Abstract
Proximal myotonic myopathy (PROMM) is a recently described autosomal dominantly inherited disorder resulting in proximal muscle weakness, myotonia, and cataracts. A few patients with cardiac involvement (sinus bradycardia, supraventricular bigeminy, conduction abnormalities) have been reported. The cases of three relatives with PROMM (weakness of neck flexors and proximal extremity muscles, calf hypertrophy, myotonia, cataracts) are reported: a 54 year old man, his 73 year old mother, and 66 year old aunt. All three presented with conduction abnormalities and one had repeated, life threatening, sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. This illustrates that severe cardiac involvement may occur in PROMM. Keywords: proximal myotonic myopathy; cardiomyopathy; ventricular tachycardia; genetic disorders
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (102.0 KB).
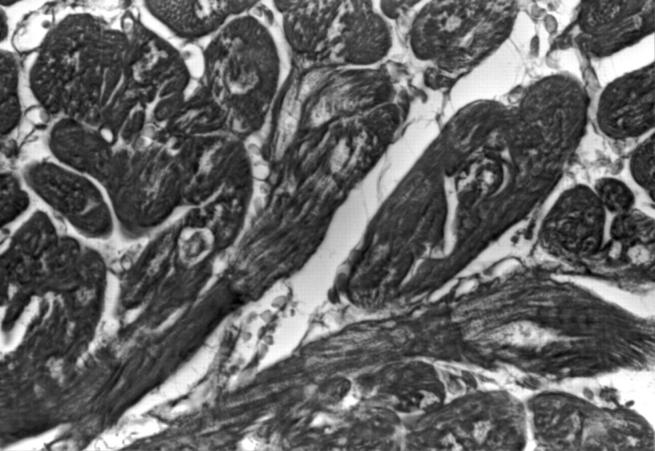
Figure 1 .
Myocardial biopsy specimen showing considerable variation in diameters of the myocytes and slight, focal rarefication of myofibrils (trichrome staining; original magnification ×40).