Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To measure plasma interferon γ, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), and interleukin 6 and to assess their correlation with cardiac troponin T in unstable angina. DESIGN—Blood sampling in patients undergoing coronary arteriography for known or suspected ischaemic heart disease. PATIENTS—76 patients divided in three groups: 29 with unstable angina (group 1), 28 with stable angina (group 2), and 19 without ischaemic heart disease and with angiographically normal coronary arteries (group 3). MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES—Plasma interleukin 6, interferon γ, MCP-1, and troponin T in the three groups of patients. RESULTS—Interleukin 6 was increased in group 1 (median 2.19 (range 0.53-50.84) pg/ml) compared with the control group (1.62 (0.79-3.98) pg/ml) (p < 0.005), whereas interferon γ was higher in group 1 (range 0-5.51 pg/ml) than in the other two groups (range 0-0.74 pg/ml and 0-0.37 pg/ml; p < 0.005 and p < 0.001, respectively). Patients with unstable angina (group 1) and positive troponin T had higher concentrations of interferon γ than those with negative troponin T (0-5.51 pg/ml v 0-0.60 pg/ml, p < 0.001). Plasma MCP-1 was also higher in group 1 (median 267 (range 6-8670) pg/ml) than in the other two groups (134 (19-890) pg/ml and 84.5 (5-325) pg/ml; p < 0.005 and p < 0.001, respectively), and among group 1 patients with a positive troponin T assay than in those with normal troponin T (531 (14.5-8670) pg/ml v 69 (6-3333) pg/ml; p < 0.01). There was no difference in plasma interleukin 6 in group 1 patients between those with and without raised troponin T. CONCLUSIONS—The inflammatory cytokines interferon γ and MCP-1 are increased in patients with unstable angina, particularly in those with raised concentrations of troponin T, suggesting that they are probably related to myocardial cell damage or to plaque rupture and thrombus formation. Keywords: inflammatory cytokines; troponin T; unstable angina
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (137.9 KB).
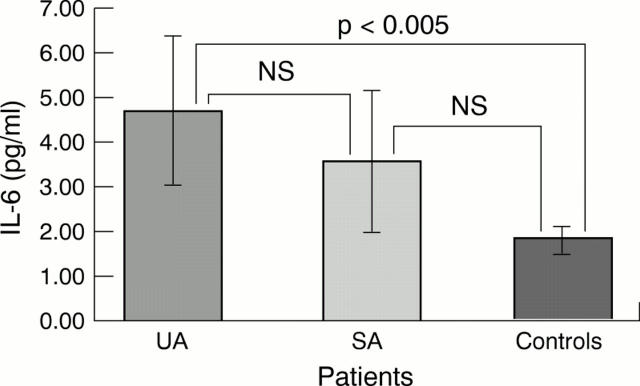
Figure 1 .
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) concentrations were higher in unstable angina (UA) than in controls. There was no difference between unstable angina and stable angina (SA). Data are means, error bars = SEM.
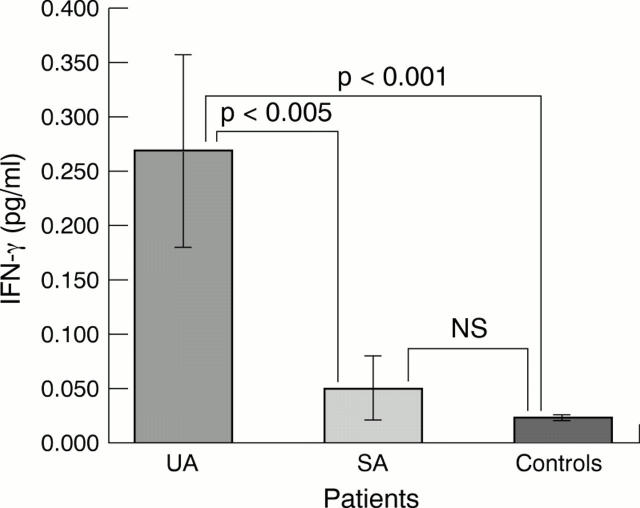
Figure 2 .
Interferon γ (IFN-γ) concentrations were higher in unstable angina (UA) than in stable angina (SA) or controls. There was no difference between stable angina and controls. Data means, error bars = SEM.
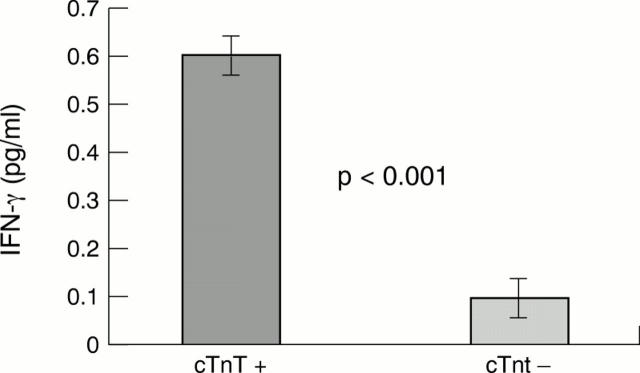
Figure 3 .
Among patients with unstable angina, those with positive cardiac troponin T (cTnT+) had significantly higher concentrations of interferon γ (IFN-γ) than those with negative troponin T (cTnT−). Data means, error bars = SEM.
Figure 4 .
Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) concentrations were higher in unstable angina (UA) than in stable angina (SA) or controls. There was no difference between stable angina and controls. Data means, error bars = SEM.
Figure 5 .
Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) concentrations were higher in unstable angina (UA) patients with positive cardiac troponin T (cTnT+) than in those with negative troponin T (cTnT−). Data means, error bars = SEM.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benamer H., Steg P. G., Benessiano J., Vicaut E., Gaultier C. J., Boccara A., Aubry P., Nicaise P., Brochet E., Juliard J. M. Comparison of the prognostic value of C-reactive protein and troponin I in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1998 Oct 1;82(7):845–850. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biasucci L. M., D'Onofrio G., Liuzzo G., Zini G., Monaco C., Caligiuri G., Tommasi M., Rebuzzi A. G., Maseri A. Intracellular neutrophil myeloperoxidase is reduced in unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction, but its reduction is not related to ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Mar 1;27(3):611–616. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biasucci L. M., Vitelli A., Liuzzo G., Altamura S., Caligiuri G., Monaco C., Rebuzzi A. G., Ciliberto G., Maseri A. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in unstable angina. Circulation. 1996 Sep 1;94(5):874–877. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.5.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunwald E. Unstable angina. A classification. Circulation. 1989 Aug;80(2):410–414. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman J. L., Mehta J. L., Saldeen T. G., Emerson S., Wallin R., Davda R., Davidson A. Increased neutrophil elastase release in unstable angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Jun;15(7):1559–1563. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)92826-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D. J., Roy L., Catella F., FitzGerald G. A. Platelet activation in unstable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 16;315(16):983–989. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610163151602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawaz M., Neumann F. J., Dickfeld T., Koch W., Laugwitz K. L., Adelsberger H., Langenbrink K., Page S., Neumeier D., Schömig A. Activated platelets induce monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secretion and surface expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on endothelial cells. Circulation. 1998 Sep 22;98(12):1164–1171. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.12.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm C. W., Heeschen C., Goldmann B., Vahanian A., Adgey J., Miguel C. M., Rutsch W., Berger J., Kootstra J., Simoons M. L. Benefit of abciximab in patients with refractory unstable angina in relation to serum troponin T levels. c7E3 Fab Antiplatelet Therapy in Unstable Refractory Angina (CAPTURE) Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999 May 27;340(21):1623–1629. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199905273402103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haught W. H., Mansour M., Rothlein R., Kishimoto T. K., Mainolfi E. A., Hendricks J. B., Hendricks C., Mehta J. L. Alterations in circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and L-selectin: further evidence for chronic inflammation in ischemic heart disease. Am Heart J. 1996 Jul;132(1 Pt 1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(96)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F., Thompson S. G., Pyke S. D., Gallimore J. R., Pepys M. B. Production of C-reactive protein and risk of coronary events in stable and unstable angina. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilities Angina Pectoris Study Group. Lancet. 1997 Feb 15;349(9050):462–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)07591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukielka G. L., Smith C. W., Manning A. M., Youker K. A., Michael L. H., Entman M. L. Induction of interleukin-6 synthesis in the myocardium. Potential role in postreperfusion inflammatory injury. Circulation. 1995 Oct 1;92(7):1866–1875. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.7.1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P. Molecular bases of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 1995 Jun 1;91(11):2844–2850. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.11.2844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzo G., Biasucci L. M., Gallimore J. R., Grillo R. L., Rebuzzi A. G., Pepys M. B., Maseri A. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid a protein in severe unstable angina. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 18;331(7):417–424. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408183310701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone A., De Servi S., Ricevuti G., Mazzucchelli I., Fossati G., Pasotti D., Bramucci E., Angoli L., Marsico F., Specchia G. Increased expression of neutrophil and monocyte adhesion molecules in unstable coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1993 Aug;88(2):358–363. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendall M. A., Patel P., Asante M., Ballam L., Morris J., Strachan D. P., Camm A. J., Northfield T. C. Relation of serum cytokine concentrations to cardiovascular risk factors and coronary heart disease. Heart. 1997 Sep;78(3):273–277. doi: 10.1136/hrt.78.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow D. A., Rifai N., Antman E. M., Weiner D. L., McCabe C. H., Cannon C. P., Braunwald E. C-reactive protein is a potent predictor of mortality independently of and in combination with troponin T in acute coronary syndromes: a TIMI 11A substudy. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jun;31(7):1460–1465. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott I., Neumann F. J., Gawaz M., Schmitt M., Schömig A. Increased neutrophil-platelet adhesion in patients with unstable angina. Circulation. 1996 Sep 15;94(6):1239–1246. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.6.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuzzi A. G., Quaranta G., Liuzzo G., Caligiuri G., Lanza G. A., Gallimore J. R., Grillo R. L., Cianflone D., Biasucci L. M., Maseri A. Incremental prognostic value of serum levels of troponin T and C-reactive protein on admission in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1998 Sep 15;82(6):715–719. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridker P. M., Cushman M., Stampfer M. J., Tracy R. P., Hennekens C. H. Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1997 Apr 3;336(14):973–979. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199704033361401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999 Jan 14;340(2):115–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199901143400207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schratzberger P., Dunzendorfer S., Reinisch N., Kähler C. M., Herold M., Wiedermann C. J. Release of chemoattractants for human monocytes from endothelial cells by interaction with neutrophils. Cardiovasc Res. 1998 May;38(2):516–521. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(98)00014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serneri G. G., Abbate R., Gori A. M., Attanasio M., Martini F., Giusti B., Dabizzi P., Poggesi L., Modesti P. A., Trotta F. Transient intermittent lymphocyte activation is responsible for the instability of angina. Circulation. 1992 Sep;86(3):790–797. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.3.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. K. New insights into the pathogenesis and prevention of acute coronary syndromes. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Jun 26;79(12B):17–23. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terres W., Kümmel P., Sudrow A., Reuter H., Meinertz T., Hamm C. W. Enhanced coagulation activation in troponin T-positive unstable angina pectoris. Am Heart J. 1998 Feb;135(2 Pt 1):281–286. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(98)70094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaddi K., Nicolini F. A., Mehta P., Mehta J. L. Increased secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma by mononuclear leukocytes in patients with ischemic heart disease. Relevance in superoxide anion generation. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):694–699. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez R., Caref E. B., Torres F., Reina M., Espina A., El-Sherif N. Improved diagnostic value of combined time and frequency domain analysis of the signal-averaged electrocardiogram after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Feb;33(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00581-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wal A. C., Becker A. E., van der Loos C. M., Das P. K. Site of intimal rupture or erosion of thrombosed coronary atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by an inflammatory process irrespective of the dominant plaque morphology. Circulation. 1994 Jan;89(1):36–44. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]