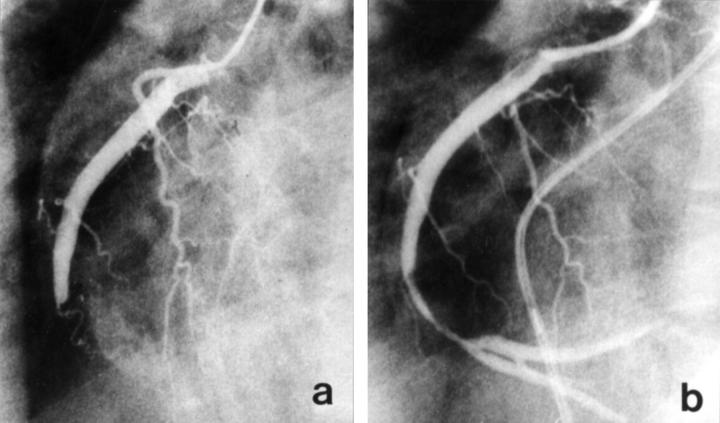
Figure 1 .
Right coronary arteriogram on admission shows total obstruction of right coronary artery (a). Arteriogram after PTCA shows successful recanalisation. There is diffuse thrombi in the coronary artery (b).
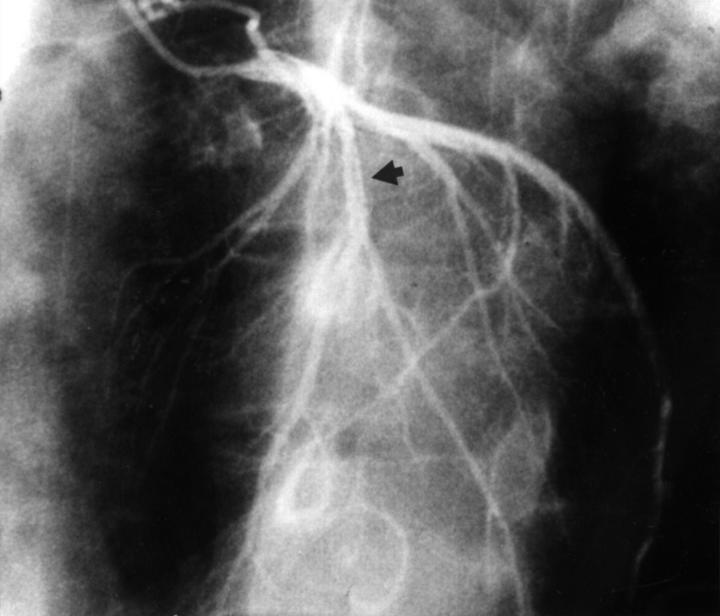
Figure 2 .
Left coronary arteriogram after three months shows diffuse organising thrombi in left anterior descending artery (arrows).