Abstract
With the increasing trend of cross mixing of populations, aconitine induced poisoning and its related arrhythmias may be more frequently encountered worldwide. However, the clinical experience is often too limited to draw any conclusion on the optimal treatment for tachycardia induced by aconitine intoxication. The clinical presentation, serial electrocardiographic changes, and responses to antiarrhythmic agents are reported in a patient with aconitine induced life threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Amiodarone was effective in suppressing polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, which might provide an example of successful pharmacological intervention in aconitine induced ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Keywords: aconitine; herbal medicine; life threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmia; amiodarone
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (89.8 KB).
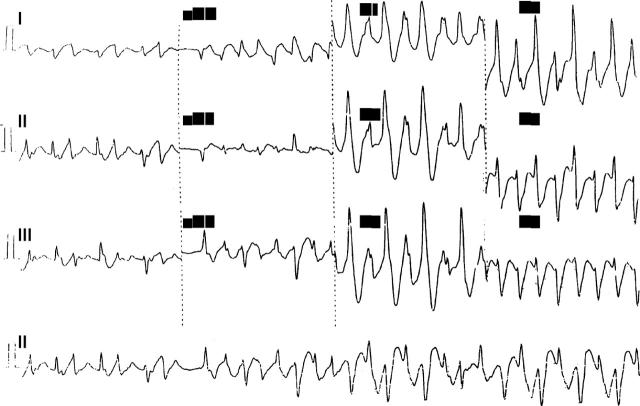
Figure 1 .
A 12 lead ECG revealing polymorphic and bidirectional ventricular tachycardia.
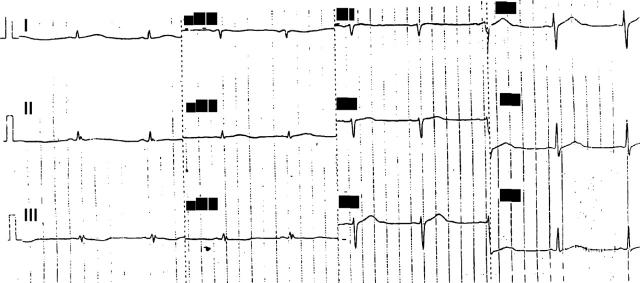
Figure 2 .
Sinus bradycardia after administration of intravenous amiodarone.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan T. Y., Chan J. C., Tomlinson B., Critchley J. A. Chinese herbal medicines revisited: a Hong Kong perspective. Lancet. 1993 Dec 18;342(8886-8887):1532–1534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)80091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. Y., Critchley J. A. Usage and adverse effects of Chinese herbal medicines. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1996 Jan;15(1):5–12. doi: 10.1177/096032719601500102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez B., Vilumara A., Farré A. J. Inhibition of aconitine-induced mortality in the conscious rat: a screening test for antiarrhythmic drugs. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1987 May;9(5):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawanobori T., Hirano Y., Hiraoka M. Aconitine-induced delayed afterdepolarization in frog atrium and guinea pig papillary muscles in the presence of low concentrations of Ca2+. Jpn J Physiol. 1987;37(1):59–79. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.37.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai Y. T., But P. P., Young K., Lau C. P. Cardiotoxicity after accidental herb-induced aconite poisoning. Lancet. 1992 Nov 21;340(8830):1254–1256. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92951-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai Y. T., Lau C. P., But P. P., Fong P. C., Li J. P. Bidirectional tachycardia induced by herbal aconite poisoning. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1992 May;15(5):831–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1992.tb06849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B., Chan T. Y., Chan J. C., Critchley J. A. Herb-induced aconitine poisoning. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):370–371. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90169-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow E. Hemodynamic and arrhythmogenic effects of aconitine applied to the left atria of anesthetized cats. Effects of amiodarone and atropine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):87–100. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198101000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]