Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (110.7 KB).
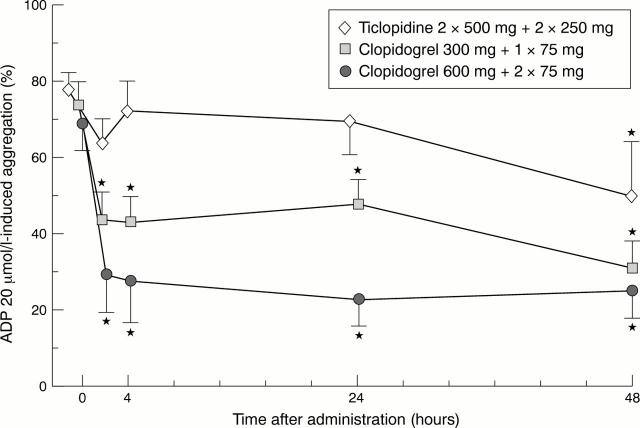
Figure 1 .
Effect of high loading dose of clopidogrel on ADP induced platelet aggregation. Patients were randomised into three treatment arms: ticlopidine 2 × 500 mg plus 2 × 250 mg daily thereafter (n = 10); clopidogrel 300 mg loading dose plus 1 × 75 mg daily (n = 10); and clopidogrel 600 mg loading dose plus 2 × 75 mg daily thereafter (n = 10). All patients received aspirin 2 × 100 mg/day concomitantly. Platelet aggregation was studied after stimulation with ADP (20 µmol/l) by light transmittance aggregometry in citrated platelet rich plasma. *Significant difference (p < 0.05) compared to starting concentrations.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand M. E., Rupprecht H. J., Urban P., Gershlick A. H., CLASSICS Investigators Double-blind study of the safety of clopidogrel with and without a loading dose in combination with aspirin compared with ticlopidine in combination with aspirin after coronary stenting : the clopidogrel aspirin stent international cooperative study (CLASSICS). Circulation. 2000 Aug 8;102(6):624–629. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.6.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawaz M., Ruf A., Neumann F. J., Pogátsa-Murray G., Dickfeld T., Zohlnhöfer D., Schömig A. Effect of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor antagonism on platelet membrane glycoproteins after coronary stent placement. Thromb Haemost. 1998 Dec;80(6):994–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohlke-Bärwolf C. Anticoagulation in valvar heart disease: new aspects and management during non-cardiac surgery. Heart. 2000 Nov;84(5):567–572. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye M., Donnellan C. Heart disease in the elderly. Heart. 2000 Nov;84(5):560–566. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.5.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn J., Teno J. M., Phillips R. S., Wu A. W., Desbiens N., Harrold J., Claessens M. T., Wenger N., Kreling B., Connors A. F., Jr Perceptions by family members of the dying experience of older and seriously ill patients. SUPPORT Investigators. Study to Understand Prognoses and Preferences for Outcomes and Risks of Treatments. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Jan 15;126(2):97–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-2-199701150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Hall J. A., Ley M. Communication and choice in dying from heart disease. J R Soc Med. 1997 Mar;90(3):128–131. doi: 10.1177/014107689709000304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Lay M., Addington-Hall J. Dying from heart disease. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1996 Jul-Aug;30(4):325–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray J. J., Stewart S. Epidemiology, aetiology, and prognosis of heart failure. Heart. 2000 May;83(5):596–602. doi: 10.1136/heart.83.5.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkel G. J., Aguirre F. V., Ligon R. W., Rocha-Singh K. J., Lucore C. L. Clopidogrel as adjunctive antiplatelet therapy during coronary stenting. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Dec;34(7):1884–1890. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. E., Addington-Hall J. M., Abery A. J., McCoy A. S., Bulpitt C., Coats A. J., Gibbs J. S. Knowledge and communication difficulties for patients with chronic heart failure: qualitative study. BMJ. 2000 Sep 9;321(7261):605–607. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7261.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schömig A., Neumann F. J., Kastrati A., Schühlen H., Blasini R., Hadamitzky M., Walter H., Zitzmann-Roth E. M., Richardt G., Alt E. A randomized comparison of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy after the placement of coronary-artery stents. N Engl J Med. 1996 Apr 25;334(17):1084–1089. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199604253341702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. J., Taylor R., Mitchell A. A comparison of four quality of life instruments in cardiac patients: SF-36, QLI, QLMI, and SEIQoL. Heart. 2000 Oct;84(4):390–394. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.4.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson W. G., Delacretaz E. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia. Heart. 2000 Nov;84(5):553–559. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft A. D., Boon N. A. Thyroid disease and the heart. Heart. 2000 Oct;84(4):455–460. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers S. E., St John Sutton M. When should ACE inhibitors or warfarin be discontinued after myocardial infarction? Heart. 2000 Oct;84(4):361–362. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. R., Roses A. D., Clifford C. P. Pharmacogenetics and the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Heart. 2000 Oct;84(4):353–354. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]