Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To relate QT parameters to infarct size and inducibility during electrophysiological studies. DESIGN—Analysis of a prospective register. SETTING—University hospital. PATIENTS—64 patients with coronary artery disease and documented life threatening ventricular arrhythmias. INTERVENTIONS—Measurements of QT-max, QTc-max, and QT dispersion (QT-d) on a simultaneous 12 lead ECG (50 mm/s). Estimation of myocardial infarct size with radionuclide left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), echocardiography (left ventricular end diastolic diameter, LVEDD), and a defect score based on a quantitative stress redistribution 201-thallium perfusion study. Electrophysiological study to assess inducibility. RESULTS—Mean (SD) QT parameters were: QT-max 440 (50) ms, QTc-max 475 (46) ms, and QT-d 47 (20) ms. Mean (SD) estimates of infarct size were: LVEF 34 (13)%, LVEDD 61 (9) mm, and defect score 18 (11). There was no significant correlation between any index of infarct size and QT parameters. QT parameters were not significantly different between patients with inducible (n = 57) and non-inducible arrhythmias (n = 7) (QT-max: 416 (30) v 443 (51) ms, p = 0.18; QTc-max 485 (34) v 473 (47) ms, p = 0.34; QT-d 47 (12) v 47 (21) ms, p = 0.73). Non-inducible patients had a significant lower defect score: 8 (9) v 19 (11), p = 0.02, but comparable LVEF: 38 (12)% v 34 (12)%, p = 0.58, and LVEDD: 54 (10) v 61 (8) mm, p = 0.13. CONCLUSIONS—QT parameters are not influenced by infarct size and do not predict inducibility during electrophysiological study in patients with coronary artery disease and malignant ventricular arrhythmias. In contrast, the amount of scar tissue determined by perfusion imaging is strongly correlated with inducibility. Keywords: QT parameters; infarct size; electrophysiological testing; perfusion imaging
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (152.2 KB).
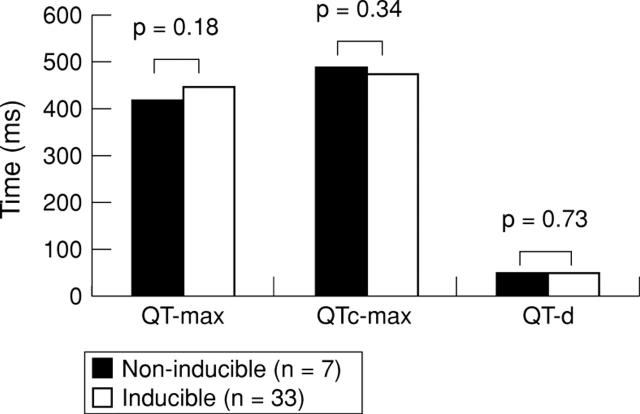
Figure 1 .
QT parameters in patients with non-inducible (n = 7) and inducible (n = 33) arrhythmias. There were no significant differences in any QT parameter between the two groups. QT-d, QT dispersion; QT-max, maximum QT interval; QTc-max, corrected maximum QT interval.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr C. S., Naas A., Freeman M., Lang C. C., Struthers A. D. QT dispersion and sudden unexpected death in chronic heart failure. Lancet. 1994 Feb 5;343(8893):327–329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. P., McComb J. M., Campbell R. W. QT dispersion in sinus beats and ventricular extrasystoles in normal hearts. Br Heart J. 1992 Jan;67(1):39–41. doi: 10.1136/hrt.67.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean J. W., Lab M. J. Arrhythmia in heart failure: role of mechanically induced changes in electrophysiology. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92697-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioia G., Bagheri B., Gottlieb C. D., Schwartzman D. S., Callans D. J., Marchlinski F. E., Heo J., Iskandrian A. E. Prediction of outcome of patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias treated with automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillators using SPECT perfusion imaging. Circulation. 1997 Jan 21;95(2):390–394. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.2.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glancy J. M., Garratt C. J., Woods K. L., de Bono D. P. QT dispersion and mortality after myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1995 Apr 15;345(8955):945–948. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90697-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradel C., Jain D., Batsford W. P., Wackers F. J., Zaret B. L. Relationship of scar and ischemia to the results of programmed electrophysiological stimulation in patients with coronary artery disease. J Nucl Cardiol. 1997 Sep-Oct;4(5):379–386. doi: 10.1016/s1071-3581(97)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans W. R., Foley D. P., Rensing B. J., Rutsch W., Heyndrickx G. R., Danchin N., Mast G., Hanet C., Lablanche J. M., Rafflenbeul W. Usefulness of quantitative and qualitative angiographic lesion morphology, and clinical characteristics in predicting major adverse cardiac events during and after native coronary balloon angioplasty. CARPORT and MERCATOR Study Groups. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Jul 1;72(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90211-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordaens L., Hollanders G., De Schrijver A., Simons M., De Backer G., Clement D. L. Incidence and prognostic significance of asymptomatic ischaemia in patients with sustained ventricular arrhythmias. Eur Heart J. 1988 Dec;9 (Suppl N):128–135. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/9.suppl_n.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. W., Okin P. M., Kligfield P., Stein K. M., Lerman B. B. Precordial QT dispersion and inducible ventricular tachycardia. Am Heart J. 1997 Dec;134(6):1005–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(97)70019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland T. M., McCarthy D. M., Makler P. T., Jr, Josephson M. E. Relation between site of origin of ventricular tachycardia and relative left ventricular myocardial perfusion and wall motion. Am J Cardiol. 1983 May 1;51(8):1329–1333. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen L., Viitasalo M., Toivonen L. Dispersions of the QT interval in postmyocardial infarction patients presenting with ventricular tachycardia or with ventricular fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1998 Mar 15;81(6):694–697. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)01002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkiömäki J. S., Koistinen M. J., Yli-Mäyry S., Huikuri H. V. Dispersion of QT interval in patients with and without susceptibility to ventricular tachyarrhythmias after previous myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Jul;26(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00122-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye M., Quinn A. C., Cobbe S. M. QT interval dispersion: a non-invasive marker of susceptibility to arrhythmia in patients with sustained ventricular arrhythmias? Br Heart J. 1994 Jun;71(6):511–514. doi: 10.1136/hrt.71.6.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savelieva I., Yi G., Guo X., Hnatkova K., Malik M. Agreement and reproducibility of automatic versus manual measurement of QT interval and QT dispersion. Am J Cardiol. 1998 Feb 15;81(4):471–477. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00927-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C. A., Voth E., Baer F. M., Horst M., Wagner R., Sechtem U. QT dispersion is determined by the extent of viable myocardium in patients with chronic Q-wave myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997 Dec 2;96(11):3913–3920. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.11.3913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers T. D., Beller G. A., Gibson R. S., Watson D. D., DiMarco J. P. Prevalence of ischemia by quantitative thallium-201 scintigraphy in patients with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation inducible by programmed stimulation. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Apr 1;59(8):828–832. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)91100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén J. C., Horacek B. M., Spencer C. A., Klassen G. A., Montague T. J. QT interval variability on the body surface. J Electrocardiol. 1984 Apr;17(2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(84)81093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart P. Mechano-electric feedback in the human heart. Cardiovasc Res. 1996 Jul;32(1):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. E. Prolongation of the QT interval as an indicator of risk of a cardiac event. Eur Heart J. 1988 May;9 (Suppl G):139–144. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/9.suppl_g.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T., Pick R., Silver M. A., Moe G. W., Janicki J. S., Zucker I. H., Armstrong P. W. Fibrillar collagen and remodeling of dilated canine left ventricle. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1387–1401. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellens H. J., Brugada P., Stevenson W. G. Programmed electrical stimulation of the heart in patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias: what is the significance of induced arrhythmias and what is the correct stimulation protocol? Circulation. 1985 Jul;72(1):1–7. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunus A., Gillis A. M., Duff H. J., Wyse D. G., Mitchell L. B. Increased precordial QTc dispersion predicts ventricular fibrillation during acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Sep 15;78(6):706–708. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(96)00405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zareba W., Moss A. J., le Cessie S. Dispersion of ventricular repolarization and arrhythmic cardiac death in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1994 Sep 15;74(6):550–553. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(94)90742-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo A., Arendts W., Hohnloser S. H. Variability of QT dispersion measurements in the surface electrocardiogram in patients with acute myocardial infarction and in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol. 1994 Dec 1;74(11):1113–1118. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(94)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]