Abstract
BACKGROUND—Endothelial dysfunction plays an important role in the development of atherosclerotic vascular disease, which is the leading cause of mortality in patients with chronic renal failure. OBJECTIVE—To examine the relation between predialysis renal failure and endothelial function. DESIGN—Two groups were studied: 80 patients with non-diabetic chronic renal failure and 26 healthy controls, with similar age and sex distributions. Two indices of endothelial function were assessed: high resolution ultrasonography to measure flow mediated endothelium dependent dilatation of the brachial artery following reactive hyperaemia, and plasma concentration of von Willebrand factor. Endothelium independent dilatation was also assessed following sublingual glyceryl trinitrate. The patients were divided into those with and without overt atherosclerotic vascular disease. RESULTS—Although patients with chronic renal failure had significantly impaired endothelium dependent dilatation compared with controls (median (interquartile range), 2.6% (0.7% to 4.8%) v 6.5% (4.8% to 8.3%); p < 0.001) and increased von Willebrand factor (254 (207 to 294) v 106 (87 to 138) iu/dl; p < 0.001), there was no difference between renal failure patients with and without atherosclerotic vascular disease. Within the chronic renal failure group, endothelium dependent dilatation and von Willebrand factor were similar in patients in the upper and lower quartiles of glomerular filtration rate (2.7% (0.7% to 6.7%) v 2.8% (1.1% to 5.0%); and 255 (205 to 291) v 254 (209 to 292) iu/dl, respectively). Endothelium independent dilatation did not differ between the renal failure or control groups and was also similar in patients with renal failure irrespective of the degree of renal failure or the presence of atherosclerotic vascular disease. CONCLUSIONS—Endothelial function is abnormal in chronic renal failure, even in patients with mild renal insufficiency and those without atherosclerotic vascular disease, suggesting that uraemia may directly promote the development of atherosclerosis early in the progression of chronic renal failure. Keywords: atherosclerosis; endothelial function; flow mediated dilatation; renal failure
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (123.1 KB).
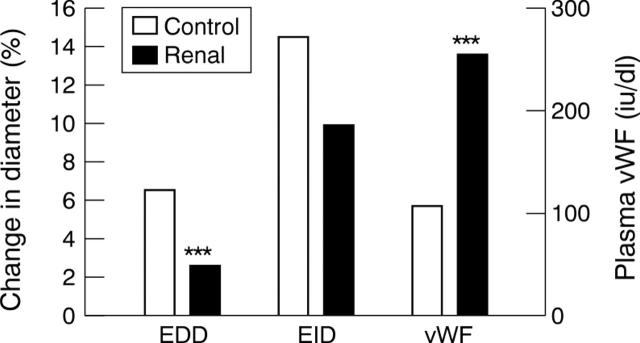
Figure 1 .
Endothelium dependent and independent dilatation of the brachial artery and von Willebrand factor concentration in the renal failure and control groups. EDD, endothelium dependent dilatation; EID, endothelium independent dilatation; vWF, von Willebrand factor; ***p < 0.001 after controlling for differences in the baseline characteristics.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson T. J., Uehata A., Gerhard M. D., Meredith I. T., Knab S., Delagrange D., Lieberman E. H., Ganz P., Creager M. A., Yeung A. C. Close relation of endothelial function in the human coronary and peripheral circulations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 1;26(5):1235–1241. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boneu B., Abbal M., Plante J., Bierme R. Letter: Factor-VIII complex and endothelial damage. Lancet. 1975 Jun 28;1(7922):1430–1430. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celermajer D. S., Sorensen K. E., Bull C., Robinson J., Deanfield J. E. Endothelium-dependent dilation in the systemic arteries of asymptomatic subjects relates to coronary risk factors and their interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Nov 15;24(6):1468–1474. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celermajer D. S., Sorensen K. E., Gooch V. M., Spiegelhalter D. J., Miller O. I., Sullivan I. D., Lloyd J. K., Deanfield J. E. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93147-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Azhar S., Hoffman B. B. Inactivation of endothelial derived relaxing factor by oxidized lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):10–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI115549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaber A. B., Eidemak I., Jensen T., Feldt-Rasmussen B., Strandgaard S. Vascular endothelial cell function and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Feb;5(8):1581–1584. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V581581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. G., Armstrong M. L., Freiman P. C., Heistad D. D. Restoration of endothelium-dependent relaxation by dietary treatment of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1808–1811. doi: 10.1172/JCI113276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joannides R., Haefeli W. E., Linder L., Richard V., Bakkali E. H., Thuillez C., Lüscher T. F. Nitric oxide is responsible for flow-dependent dilatation of human peripheral conduit arteries in vivo. Circulation. 1995 Mar 1;91(5):1314–1319. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.5.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joki N., Hase H., Nakamura R., Yamaguchi T. Onset of coronary artery disease prior to initiation of haemodialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997 Apr;12(4):718–723. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.4.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungers P., Massy Z. A., Nguyen Khoa T., Fumeron C., Labrunie M., Lacour B., Descamps-Latscha B., Man N. K. Incidence and risk factors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular accidents in predialysis chronic renal failure patients: a prospective study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997 Dec;12(12):2597–2602. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.12.2597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari J. A., Donald A. E., Vallance D. T., Bruckdorfer K. R., Leone A., Mullen M. J., Bunce T., Dorado B., Deanfield J. E., Rees L. Physiology and biochemistry of endothelial function in children with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997 Aug;52(2):468–472. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasiske B. L., Guijarro C., Massy Z. A., Wiederkehr M. R., Ma J. Z. Cardiovascular disease after renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996 Jan;7(1):158–165. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V71158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama S., Tomonari H., Yoshida H., Hikita M., Sakai O. [Endothelial cell dysfunction in patients with impaired renal function]. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1996 Aug;38(8):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher T. F., Tanner F. C., Noll G. Lipids and endothelial function: effects of lipid-lowering and other therapeutic interventions. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996 Aug;7(4):234–240. doi: 10.1097/00041433-199608000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLenachan J. M., Vita J., Fish D. R., Treasure C. B., Cox D. A., Ganz P., Selwyn A. P. Early evidence of endothelial vasodilator dysfunction at coronary branch points. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1169–1173. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Cooper J. A., Stirling Y., Howarth D. J., Ruddock V., Miller G. J. Factor VIII, ABO blood group and the incidence of ischaemic heart disease. Br J Haematol. 1994 Nov;88(3):601–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb05079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith I. T., Currie K. E., Anderson T. J., Roddy M. A., Ganz P., Creager M. A. Postischemic vasodilation in human forearm is dependent on endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Am J Physiol. 1996 Apr;270(4 Pt 2):H1435–H1440. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1996.270.4.H1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F., Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Braughler J. M. Properties and regulation of guanylate cyclase and some proposed functions for cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:175–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine A. E., Margreiter R., Brunner F. P., Ehrich J. H., Geerlings W., Landais P., Loirat C., Mallick N. P., Selwood N. H., Tufveson G. Report on management of renal failure in Europe, XXII, 1991. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1992;7 (Suppl 2):7–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E. von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22777–22780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Osborne J. A., Jaraki O., Rabbani L. E., Mullins M., Singel D., Loscalzo J. Adverse vascular effects of homocysteine are modulated by endothelium-derived relaxing factor and related oxides of nitrogen. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):308–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI116187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Wada H., Mukai K., Kihira H., Yano S., Minamikawa K., Wakita Y., Nakase T., Nagaya S., Deguchi K. Increased vascular endothelial cell markers in patients with chronic renal failure on maintenance haemodialysis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994 Oct;5(5):713–717. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199410000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Leone A., Calver A., Collier J., Moncada S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):572–575. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90865-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Guldener C., Janssen M. J., Lambert J., ter Wee P. M., Jakobs C., Donker A. J., Stehouwer C. D. No change in impaired endothelial function after long-term folic acid therapy of hyperhomocysteinaemia in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998 Jan;13(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/ndt/13.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Guldener C., Lambert J., Janssen M. J., Donker A. J., Stehouwer C. D. Endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and distensibility of large arteries in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997;12 (Suppl 2):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]