Abstract
Objective—To examine the effect of concomitant intake of β blockers with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, diuretics, or both on plasma renin concentrations in a population based sample (MONICA survey, Augsburg, Germany). Subject and methods—728 individuals were studied, of whom 171 were treated using monotherapy (ACE inhibitor (n = 21), diuretic (n = 10), or β blocker (n = 72)), or combination treatment (ACE inhibitor + diuretic (n = 32), ACE inhibitor + β blocker (n = 7), diuretic + β blocker (n = 22), ACE inhibitor + diuretic + β blocker (n = 7)). The remaining 557 individuals were untreated. Indications for treatment were hypertension (75%), coronary artery disease with (12%) or without (3%) hypertension, or unknown (10%). Results—Mean (SEM) renin concentrations in individuals treated with an ACE inhibitor (41 (8) mU/l), a diuretic (41 (10) mU/l), or the combination of an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic (54 (10) mU/l) were raised compared with untreated individuals (17 (1) mU/l; p < 0.05 each). Monotherapy with a β blocker, however, decreased mean renin concentrations (12 (1) mU/l; p < 0.01 v untreated). Renin concentrations in individuals taking a β blocker with either an ACE inhibitor (21 (8) mU/l), or a diuretic (22 (4) mU/l), or with both an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic (21 (7) mU/L), were significantly lower compared with renin concentrations in groups not receiving β blocker treatment (p < 0.05 each). Conclusion—These data suggest that the upregulation of renin by treatment with ACE inhibitors, diuretics, or both can be largely prevented by concomitant β blocker treatment. Keywords: adrenergic β receptor blocker; angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; renin; hypertension
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (128.3 KB).
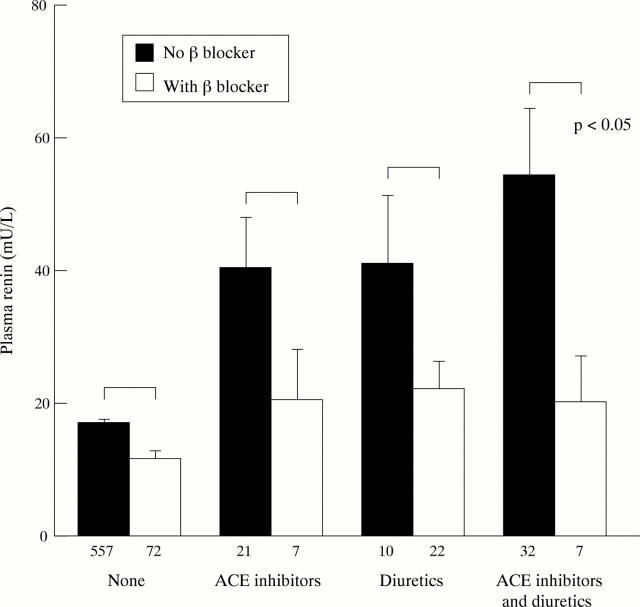
Figure 1 .
Mean (SEM) renin concentrations in subjects on no medication or on chronic treatment with ACE inhibitors, diuretics, or both (closed bars), and concentrations in subjects receiving β blocker monotherapy or β blocker with an ACE inhibitor, a diuretic, or both (open bars). Numbers indicate individuals receiving the respective treatments.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azizi M., Chatellier G., Guyene T. T., Murieta-Geoffroy D., Ménard J. Additive effects of combined angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II antagonism on blood pressure and renin release in sodium-depleted normotensives. Circulation. 1995 Aug 15;92(4):825–834. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.4.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., de Bruin R. J., van Gool J. M., van den Hoek M. J., Beerendonk C. C., Rosmalen F., Haima P., Schalekamp M. A. Clinical validation of renin monoclonal antibody-based sandwich assays of renin and prorenin, and use of renin inhibitor to enhance prorenin immunoreactivity. Clin Chem. 1996 Jul;42(7):1051–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustan H. P., Roccella E. J., Garrison H. H. Controlling hypertension. A research success story. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Sep 23;156(17):1926–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn E. J., McGhie A. L., Bedotto J. B., Corbett J. R., Malloy C. R., Hatfield B. A., Deitchman D., Willard J. E., Grayburn P. A. Effects of bucindolol on neurohormonal activation in congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Jan 1;67(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90102-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. Beta-blockers in hypertensive and coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Jun 24;156(12):1267–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R., Karlberg B. E., Odar-Cederlöf I., Andersson P. O., Lins L. E., Nilsson O. R., Tolagen K. Timolol and hydrochlorothiazide-amiloride in primary hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Dec;28(6):707–714. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer S., Rinne B., Eckardt K. U., Le Hir M., Schricker K., Kaissling B., Riegger G., Kurtz A. Role of renal nerves for the expression of renin in adult rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):F738–F745. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.5.F738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horký K., Gregorová I., Dvoráková J. The effect of renin and aldosterone inhibition by beta-adrenergic blockade on the response to the new diuretic azosemide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb 19;69(4):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser V., Nussberger J., Juillerat L., Burnier M., Waeber B., Bidiville J., Pauly N., Brunner H. R. Reactive hyperreninemia is a major determinant of plasma angiotensin II during ACE inhibition. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;15(2):276–282. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199002000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer M., Bristow M. R., Cohn J. N., Colucci W. S., Fowler M. B., Gilbert E. M., Shusterman N. H. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996 May 23;334(21):1349–1355. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199605233342101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schunkert H., Danser A. H., Hense H. W., Derkx F. H., Kürzinger S., Riegger G. A. Effects of estrogen replacement therapy on the renin-angiotensin system in postmenopausal women. Circulation. 1997 Jan 7;95(1):39–45. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schunkert H., Hense H. W., Muscholl M., Luchner A., Kürzinger S., Danser A. H., Riegger G. A. Associations between circulating components of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and left ventricular mass. Heart. 1997 Jan;77(1):24–31. doi: 10.1136/hrt.77.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schunkert H., Ingelfinger J. R., Hirsch A. T., Pinto Y., Remme W. J., Jacob H., Dzau V. J. Feedback regulation of angiotensin converting enzyme activity and mRNA levels by angiotensin II. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):312–318. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeuw A. H., Leenen F. H., Geyskes G. G., Boer P. Atenolol and chlorthalidone on blood pressure, heart rate, and plasma renin activity in hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):294–302. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacs N. C., Kim M., Denzon M., Hargrave B., Ganong W. F. Pharmacological evidence for involvement of the sympathetic nervous system in the increase in renin secretion produced by a low sodium diet in rats. Life Sci. 1990;47(25):2317–2322. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urata H., Kinoshita A., Misono K. S., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22348–22357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waagstein F., Bristow M. R., Swedberg K., Camerini F., Fowler M. B., Silver M. A., Gilbert E. M., Johnson M. R., Goss F. G., Hjalmarson A. Beneficial effects of metoprolol in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Metoprolol in Dilated Cardiomyopathy (MDC) Trial Study Group. Lancet. 1993 Dec 11;342(8885):1441–1446. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92930-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda S., Kako T., Koketsu M., Hayano J., Asakawa T., Fujinami T., Kato T. Single administration of captopril and combined use with beta-blocker and/or thiazide diuretic in the treatment of essential hypertension. Angiology. 1991 Nov;42(11):914–923. doi: 10.1177/000331979104201107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Meiracker A. H., Man in 't Veld A. J., Admiraal P. J., Ritsema van Eck H. J., Boomsma F., Derkx F. H., Schalekamp M. A. Partial escape of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition during prolonged ACE inhibitor treatment: does it exist and does it affect the antihypertensive response? J Hypertens. 1992 Aug;10(8):803–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]