Abstract
Background—Haemostasis plays a major part in the process initiating a myocardial infarction. The impact of haemostatic variables on long term prognosis is unknown. Objective—To evaluate von Willebrand factor (vWF), tissue plasminogen activator antigen (t-PA) and its activity before and after venous occlusion, plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1), dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS), and established clinical risk factors as long term predictors for reinfarction and mortality. Patients—123 consecutive survivors of myocardial infarction followed up for 10 years. Design—Study entry took place between 1982 and 1983. Fifty seven patients died (54 of cardiovascular disease) during the mean observation time of 10 years. Results—Cox's univariate regression analysis showed that cardiovascular mortality was significantly associated with age, hypertension, previous history of angina pectoris, DHEAS, mass concentration of t-PA, and vWF. These associations were significant for vWF and mass concentration of t-PA after adjusting for age and hypertension. Conclusions—A low concentration of DHEAS and high levels of the endothelially derived haemostatic variables vWF and mass concentration of t-PA are predictors of cardiovascular mortality in survivors of myocardial infarction. This association is independent of established clinical risk factors for mass concentration of t-PA and vWF. Keywords: myocardial infarction; risk factors; fibrinolysis; tissue plasminogen activator; plasminogen activator inhibitor; von Willebrand factor; dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (101.6 KB).
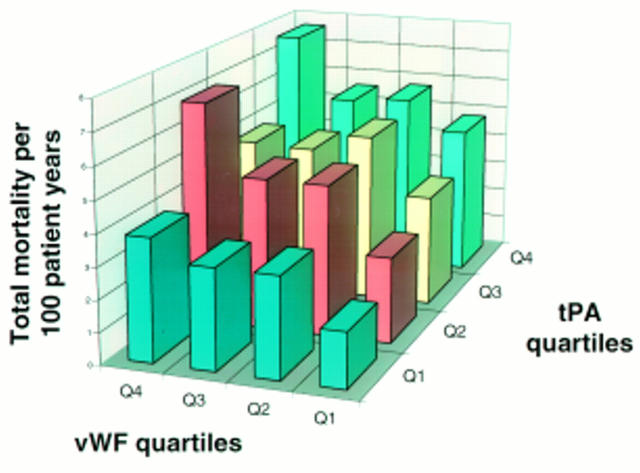
Figure 1 .
Relation between the incidence of cardiovascular mortality (per 100 patient-years) after 10 years' follow up and quartiles Q1 to Q4 of the mass concentration of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and von Willebrand factor (vWF).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett-Connor E., Khaw K. T., Yen S. S. A prospective study of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, mortality, and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 11;315(24):1519–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612113152405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David M., Dikstein S., Bismuth G., Sulman F. G. Anti-hypercholesterolemic effect of dehydroepiandrosterone in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1136–1140. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brännström M., Jansson J. H., Boman K., Nilsson T. K. Endothelial haemostatic factors may be associated with mortality in patients on long-term anticoagulant treatment. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Aug;74(2):612–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Leiter E. H., Schwizer R. W. Therapeutic effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):830–833. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contoreggi C. S., Blackman M. R., Andres R., Muller D. C., Lakatta E. G., Fleg J. L., Harman S. M. Plasma levels of estradiol, testosterone, and DHEAS do not predict risk of coronary artery disease in men. J Androl. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):460–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortellaro M., Boschetti C., Cofrancesco E., Zanussi C., Catalano M., de Gaetano G., Gabrielli L., Lombardi B., Specchia G., Tavazzi L. The PLAT Study: hemostatic function in relation to atherothrombotic ischemic events in vascular disease patients. Principal results. PLAT Study Group. Progetto Lombardo Atero-Trombosi (PLAT) Study Group. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Sep;12(9):1063–1070. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.9.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., McKeown L. P., Magruder L., Hansmann K., Vail M., Parker R. I. Platelet von Willebrand factor. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991 Jun;66(6):634–640. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines A. P., Howarth D., North W. R., Goldenberg E., Stirling Y., Meade T. W., Raftery E. B., Millar Craig M. W. Haemostatic variables and the outcome of myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Dec 30;50(4):800–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Wiman B., de Faire U., Blombäck M. Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1557–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. M., Gordon G. B., Achuff S. C., Trejo J. F., Weisman H. F., Kwiterovich P. O., Jr, Pearson T. A. Plasma dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in patients undergoing diagnostic coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Nov;16(6):862–870. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. H., Nilsson T. K., Johnson O. von Willebrand factor in plasma: a novel risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction and death. Br Heart J. 1991 Nov;66(5):351–355. doi: 10.1136/hrt.66.5.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. H., Nilsson T. K., Olofsson B. O. Tissue plasminogen activator and other risk factors as predictors of cardiovascular events in patients with severe angina pectoris. Eur Heart J. 1991 Feb;12(2):157–161. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Lechner K., Niessner H., Gössinger H., Kundi M. Impaired fibrinolytic capacity predisposes for recurrence of venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Oct 31;52(2):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaCroix A. Z., Yano K., Reed D. M. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, incidence of myocardial infarction, and extent of atherosclerosis in men. Circulation. 1992 Nov;86(5):1529–1535. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.5.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Mellows S., Brozovic M., Miller G. J., Chakrabarti R. R., North W. R., Haines A. P., Stirling Y., Imeson J. D., Thompson S. G. Haemostatic function and ischaemic heart disease: principal results of the Northwick Park Heart Study. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Ruddock V., Stirling Y., Chakrabarti R., Miller G. J. Fibrinolytic activity, clotting factors, and long-term incidence of ischaemic heart disease in the Northwick Park Heart Study. Lancet. 1993 Oct 30;342(8879):1076–1079. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell L. E., Sprecher D. L., Borecki I. B., Rice T., Laskarzewski P. M., Rao D. C. Evidence for an association between dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and nonfatal, premature myocardial infarction in males. Circulation. 1994 Jan;89(1):89–93. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T. K., Johnson O. The extrinsic fibrinolytic system in survivors of myocardial infarction. Thromb Res. 1987 Dec 15;48(6):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Mellbring G., Damber J. E. Relationships between tissue plasminogen activator, steroid hormones and deep vein thrombosis. Acta Chir Scand. 1985;151(6):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridker P. M., Vaughan D. E., Stampfer M. J., Manson J. E., Hennekens C. H. Endogenous tissue-type plasminogen activator and risk of myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1993 May 8;341(8854):1165–1168. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90998-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Słowínska-Srzednicka J., Zgliczyński S., Ciświcka-Sznajderman M., Srzednicki M., Soszyński P., Biernacka M., Woroszyłska M., Ruzyło W., Sadowski Z. Decreased plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and dihydrotestosterone concentrations in young men after myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Oct;79(2-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. G., Kienast J., Pyke S. D., Haverkate F., van de Loo J. C. Hemostatic factors and the risk of myocardial infarction or sudden death in patients with angina pectoris. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilities Angina Pectoris Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 9;332(10):635–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503093321003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Faire U., Friberg L., Lorich U., Lundman T. A validation of cause-of-death certification in 1,156 deaths. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200(3):223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb08223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]