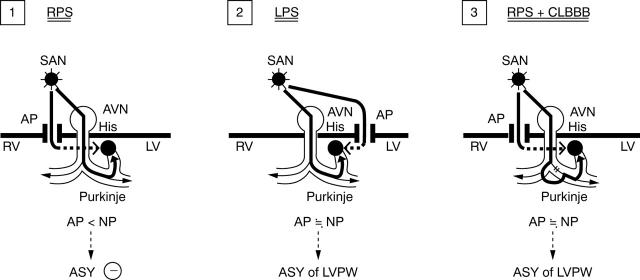
Figure 5 .
Speculation on the mechanism causing asynchronous left ventricular posterior wall systolic motion. (1) RPS, accessory pathway located in the right posterior septum. Electric current by the accessory pathway (AP) does not reach left ventricular wall during the systolic phase, resulting in the absence of asynchronous (ASY) left ventricular wall motion. (2) LPS, accessory pathway located in the left posterior septum. Electric current by the accessory pathway reaches the left ventricular wall in close timing with that by normal pathway (NP) during the systolic phase, resulting in asynchronous left ventricular wall systolic motion. (3) RPS + CLBBB, right posterior septum accessory pathway with complete left bundle branch block. Because of delayed conduction through the normal pathway owing to complete left bundle branch block, electric current by the right posterior septal pathway reaches the left ventricular wall in close timing with that by the normal pathway, resulting in asynchronous left ventricular wall motion. AVN, atrioventricular node; His, His bundle; LPS, left posterior septal accessory pathway; LV, left ventricle; LVPW, left ventricular posterior wall; RPS, right posterior septal accessory pathway; RV, right ventricle; SAN, sinoatrial node.