Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To describe the mode of presentation and the clinical course of patients with ventricular pre-excitation (Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome), with special emphasis on asymptomatic cases in the general population. METHODS—Over an eight year period (1990-97) a prospective population based survey of cases with WPW pattern was conducted in a defined population in north west Greece (340 000 inhabitants). ECGs with WPW pattern were obtained from a widespread pool of ECGs within the health system. RESULTS—During the study period, 157 cases with WPW pattern were identified (49 female, 108 male). Ages ranged from infants to 84 years, mean (SD) 49.1 (21.0) years in female and 39.6 (20.6) years in male subjects (p < 0.01); 78 (49%) had no history of syndrome related symptoms. Asymptomatic subjects (n = 77; 24 female, 53 male) were older than symptomatic subjects (mean age 46.7 (21.0) v 38.5 (20.6) years, p < 0.03). Documented supraventricular tachycardia was recorded in 27 patients (17%) and atrial fibrillation in 12 (8%) (mean age at first episode 31.2 (18.3) and 51.6 (20.7) years, respectively, p < 0.01). During follow up (mean 55 months) no case of sudden death occurred. Three asymptomatic subjects reported episodes of brief palpitation. CONCLUSIONS—WPW pattern is more common, and diagnosed at a younger age, in men than in women. About half the patients with WPW pattern on ECG are asymptomatic at diagnosis and tend to remain so thereafter. No sudden cardiac death occurred during the study period. Keywords: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome; epidemiology
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (101.4 KB).
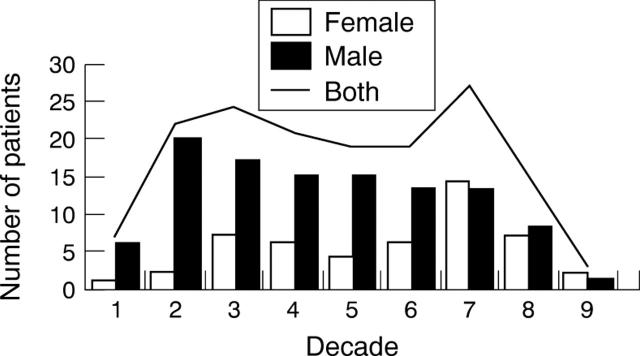
Figure 1 .
Age distribution at diagnosis of Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern among residents of north west Greece.
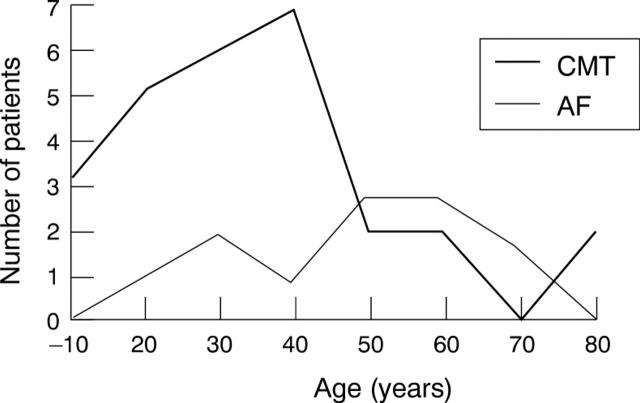
Figure 2 .
Age at onset of first arrhythmic event in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in north west Greece. AF, atrial fibrillation; CMT, circus movement tachycardia.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind R. A., Wyndham C. R., Swiryn S. P., Palileo E. V., Strasberg B., Lam W., Westveer D., Rosen K. M. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Mar;47(3):562–569. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman K. J., Gallastegui J. L., Bauman J. L., Hariman R. J. The predictive value of electrophysiologic studies in untreated patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Mar 1;15(3):640–647. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkman N. L., Lamb L. E. The Wolff-Parkinson-White electrocardiogram. A follow-up study of five to twenty-eight years. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 29;278(9):492–494. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802292780906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calkins H., Langberg J., Sousa J., el-Atassi R., Leon A., Kou W., Kalbfleisch S., Morady F. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients. Abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. 1992 Apr;85(4):1337–1346. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.4.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. W., Smith R. A., Gallagher J. J., Pritchett E. L., Wallace A. G. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Oct;40(4):514–520. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(77)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick A. P., Gonzales R. P., Lesh M. D., Modin G. W., Lee R. J., Scheinman M. M. New algorithm for the localization of accessory atrioventricular connections using a baseline electrocardiogram. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Jan;23(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flensted-Jensen E. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. A long-term follow-up of 47 cases. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Jul-Aug;186(1-2):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. J., Pritchett E. L., Sealy W. C., Kasell J., Wallace A. G. The preexcitation syndromes. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1978 Jan-Feb;20(4):285–327. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(78)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guize L., Soria R., Chaouat J. C., Chrétien J. M., Houe D., Le Heuzey J. Y. Prévalence et évolution du syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White dans une population de 138 048 sujets. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1985;136(6):474–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. J., Bashore T. M., Sellers T. D., Pritchett E. L., Smith W. M., Gallagher J. J. Ventricular fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 15;301(20):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911153012003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. J., Prystowsky E. N., Yee R., Sharma A. D., Laupacis A. Asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White. Should we intervene? Circulation. 1989 Dec;80(6):1902–1905. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.6.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounis N. G., Zavras G. M., Papadaki P. J., Soufras G. D., Kitrou M. P., Poulos E. A. Pregnancy-induced increase of supraventricular arrhythmias in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Clin Cardiol. 1995 Mar;18(3):137–140. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960180306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahn A. D., Manfreda J., Tate R. B., Mathewson F. A., Cuddy T. E. The natural history of electrocardiographic preexcitation in men. The Manitoba Follow-up Study. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Mar 15;116(6):456–460. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-6-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch J. W., Klein G. J., Yee R., Murdock C. Prognostic value of electrophysiology testing in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern. Circulation. 1990 Nov;82(5):1718–1723. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.5.1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantakas M. E., McCue C. M., Miller W. W. Natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome discovered in infancy. Am J Cardiol. 1978 May 22;41(6):1097–1103. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90863-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger T. M., Packer D. L., Hammill S. C., Feldman B. J., Bailey K. R., Ballard D. J., Holmes D. R., Jr, Gersh B. J. A population study of the natural history of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1953-1989. Circulation. 1993 Mar;87(3):866–873. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.3.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfit W. L., Sterba R. Long-term status and survival in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Cleve Clin J Med. 1989 Sep;56(6):601–606. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.56.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K., Rowland E., Krikler D. M. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: atrial fibrillation as the presenting arrhythmia. Br Heart J. 1988 May;59(5):578–580. doi: 10.1136/hrt.59.5.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZEKELY P., SNAITH L. Paroxysmal tachycardia in pregnancy. Br Heart J. 1953 Apr;15(2):195–198. doi: 10.1136/hrt.15.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano S., Komori S., Amano T., Kohno I., Ishihara T., Sawanobori T., Ijiri H., Tamura K. Prevalence of ventricular preexcitation in Japanese schoolchildren. Heart. 1998 Apr;79(4):374–378. doi: 10.1136/hrt.79.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. D., Klein G. J., Guiraudon G. M., Milstein S. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: incidence after surgical ablation of the accessory pathway. Circulation. 1985 Jul;72(1):161–169. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz J. F., Tracy C. M., Fletcher R. D. Radiofrequency endocardial catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathway atrial insertion sites. Circulation. 1993 Feb;87(2):487–499. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans C., Smeets J. L., Rodriguez L. M., Vrouchos G., van den Dool A., Wellens H. J. Aborted sudden death in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1995 Sep 1;76(7):492–494. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topaz O., Perin E., Cox M., Mallon S. M., Castellanos A., Myerburg R. J. Young adult survivors of sudden cardiac arrest: analysis of invasive evaluation of 22 subjects. Am Heart J. 1989 Aug;118(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(89)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]