Abstract
Objective—To assess whether inotropic stress myocardial perfusion imaging, echocardiography, or a combination of the two could enhance the detection of multivessel disease, over and above clinical and exercise electrocardiographic data. Design—100 consecutive patients investigated by exercise electrocardiography and diagnostic coronary arteriography underwent simultaneous inotropic stress Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT (MIBI) imaging and echocardiography. MIBI imaging and echocardiographic data were analysed using a 12 segment left ventricular model, and each segment was ascribed to a particular coronary artery territory. The presence of perfusion defects with MIBI imaging or of wall thickening abnormality with echocardiography in at least two coronary artery territories at peak stress was taken as diagnostic of multivessel disease. Arteriographic evidence of ⩾ 50% stenosis was considered significant. Results—56 patients had multivessel disease. The sensitivity of the combination of MIBI imaging and echocardiography for detecting this was greater than either MIBI imaging or echocardiography alone (82%, 68%, and 68%, respectively; p = 0.005). Clinical and exercise electrocardiographic variables gave an R2 value of 18.2% for predicting multivessel disease. The addition of either MIBI imaging (R2 = 29.2%; p = 0.002) or echocardiography (R2 = 28.8%; p < 0.001) enhanced the detection of multivessel disease, and the inclusion of both had further incremental value (R2 = 34.8%; p = 0.003). Age (p = 0.03), MIBI imaging (p = 0.007), and echocardiography (p = 0.001) were independent predictors of multivessel disease. Conclusions—The assessment of both myocardial perfusion and contractile function by simultaneous inotropic stress MIBI imaging and echocardiography optimises the non-invasive detection of multivessel disease. Keywords: multivessel disease; inotropic stress; SPECT imaging; echocardiography
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (130.2 KB).
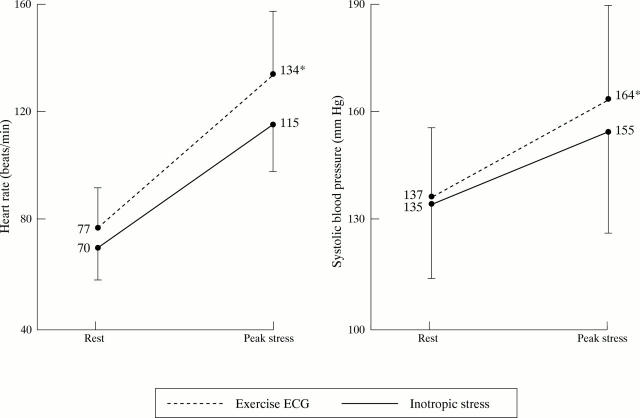
Figure 1 .
Heart rate and systolic blood pressure changes during exercise electrocardiography and inotropic stress testing.
Figure 2 .
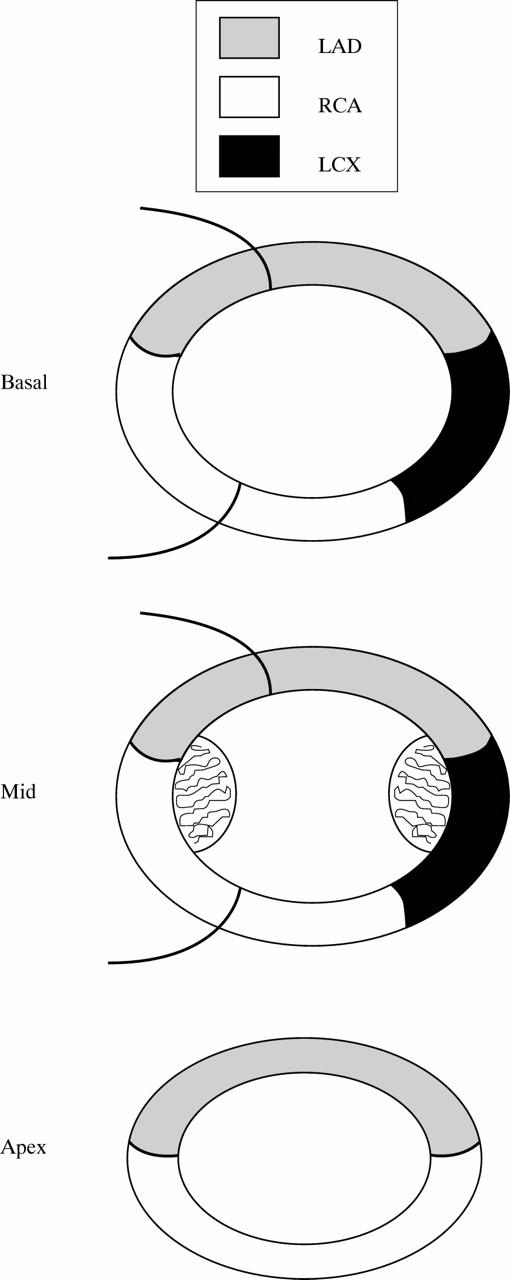
Twelve segments model of the left ventricular myocardium consisting of five segments at the basal level, five at the mid-papillary level, and two at the apex. LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; RCA, right coronary artery; LCX, left circumflex coronary artery.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christian T. F., Miller T. D., Bailey K. R., Gibbons R. J. Noninvasive identification of severe coronary artery disease using exercise tomographic thallium-201 imaging. Am J Cardiol. 1992 Jul 1;70(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)91382-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. L., Chan K. L., Jaarsma W., Bach D. S., Muller D. W., Starling M. R., Armstrong W. F. Arbutamine echocardiography: efficacy and safety of a new pharmacologic stress agent to induce myocardial ischemia and detect coronary artery disease. The International Arbutamine Study Group. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 1;26(5):1168–1175. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. L., Ottenweller J. E., George A. K., Duvvuri S. Comparison of dobutamine and exercise echocardiography for detecting coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Dec 1;72(17):1226–1231. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90288-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash H., Massie B. M., Botvinick E. H., Brundage B. H. The noninvasive identification of left main and three-vessel coronary artery disease by myocardial stress perfusion scintigraphy and treadmill exercise electrocardiography. Circulation. 1979 Aug;60(2):276–284. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson C. J., Sheikh K. H., Kisslo K. B., Phillips H. R., Peter R. H., Behar V. S., Kong Y. H., Krucoff M., Ohman E. M., Tcheng J. E. Intracoronary ultrasound evaluation of interventional technologies. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Nov 15;68(13):1305–1309. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90236-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis C. A., Pool P. E., Perrins E. J., Mohiuddin S. M., Sklar J., Kostuk W. J., Muller D. W., Starling M. R. Stress testing with closed-loop arbutamine as an alternative to exercise. The International Arbutamine Study Group. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 1;26(5):1151–1158. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanti G., Sciagrà R., Comeglio M., Taddei T., Bonechi F., Giusti F., Malfanti P., Bisi G. Diagnostic accuracy of peak exercise echocardiography in coronary artery disease: comparison with thallium-201 myocardial scintigraphy. Am Heart J. 1991 Dec;122(6):1609–1616. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90278-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht H. S., DeBord L., Shaw R., Chin H., Dunlap R., Ryan C., Myler R. K. Supine bicycle stress echocardiography versus tomographic thallium-201 exercise imaging for the detection of coronary artery disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(14)80488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann R., Lethen H., Kleinhans E., Weiss M., Flachskampf F. A., Hanrath P. Comparative evaluation of bicycle and dobutamine stress echocardiography with perfusion scintigraphy and bicycle electrocardiogram for identification of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Sep 1;72(7):555–559. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90351-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung J., Chaitman B. R., Lam J., Lesperance J., Dupras G., Fines P., Cherkaoui O., Robert P., Bourassa M. G. A logistic regression analysis of multiple noninvasive tests for the prediction of the presence and extent of coronary artery disease in men. Am Heart J. 1985 Aug;110(2):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul S., Senior R., Dittrich H., Raval U., Khattar R., Lahiri A. Detection of coronary artery disease with myocardial contrast echocardiography: comparison with 99mTc-sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography. Circulation. 1997 Aug 5;96(3):785–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiat H., Iskandrian A. S., Villegas B. J., Starling M. R., Berman D. S. Arbutamine stress thallium-201 single-photon emission computed tomography using a computerized closed-loop delivery system. Multicenter trial for evaluation of safety and diagnostic accuracy. The International Arbutamine Study Group. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 1;26(5):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler T. S., Diamond G. A. Exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy in the diagnosis and prognosis of coronary artery disease. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Nov 1;113(9):684–702. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-9-684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddahi J., Abdulla A., Garcia E. V., Swan H. J., Berman D. S. Noninvasive identification of left main and triple vessel coronary artery disease: improved accuracy using quantitative analysis of regional myocardial stress distribution and washout of thallium-201. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Jan;7(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwick T., D'Hondt A. M., Baudhuin T., Willemart B., Wijns W., Detry J. M., Melin J. Optimal use of dobutamine stress for the detection and evaluation of coronary artery disease: combination with echocardiography or scintigraphy, or both? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Jul;22(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90830-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwick T., Willemart B., D'Hondt A. M., Baudhuin T., Wijns W., Detry J. M., Melin J. Selection of the optimal nonexercise stress for the evaluation of ischemic regional myocardial dysfunction and malperfusion. Comparison of dobutamine and adenosine using echocardiography and 99mTc-MIBI single photon emission computed tomography. Circulation. 1993 Feb;87(2):345–354. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazeika P. K., Nadazdin A., Oakley C. M. Dobutamine stress echocardiography for detection and assessment of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 May;19(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90325-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. M., Sciacca R. R., Blood D. K., Cannon P. J. Discriminant function analysis using thallium-20 1 scintiscans and exercise stress test variables to predict the presence and extent of cornary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Jun;49(8):1917–1926. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard T. W., Gibson R. S., Ryan J. M., Gascho J. A., Watson D. D., Beller G. A. Prevalence of high-risk thallium-201 scintigraphic findings in left main coronary artery stenosis: comparison with patients with multiple- and single-vessel coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Feb 1;53(4):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell D. J., Underwood S. R., Swanton R. H., Walker J. M., Ell P. J. Dobutamine thallium myocardial perfusion tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Nov 15;18(6):1471–1479. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock S. G., Abbott R. D., Boucher C. A., Watson D. D., Kaul S. A model to predict multivessel coronary artery disease from the exercise thallium-201 stress test. Am J Med. 1991 Mar;90(3):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiñones M. A., Verani M. S., Haichin R. M., Mahmarian J. J., Suarez J., Zoghbi W. A. Exercise echocardiography versus 201Tl single-photon emission computed tomography in evaluation of coronary artery disease. Analysis of 292 patients. Circulation. 1992 Mar;85(3):1026–1031. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.3.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger V. L., Pellikka P. A., Oh J. K., Bailey K. R., Tajik A. J. Identification of multivessel coronary artery disease by exercise echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Jul;24(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S. G., Segar D. S., Ryan T., Brown S. E., Dohan A. M., Williams R., Fineberg N. S., Armstrong W. F., Feigenbaum H. Echocardiographic detection of coronary artery disease during dobutamine infusion. Circulation. 1991 May;83(5):1605–1614. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.5.1605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segar D. S., Brown S. E., Sawada S. G., Ryan T., Feigenbaum H. Dobutamine stress echocardiography: correlation with coronary lesion severity as determined by quantitative angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 May;19(6):1197–1202. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90324-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R., Basu S., Handler C., Raftery E. B., Lahiri A. Diagnostic accuracy of dobutamine stress echocardiography for detection of coronary heart disease in hypertensive patients. Eur Heart J. 1996 Feb;17(2):289–295. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R., Glenville B., Basu S., Sridhara B. S., Anagnostou E., Stanbridge R., Edmondson S. J., Handler C. E., Raftery E. B., Lahiri A. Dobutamine echocardiography and thallium-201 imaging predict functional improvement after revascularisation in severe ischaemic left ventricular dysfunction. Br Heart J. 1995 Oct;74(4):358–364. doi: 10.1136/hrt.74.4.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verzijlbergen J. F., Suttorp M. J., Ascoop C. A., Zwinderman A. H., Niemeyer M. G., van der Wall E. E., Pauwels E. K. Combined assessment of technetium-99m SESTAMIBI planar myocardial perfusion images at rest and during exercise with rest/exercise left ventricular wall motion studies evaluated from gated myocardial perfusion studies. Am Heart J. 1992 Jan;123(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90747-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]