Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To assess the changes in quality of life, arrhythmia symptoms, and hospital resource utilisation following catheter ablation of typical atrial flutter. DESIGN—Patient questionnaire to compare the time interval following ablation with a similar time interval before ablation. SETTING—Tertiary referral centre. PATIENTS—63 consecutive patients were studied. Four patients subsequently underwent an ablate and pace procedure, two died of co-morbid illnesses, and two were lost to follow up. The remaining 55 patients form the basis of the report. RESULTS—Patients were followed for a mean (SD) of 12 (9.5) months. Atrial flutter ablation resulted in an improvement in quality of life (3.8 v 2.5, p < 0.001) and reductions in symptom frequency score (2.0 v 3.5, p < 0.001) and symptom severity score (2.0 v 3.8, p < 0.001) compared with preablation values. There was a reduction in the number of patients visiting accident and emergency departments (11% v 53%, p < 0.001), requiring cardioversion (7% v 51%, p < 0.001), or being admitted to hospital for a rhythm problem (11% v 56%, p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis confirmed that patients with atrial flutter and concomitant atrial fibrillation before ablation and those with atrial flutter alone both derived significant benefit from atrial flutter ablation. Patients with concomitant atrial fibrillation had an improvement in quality of life (3.5 v 2.5, p < 0.001) and reductions in symptom frequency score (2.3 v 3.5, p < 0.001) and symptom severity score (2.2 v 3.7, p < 0.001) compared with preablation values. CONCLUSIONS—Ablation of atrial flutter is recommended both in patients with atrial flutter alone and in those with concomitant atrial fibrillation. Keywords: atrial flutter; radiofrequency ablation; quality of life
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (143.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
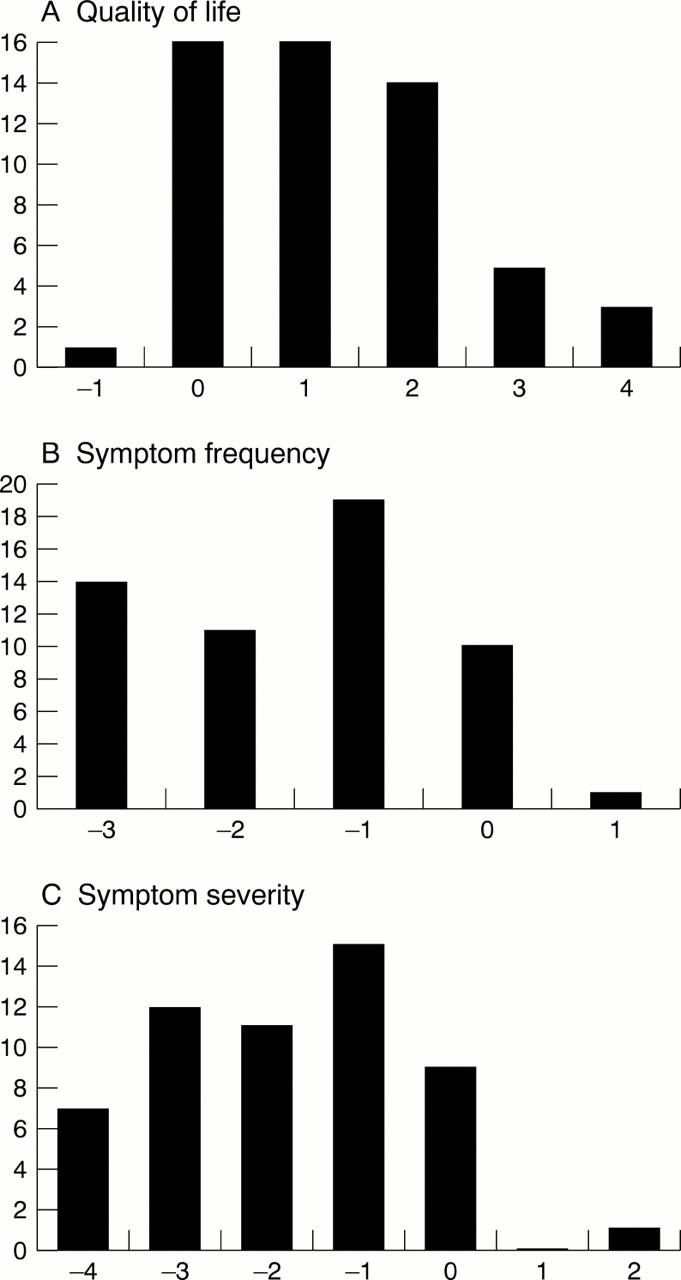
Changes in each patient's scores following ablation. Quality of life, symptom frequency, and symptom severity score changes are shown. An improvement in quality of life is denoted by positive values (A); a reduction in symptom frequency and severity following ablation is denoted by negative values (B, C). The time interval following ablation is compared with a similar time interval before ablation.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allessie M. A. Atrial electrophysiologic remodeling: another vicious circle? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998 Dec;9(12):1378–1393. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1998.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anselme F., Saoudi N., Poty H., Douillet R., Cribier A. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of common atrial flutter: significance of palpitations and quality-of-life evaluation in patients with proven isthmus block. Circulation. 1999 Feb 2;99(4):534–540. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera J. A., Sanchez-Quintana D., Ho S. Y., Medina A., Wanguemert F., Gross E., Grillo J., Hernandez E., Anderson R. H. Angiographic anatomy of the inferior right atrial isthmus in patients with and without history of common atrial flutter. Circulation. 1999 Jun 15;99(23):3017–3023. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.23.3017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauchemez B., Haissaguerre M., Fischer B., Thomas O., Clementy J., Coumel P. Electrophysiological effects of catheter ablation of inferior vena cava-tricuspid annulus isthmus in common atrial flutter. Circulation. 1996 Jan 15;93(2):284–294. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio F. G., López-Gil M., Goicolea A., Arribas F., Barroso J. L. Radiofrequency ablation of the inferior vena cava-tricuspid valve isthmus in common atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Mar 15;71(8):705–709. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)91014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L., Canavan T. E., Schuessler R. B., Cain M. E., Lindsay B. D., Stone C., Smith P. K., Corr P. B., Boineau J. P. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. II. Intraoperative electrophysiologic mapping and description of the electrophysiologic basis of atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991 Mar;101(3):406–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick A. P., Kourouyan H. D., Siu A., Lee R. J., Lesh M. D., Epstein L. M., Griffin J. C., Scheinman M. M. Quality of life and outcomes after radiofrequency His-bundle catheter ablation and permanent pacemaker implantation: impact of treatment in paroxysmal and established atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J. 1996 Mar;131(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(96)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iesaka Y., Takahashi A., Goya M., Yamane T., Tokunaga T., Amemiya H., Fujiwara H., Nitta J., Nogami A., Aonuma K. High energy radiofrequency catheter ablation for common atrial flutter targeting the isthmus between the inferior vena cava and tricuspid valve annulus using a super long tip electrode. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1998 Feb;21(2):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1998.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katritsis D., Iliodromitis E., Fragakis N., Adamopoulos S., Kremastinos D. Ablation therapy of type I atrial flutter may eradicate paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Aug 1;78(3):345–347. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(96)00291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Khrestian C., Waldo A. L. Simultaneous multisite mapping studies during induced atrial fibrillation in the sterile pericarditis model. Insights into the mechanism of its maintenance. Circulation. 1997 Jan 21;95(2):511–521. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.2.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Tai C. T., Yu W. C., Chen Y. J., Hsieh M. H., Tsai C. F., Chang M. S., Chen S. A. Effects of radiofrequency catheter ablation on quality of life in patients with atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Aug 1;84(3):278–283. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movsowitz C., Callans D. J., Schwartzman D., Gottlieb C., Marchlinski F. E. The results of atrial flutter ablation in patients with and without a history of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Jul 1;78(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(96)00233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabar A., Rodriguez L. M., Timmermans C., van den Dool A., Smeets J. L., Wellens H. J. Effect of right atrial isthmus ablation on the occurrence of atrial fibrillation: observations in four patient groups having type I atrial flutter with or without associated atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1999 Mar 23;99(11):1441–1445. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.11.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale A., Newby K. H., Pisanó E., Leonelli F., Fanelli R., Potenza D., Beheiry S., Tomassoni G. Prospective randomized comparison of antiarrhythmic therapy versus first-line radiofrequency ablation in patients with atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000 Jun;35(7):1898–1904. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00635-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olgin J. E., Kalman J. M., Lesh M. D. Conduction barriers in human atrial flutter: correlation of electrophysiology and anatomy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1996 Nov;7(11):1112–1126. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1996.tb00488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poty H., Saoudi N., Abdel Aziz A., Nair M., Letac B. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of type 1 atrial flutter. Prediction of late success by electrophysiological criteria. Circulation. 1995 Sep 15;92(6):1389–1392. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.6.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roithinger F. X., Lesh M. D. What is the relationship of atrial flutter and fibrillation? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1999 Apr;22(4 Pt 1):643–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1999.tb00506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher B., Pfeiffer D., Tebbenjohanns J., Lewalter T., Jung W., Lüderitz B. Acute and long-term effects of consecutive radiofrequency applications on conduction properties of the subeustachian isthmus in type I atrial flutter. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998 Feb;9(2):152–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1998.tb00896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman D., Callans D. J., Gottlieb C. D., Dillon S. M., Movsowitz C., Marchlinski F. E. Conduction block in the inferior vena caval-tricuspid valve isthmus: association with outcome of radiofrequency ablation of type I atrial flutter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Nov 15;28(6):1519–1531. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(96)00345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai C. T., Chen S. A., Chiang C. E., Lee S. H., Wen Z. C., Huang J. L., Chen Y. J., Yu W. C., Feng A. N., Lin Y. J. Long-term outcome of radiofrequency catheter ablation for typical atrial flutter: risk prediction of recurrent arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998 Feb;9(2):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1998.tb00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


