Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To obtain normal values for intracardiac pressures in the human fetus. DESIGN—Intracardiac pressures were measured directly in the four chambers of the human fetal heart during clinically indicated invasive obstetric procedures. SETTING—Department of fetal medicine in a tertiary referral centre. PATIENTS—39 fetuses between 16 and 29 weeks of gestation. RESULTS—The ventricular waveforms obtained were similar to those found in postnatal life. There was an increase in ventricular systolic and end diastolic pressures with advancing gestation. There was no difference between left and right ventricular pressures. Atrial pressures were equal and remained constant in the gestational age range studied. CONCLUSIONS—Fetal cardiovascular pressure measurements in the normal fetus assist in understanding the fetal circulation, and provide a basis for the assessment of cases of congenital heart disease that may be amenable to intrauterine treatment. Keywords: fetus; ventricular pressure; congenital heart disease
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (123.0 KB).
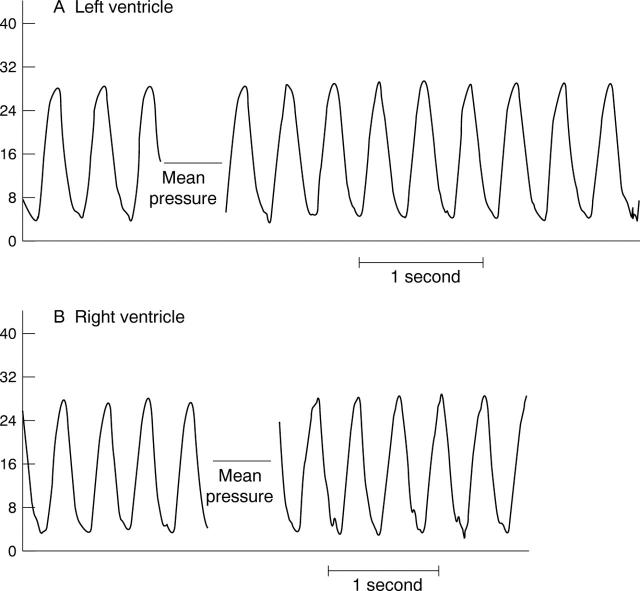
Figure 1 .
Pressure waveform of (A) left and (B) right ventricle in a normal fetal heart at 22 weeks' gestation
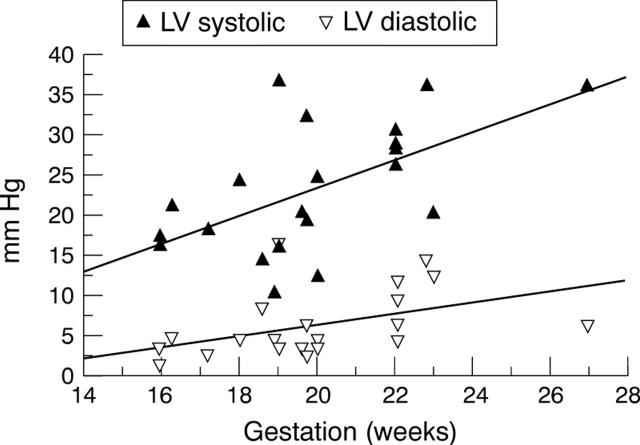
Figure 2 .
Plot of left ventricular pressure showing regression lines (coefficient 1.7416 (systolic), 0.7018 (diastolic)). LV, left ventricle.
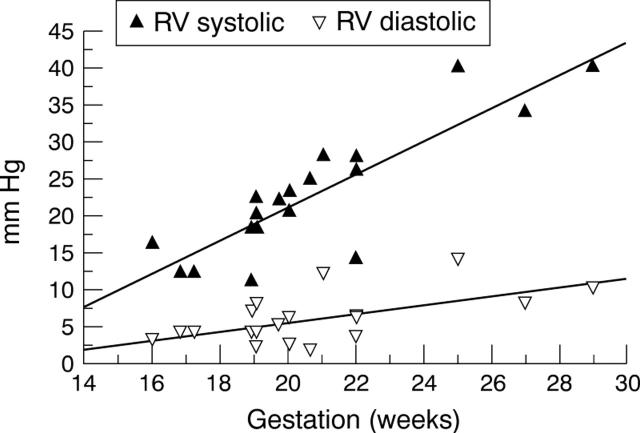
Figure 3 .
Plot of right ventricular pressure showing regression lines (coefficient 2.2410 (systolic), 0.6037 (diastolic)). RV, right ventricle.
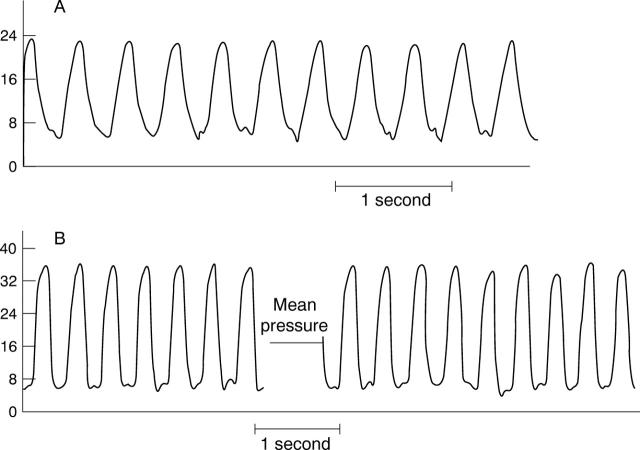
Figure 4 .
Left ventricular pressure waveforms at (A) 16 weeks and (B) 27 weeks showing the change in appearance of atrial contraction.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akita A., Harima N., Nawata S., Nakata M., Kato H. [Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of intrauterine blood flow dynamics in the fetuses with a ventricular septal defect]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1991 Dec;43(12):1606–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan L. D., Chita S. K., Al-Ghazali W., Crawford D. C., Tynan M. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the normal human fetal heart. Br Heart J. 1987 Jun;57(6):528–533. doi: 10.1136/hrt.57.6.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan L. D., Crawford D. C., Anderson R. H., Tynan M. J. Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal congenital heart disease. Br Heart J. 1984 Nov;52(5):542–548. doi: 10.1136/hrt.52.5.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan L. D., Tynan M. J., Campbell S., Wilkinson J. L., Anderson R. H. Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus. Br Heart J. 1980 Oct;44(4):444–451. doi: 10.1136/hrt.44.4.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. F., Bissonnette J. M., Faber J. J., Thornburg K. L. Central shunt flows and pressures in the mature fetal lamb. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):H60–H66. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.1.H60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. F., Faber J. J., Morton M. J., Parks C. M., Pinson C. W., Thornburg K. L. Flow through the foramen ovale of the fetal and new-born lamb. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:29–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. A., Manring A., Glick K. L., Crenshaw C. C., Jr Biophysics of the developing heart. III. A comparison of the left ventricular dynamics of the fetal and neonatal lamb heart. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 May 15;143(2):195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better D. J., Kaufman S., Allan L. D. The normal pattern of pulmonary venous flow on pulsed Doppler examination of the human fetus. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1996 May-Jun;9(3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(96)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao R. C., Ho E. S., Hsieh K. S. Fluctuations of interventricular shunting in a fetus with an isolated ventricular septal defect. Am Heart J. 1994 Apr;127(4 Pt 1):955–958. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(94)90576-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. J., Tate C. A., Phillips S. Developmental regulation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump in the rabbit heart. Pediatr Res. 1992 May;31(5):474–479. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199205000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itskovitz J., LaGamma E. F., Rudolph A. M. Baroreflex control of the circulation in chronically instrumented fetal lambs. Circ Res. 1983 May;52(5):589–596. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.5.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Plappert T., Doubilet P., Saltzman D. H., Cartier M., Zollars L., Leatherman G. F., St John Sutton M. G. Changes in intracardiac blood flow velocities and right and left ventricular stroke volumes with gestational age in the normal human fetus: a prospective Doppler echocardiographic study. Circulation. 1986 Dec;74(6):1208–1216. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.6.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiserud T., Eik-Nes S. H., Blaas H. G., Hellevik L. R. Ultrasonographic velocimetry of the fetal ductus venosus. Lancet. 1991 Dec 7;338(8780):1412–1414. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92720-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler F. H., Brace R. A. Fetal and maternal arterial pressures and heart rates: histograms, correlations, and rhythms. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):R433–R444. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.3.R433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell D. J., Johnson P., Hurley P., Neales K., Allan L., Knott P. Fetal blood sampling and pregnancy loss in relation to indication. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1991 Sep;98(9):892–897. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1991.tb13511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell D., Allan L., Tynan M. J. Balloon dilatation of the aortic valve in the fetus: a report of two cases. Br Heart J. 1991 May;65(5):256–258. doi: 10.1136/hrt.65.5.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides K. H., Clewell W. H., Rodeck C. H. Measurement of human fetoplacental blood volume in erythroblastosis fetalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Jul;157(1):50–53. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwo M. U., Lorenz J. M., Gardiner J. C. A standard protocol for blood pressure measurement in the newborn. Pediatrics. 1997 Jun;99(6):E10–E10. doi: 10.1542/peds.99.6.e10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. L., Appleton C. P., Anderson C. F., Shenker L., Sahn D. J. Doppler studies of vena cava flows in human fetuses. Insights into normal and abnormal cardiac physiology. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):498–505. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller M. D., Morton M. J., Reid D. L., Thornburg K. L. Fetal lamb ventricles respond differently to filling and arterial pressures and to in utero ventilation. Pediatr Res. 1987 Dec;22(6):621–626. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198712000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K. G., Di Tommaso M., Silverman N. H., Rudolph A. M. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of fetal descending aortic and umbilical blood flows. Validation studies in fetal lambs. Circulation. 1991 May;83(5):1731–1737. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.5.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. L. Blood pressure in very low birth weight infants in the first 70 days of life. J Pediatr. 1988 Feb;112(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg K. L., Morton M. J. Filling and arterial pressures as determinants of RV stroke volume in the sheep fetus. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):H656–H663. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.5.H656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner C. P., Heilskov J., Pelzer G., Grant S., Wenstrom K., Williamson R. A. Normal values for human umbilical venous and amniotic fluid pressures and their alteration by fetal disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Sep;161(3):714–717. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Mooren K., Barendregt L. G., Wladimiroff J. W. Fetal atrioventricular and outflow tract flow velocity waveforms during normal second half of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Sep;165(3):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]