Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate whether infusion of adrenomedullin, a potent vasorelaxant peptide, has beneficial haemodynamic and hormonal effects in patients with pulmonary hypertension. PATIENTS AND DESIGN—The haemodynamic and hormonal responses to intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin (0.05 µg/kg/min) or placebo were examined in 13 patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension. RESULTS—Infusion of adrenomedullin produced a 44% increase in cardiac index (mean (SD) 1.8 (0.2) to 2.6 (0.3) l/min/m2, p < 0.05) and a 32% decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance (19.7 (1.4) to 13.4 (1.3) units, p < 0.05), with a 4% reduction in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (62 (4) to 59 (4) mm Hg, NS). Adrenomedullin also decreased mean systemic arterial pressure (81 (3) to 72 (4) mm Hg, p < 0.05) and increased heart rate (73 (4) to 79 (4) beats/min, p < 0.05). Adrenomedullin decreased plasma aldosterone (9.8 (2.5) to 7.1 (1.5) ng/dl, p < 0.05) without significant changes in plasma renin activity. Plasma atrial and brain natriuretic peptides tended to decrease with adrenomedullin, although these changes did not reach significance. The haemodynamic and hormonal variables remained unchanged during placebo infusion. CONCLUSIONS—Intravenous adrenomedullin has beneficial haemodynamic and hormonal effects in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension. Keywords: adrenomedullin; pulmonary hypertension; haemodynamics
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (194.7 KB).
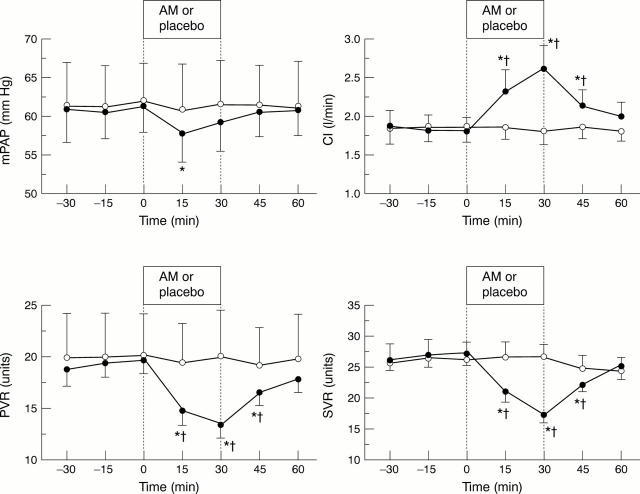
Figure 1 .
Changes in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP), cardiac index (CI), pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and systemic vascular resistance (SVR) during the intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin (•) or placebo (◯) in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Data are means, error bars = SEM. *p < 0.05 v value at time 0; †p < 0.05 v placebo group.
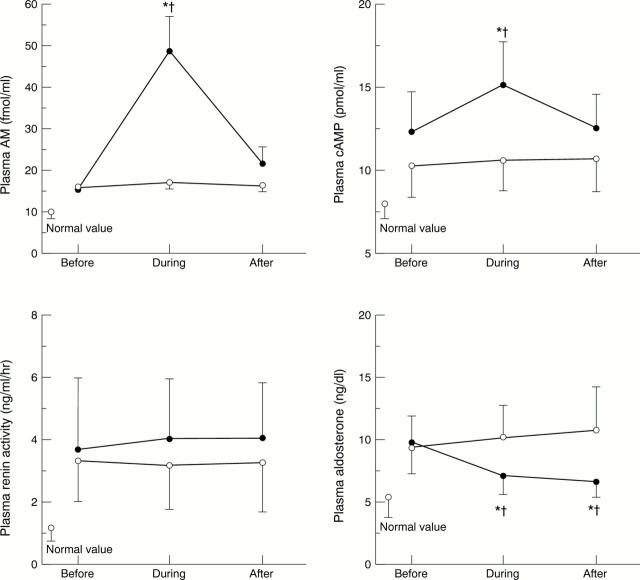
Figure 2 .
Changes in plasma adrenomedullin, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP), renin activity, and aldosterone during intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin (•) or placebo (◯) in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Data are means, error bars = SEM. AM, adrenomedullin. *p < 0.05 v before; †p < 0.05 v placebo group.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antman E. M., Marsh J. D., Green L. H., Grossman W. Blood oxygen measurements in the assessment of intracardiac left to right shunts: a critical appraisal of methodology. Am J Cardiol. 1980 Aug;46(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(80)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J., Rubin L. J., Long W. A., McGoon M. D., Rich S., Badesch D. B., Groves B. M., Tapson V. F., Bourge R. C., Brundage B. H. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1996 Feb 1;334(5):296–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199602013340504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton J., Lin B., Chang J. K., Steinberg S., Hyman A., Lippton H. Pulmonary vasodilation to adrenomedullin: a novel peptide in humans. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jun;268(6 Pt 2):H2211–H2215. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1995.268.6.H2211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M., Satoh T., Takezawa J., Ui M. An ultrasensitive method for the simultaneous determination of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in small-volume samples from blood and tissue. Biochem Med. 1977 Dec;18(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki Y., Kitamura K., Kangawa K., Kawamoto M., Matsuo H., Eto T. Distribution and characterization of immunoreactive adrenomedullin in human tissue and plasma. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 24;338(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka Y., Ishizaka Y., Tanaka M., Kitamura K., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Eto T. Adrenomedullin stimulates cyclic AMP formation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):642–646. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakishita M., Nishikimi T., Okano Y., Satoh T., Kyotani S., Nagaya N., Fukushima K., Nakanishi N., Takishita S., Miyata A. Increased plasma levels of adrenomedullin in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 1999 Jan;96(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kangawa K., Kawamoto M., Ichiki Y., Nakamura S., Matsuo H., Eto T. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):553–560. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippton H., Chang J. K., Hao Q., Summer W., Hyman A. L. Adrenomedullin dilates the pulmonary vascular bed in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 May;76(5):2154–2156. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.5.2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin V. V., Genthner D. E., Panella M. M., Rich S. Reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance with long-term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1998 Jan 29;338(5):273–277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199801293380501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya N., Nishikimi T., Okano Y., Uematsu M., Satoh T., Kyotani S., Kuribayashi S., Hamada S., Kakishita M., Nakanishi N. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels increase in proportion to the extent of right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jan;31(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya N., Satoh T., Nishikimi T., Uematsu M., Furuichi S., Sakamaki F., Oya H., Kyotani S., Nakanishi N., Goto Y. Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal effects of adrenomedullin infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation. 2000 Feb 8;101(5):498–503. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.5.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya N., Uematsu M., Okano Y., Satoh T., Kyotani S., Sakamaki F., Nakanishi N., Miyatake K., Kunieda T. Effect of orally active prostacyclin analogue on survival of outpatients with primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Oct;34(4):1188–1192. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi T., Horio T., Yoshihara F., Nagaya N., Matsuo H., Kangawa K. Effect of adrenomedullin on cAMP and cGMP levels in rat cardiac myocytes and nonmyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Jul 24;353(2-3):337–344. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Tsuji T., Asai S., Tanizaki S., Sasakura K., Teraoka H., Kitamura K., Kangawa K. A simple immunoradiometric assay for measuring the entire molecules of adrenomedullin in human plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1999 Sep;287(1-2):131–143. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(99)00128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owji A. A., Smith D. M., Coppock H. A., Morgan D. G., Bhogal R., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. An abundant and specific binding site for the novel vasodilator adrenomedullin in the rat. Endocrinology. 1995 May;136(5):2127–2134. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.5.7720662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rademaker M. T., Charles C. J., Lewis L. K., Yandle T. G., Cooper G. J., Coy D. H., Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G. Beneficial hemodynamic and renal effects of adrenomedullin in an ovine model of heart failure. Circulation. 1997 Sep 16;96(6):1983–1990. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.6.1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Dantzker D. R., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Koerner S. K. Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):216–223. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Nishimura K., Sugawara A., Okumura K., Obata K., Sonoda R., Ban T., Yasue H., Imura H. Clinical application of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in patients with congestive heart failure: beneficial effects on left ventricular function. Circulation. 1987 Jul;76(1):115–124. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata J., Shimokubo T., Kitamura K., Nishizono M., Iehiki Y., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Eto T. Distribution and characterization of immunoreactive rat adrenomedullin in tissue and plasma. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 26;352(2):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00928-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szokodi I., Kinnunen P., Tavi P., Weckström M., Tóth M., Ruskoaho H. Evidence for cAMP-independent mechanisms mediating the effects of adrenomedullin, a new inotropic peptide. Circulation. 1998 Mar 24;97(11):1062–1070. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.97.11.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., de Vroomen M., Gournay V., Roman C., Rudolph A. M., Heymann M. A. Mechanisms of adrenomedullin-induced increase of pulmonary blood flow in fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1999 Feb;45(2):276–281. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199902000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Baba K., Doi Y., Yano K. Effect of adrenomedullin on aldosterone secretion by dispersed rat adrenal zona glomerulosa cells. Life Sci. 1995;56(6):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00903-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshibayashi M., Kamiya T., Kitamura K., Saito Y., Kangawa K., Nishikimi T., Matsuoka H., Eto T., Matsuo H. Plasma levels of adrenomedullin in primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension in patients <20 years of age. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Jun 1;79(11):1556–1558. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara F., Nishikimi T., Horio T., Yutani C., Takishita S., Matsuo H., Ohe T., Kangawa K. Chronic infusion of adrenomedullin reduces pulmonary hypertension and lessens right ventricular hypertrophy in rats administered monocrotaline. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Aug 14;355(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]