Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (155.5 KB).
Figure 1 .
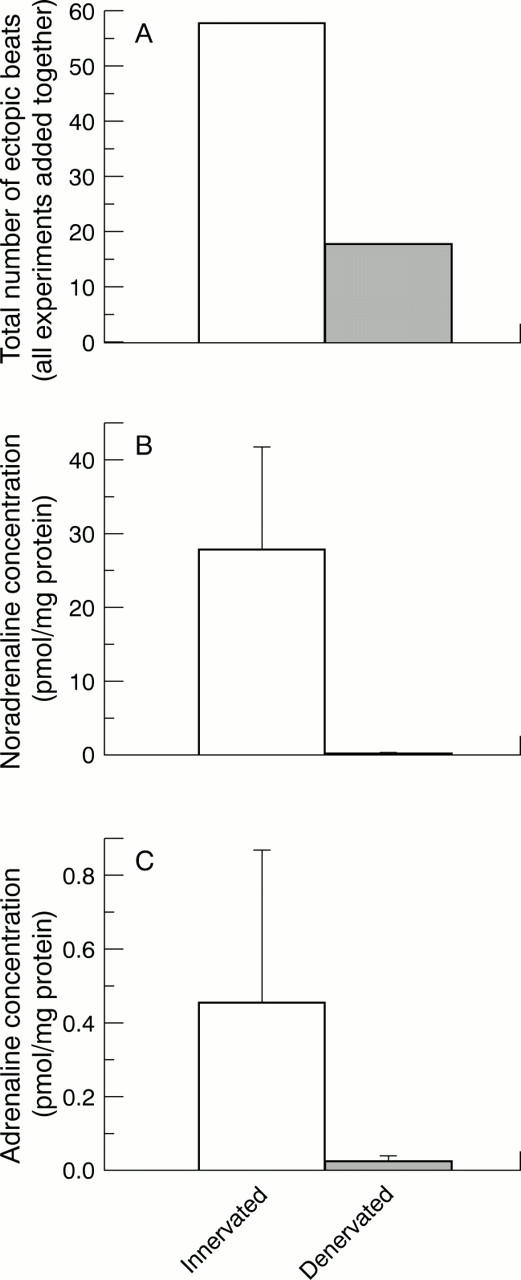
The reduction in the total number of ectopic beats (A) in cardiac denervated animals (grey columns) and innervated hearts (open columns) was comparable to the reduction in myocardial tissue noradrenaline (B) and adrenaline (C). All columns indicate means (1 SD). All differences were highly significant (p < 0.005).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allessie M. A. Atrial electrophysiologic remodeling: another vicious circle? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998 Dec;9(12):1378–1393. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1998.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alp N., Clarke N., Banning A. P. How should patients with patent foramen ovale be managed? Heart. 2001 Mar;85(3):242–244. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.3.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athanasiadis A., Haase K. K., Wullen B., Treusch A. W., Mahrholdt H., Voelker W., Baumbach A., Oberhoff M., Karsch K. R. Lesion morphology assessed by pre-interventional intravascular ultrasound does not predict the incidence of severe coronary artery dissections. Eur Heart J. 1998 Jun;19(6):870–878. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1997.0799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausma J., Wijffels M., Thoné F., Wouters L., Allessie M., Borgers M. Structural changes of atrial myocardium due to sustained atrial fibrillation in the goat. Circulation. 1997 Nov 4;96(9):3157–3163. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.9.3157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crijns H. J., Van Gelder I. C., Van Gilst W. H., Hillege H., Gosselink A. M., Lie K. I. Serial antiarrhythmic drug treatment to maintain sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion for chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Aug 1;68(4):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90828-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoud E. G., Bogun F., Goyal R., Harvey M., Man K. C., Strickberger S. A., Morady F. Effect of atrial fibrillation on atrial refractoriness in humans. Circulation. 1996 Oct 1;94(7):1600–1606. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.7.1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoud E. G., Knight B. P., Weiss R., Bahu M., Paladino W., Goyal R., Man K. C., Strickberger S. A., Morady F. Effect of verapamil and procainamide on atrial fibrillation-induced electrical remodeling in humans. Circulation. 1997 Sep 2;96(5):1542–1550. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.5.1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone A., Stabile G., Vitale D. F., Turco P., Di Stasio M., Petrazzuoli F., Gasparini M., De Matteis C., Rotunno R., Di Napoli T. Pretreatment with verapamil in patients with persistent or chronic atrial fibrillation who underwent electrical cardioversion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Sep;34(3):810–814. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. J., Stubbs J., Noble M. I. Dependence of myocardial blood flow and metabolism on cardiac innervation. Cardiovasc Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):69–80. doi: 10.1093/cvr/12.2.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X. J., Esler M. D., Dart A. M. Sympatholytic action of intravenous amiodarone in the rat heart. Circulation. 1995 Jan 15;91(2):462–470. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.2.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga G., Noble M. I., Stubbs J. The effect of an increase in aortic pressure upon the inotropic state of cat and dog left ventricles. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):597–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk E. Stable versus unstable atherosclerosis: clinical aspects. Am Heart J. 1999 Nov;138(5 Pt 2):S421–S425. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(99)70267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareh S., Villemaire C., Nattel S. Importance of refractoriness heterogeneity in the enhanced vulnerability to atrial fibrillation induction caused by tachycardia-induced atrial electrical remodeling. Circulation. 1998 Nov 17;98(20):2202–2209. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.20.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz M. R., Karasik P. L., Li C., Moubarak J., Chavez M. Electrical remodeling of the human atrium: similar effects in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997 Dec;30(7):1785–1792. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspo R., Bosch R. F., Talajic M., Nattel S. Functional mechanisms underlying tachycardia-induced sustained atrial fibrillation in a chronic dog model. Circulation. 1997 Dec 2;96(11):4027–4035. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.11.4027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goette A., Honeycutt C., Langberg J. J. Electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Time course and mechanisms. Circulation. 1996 Dec 1;94(11):2968–2974. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.11.2968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemielity M., Dyszkiewicz W., Paluszkiewicz L., Perek B., Buczkowski P., Ponizyński A. Do patients over 40 years of age benefit from surgical closure of atrial septal defects? Heart. 2001 Mar;85(3):300–303. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.3.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamalvand K., Tan K., Lloyd G., Gill J., Bucknall C., Sulke N. Alterations in atrial electrophysiology associated with chronic atrial fibrillation in man. Eur Heart J. 1999 Jun;20(12):888–895. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1998.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenbeck-Regn K., Schaller S., Flohr T., Ohnesorge B., Kopp A. F., Baum U. Subsecond multi-slice computed tomography: basics and applications. Eur J Radiol. 1999 Aug;31(2):110–124. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(99)00086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecky S. L., Gersh B. J., McGoon M. D., Whisnant J. P., Holmes D. R., Jr, Ilstrup D. M., Frye R. L. The natural history of lone atrial fibrillation. A population-based study over three decades. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):669–674. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp A. F., Ohnesorge B., Flohr T., Georg C., Schröder S., Küttner A., Martensen J., Claussen C. D. Multidetector CT des Herzens: Erste Klinische Anwendung einer retrospektiv EKG-gesteuerten Spirale mit optimierter zeitlicher und örtlicher Auflösung zur Darstellung der Herzkranzgefässe. Rofo. 2000 May;172(5):429–435. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai L. P., Su M. J., Lin J. L., Lin F. Y., Tsai C. H., Chen Y. S., Huang S. K., Tseng Y. Z., Lien W. P. Down-regulation of L-type calcium channel and sarcoplasmic reticular Ca(2+)-ATPase mRNA in human atrial fibrillation without significant change in the mRNA of ryanodine receptor, calsequestrin and phospholamban: an insight into the mechanism of atrial electrical remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Apr;33(5):1231–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Chen S. A., Yu W. C., Cheng J. J., Kaun P., Hung C. R., Chang M. S., Lin F. Y. Change of atrial refractory period after short duration of rapid atrial pacing: regional differences and possible mechanisms. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1999 Jun;22(6 Pt 1):927–934. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1999.tb06817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Yu W. C., Cheng J. J., Hung C. R., Ding Y. A., Chang M. S., Chen S. A. Effect of verapamil on long-term tachycardia-induced atrial electrical remodeling. Circulation. 2000 Jan 18;101(2):200–206. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leistad E., Aksnes G., Verburg E., Christensen G. Atrial contractile dysfunction after short-term atrial fibrillation is reduced by verapamil but increased by BAY K8644. Circulation. 1996 May 1;93(9):1747–1754. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.9.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe R. G., La Farge C. G., Gamble W. J., Hammond R. P., Morgan C. L. Norepinephrine release and left ventricular pressure in the isolated heart. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):774–790. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morillo C. A., Klein G. J., Jones D. L., Guiraudon C. M. Chronic rapid atrial pacing. Structural, functional, and electrophysiological characteristics of a new model of sustained atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1995 Mar 1;91(5):1588–1595. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.5.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Follmer C. H., Singer D. H. Amiodarone blocks calcium current in single guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):650–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkusa T., Ueyama T., Yamada J., Yano M., Fujumura Y., Esato K., Matsuzaki M. Alterations in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ regulatory proteins in the atrial tissue of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Jul;34(1):255–263. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onundarson P. T., Thorgeirsson G., Jonmundsson E., Sigfusson N., Hardarson T. Chronic atrial fibrillation--epidemiologic features and 14 year follow-up: a case control study. Eur Heart J. 1987 May;8(5):521–527. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandozi C., Bianconi L., Villani M., Gentilucci G., Castro A., Altamura G., Jesi A. P., Lamberti F., Ammirati F., Santini M. Electrophysiological characteristics of the human atria after cardioversion of persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1998 Dec 22;98(25):2860–2865. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.25.2860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanmuganathan P. S., Ghahramani P., Jackson P. R., Wallis E. J., Ramsay L. E. Aspirin for primary prevention of coronary heart disease: safety and absolute benefit related to coronary risk derived from meta-analysis of randomised trials. Heart. 2001 Mar;85(3):265–271. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideris D. A., Toumanidis S. T., Kostis E. B., Spyropoulos G., Moulopoulos S. D. Effect of adrenergic blockade on pressure-related ventricular arrhythmias. Acta Cardiol. 1991;46(2):215–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Chinushi M., Taneda K., Fujita S., Kasai H., Yamaura M., Imai S., Aizawa Y. Recovery of the right atrial effective refractory period after cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Nov 15;84(10):1261-4, A8. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terracciano C. M., Tweedie D., MacLeod K. T. The effects of changes to action potential duration on the calcium content of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1997 Feb;433(4):542–544. doi: 10.1007/s004240050312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieleman R. G., Blaauw Y., Van Gelder I. C., De Langen C. D., de Kam P. J., Grandjean J. G., Patberg K. W., Bel K. J., Allessie M. A., Crijns H. J. Digoxin delays recovery from tachycardia-induced electrical remodeling of the atria. Circulation. 1999 Oct 26;100(17):1836–1842. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.100.17.1836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieleman R. G., De Langen C., Van Gelder I. C., de Kam P. J., Grandjean J., Bel K. J., Wijffels M. C., Allessie M. A., Crijns H. J. Verapamil reduces tachycardia-induced electrical remodeling of the atria. Circulation. 1997 Apr 1;95(7):1945–1953. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.7.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieleman R. G., Gosselink A. T., Crijns H. J., van Gelder I. C., van den Berg M. P., de Kam P. J., van Gilst W. H., Lie K. I. Efficacy, safety, and determinants of conversion of atrial fibrillation and flutter with oral amiodarone. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Jan 1;79(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(96)00675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieleman R. G., Van Gelder I. C., Crijns H. J., De Kam P. J., Van Den Berg M. P., Haaksma J., Van Der Woude H. J., Allessie M. A. Early recurrences of atrial fibrillation after electrical cardioversion: a result of fibrillation-induced electrical remodeling of the atria? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jan;31(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommaso C., McDonough T., Parker M., Talano J. V. Atrial fibrillation and flutter. Immediate control and conversion with intravenously administered verapamil. Arch Intern Med. 1983 May;143(5):877–881. doi: 10.1001/archinte.143.5.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Chan N. Endothelial function and nitric oxide: clinical relevance. Heart. 2001 Mar;85(3):342–350. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder I. C., Crijns H. J., Van Gilst W. H., Verwer R., Lie K. I. Prediction of uneventful cardioversion and maintenance of sinus rhythm from direct-current electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation and flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Jul 1;68(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90707-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagoner D. R., Pond A. L., McCarthy P. M., Trimmer J. S., Nerbonne J. M. Outward K+ current densities and Kv1.5 expression are reduced in chronic human atrial fibrillation. Circ Res. 1997 Jun;80(6):772–781. doi: 10.1161/01.res.80.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffels M. C., Kirchhof C. J., Dorland R., Allessie M. A. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation. 1995 Oct 1;92(7):1954–1968. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.7.1954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffels M. C., Kirchhof C. J., Dorland R., Power J., Allessie M. A. Electrical remodeling due to atrial fibrillation in chronically instrumented conscious goats: roles of neurohumoral changes, ischemia, atrial stretch, and high rate of electrical activation. Circulation. 1997 Nov 18;96(10):3710–3720. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.10.3710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi M., Terashima M., Awano K., Kijima M., Nakatani S., Daikoku S., Ito K., Yasumura Y., Miyatake K. Morphology of vulnerable coronary plaque: insights from follow-up of patients examined by intravascular ultrasound before an acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000 Jan;35(1):106–111. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W. C., Chen S. A., Lee S. H., Tai C. T., Feng A. N., Kuo B. I., Ding Y. A., Chang M. S. Tachycardia-induced change of atrial refractory period in humans: rate dependency and effects of antiarrhythmic drugs. Circulation. 1998 Jun 16;97(23):2331–2337. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.97.23.2331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W. C., Lee S. H., Tai C. T., Tsai C. F., Hsieh M. H., Chen C. C., Ding Y. A., Chang M. S., Chen S. A. Reversal of atrial electrical remodeling following cardioversion of long-standing atrial fibrillation in man. Cardiovasc Res. 1999 May;42(2):470–476. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(99)00030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


