Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate the relation between plasma adrenomedullin and the severity of diastolic dysfunction in patients with heart failure. DESIGN—Prospective study. SETTING—University teaching hospital. PATIENTS—77 patients (mean (SEM) age 66.3 (1.2) years; 75% male) who were being followed in the outpatient clinic after admission to hospital for acute heart failure. INTERVENTIONS—Same day echocardiography with Doppler studies; determination of venous adrenomedullin concentration by radioimmunoassay. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES—Plasma adrenomedullin concentration and its correlation with systolic and diastolic function. RESULTS—31 patients (40%) had isolated diastolic dysfunction (ejection fraction > 50%), and the remaining 46 had a depressed ejection fraction (< 50%). Of the patients with diastolic dysfunction, 17 had a restrictive filling pattern. In all but one of these there was coexisting systolic failure (χ2 = 10.7, p = 0.001). Patients with systolic heart failure and a restrictive filling pattern (group 1, n = 16) had a higher plasma adrenomedullin than those with systolic failure and a non-restrictive filling pattern (group 2, n = 30) or with isolated diastolic heart failure and a non-restrictive filling pattern (group 3, n = 30) (mean (SEM): 91.7 (21.1) v 38.4 (8.8) v 34.0 (6.5) pmol/l, both p < 0.05). All heart failure values were higher (p < 0.01) than the control value (6.9 (1.2) pmol/l). Ejection fraction and left ventricular dimensions were similar in groups 1 and 2. Plasma adrenomedullin did not correlate with ejection fraction or New York Heart Association functional class. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that the presence of a restrictive filling pattern was the only independent variable associated with a high plasma adrenomedullin. CONCLUSIONS—Plasma adrenomedullin concentrations in patients with heart failure are determined by the presence of diastolic dysfunction, and are especially raised in the presence of a restrictive filling pattern. There appears to be no correlation with systolic dysfunction. Keywords: adrenomedullin; heart failure; diastolic dysfunction; Doppler echocardiography
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (150.2 KB).
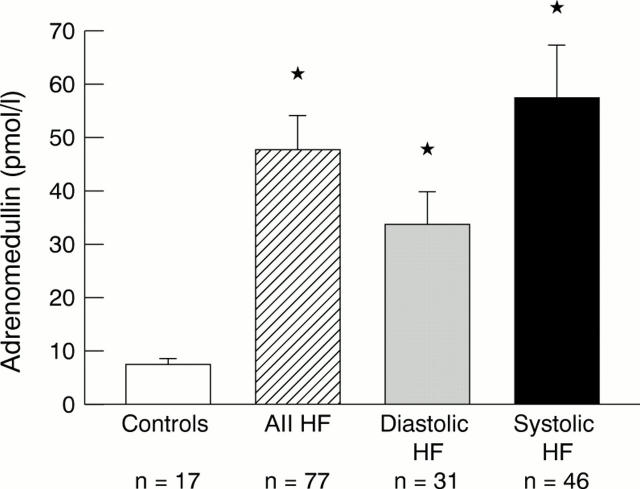
Figure 1 .
Mean plasma adrenomedullin concentrations in controls (white bar), all heart failure patients (HF) (hatched bar), patients with isolated diastolic heart failure (grey bar), and patients with systolic heart failure (black bar). Error bars = SEM. *p< 0.01 v controls.
Figure 2 .
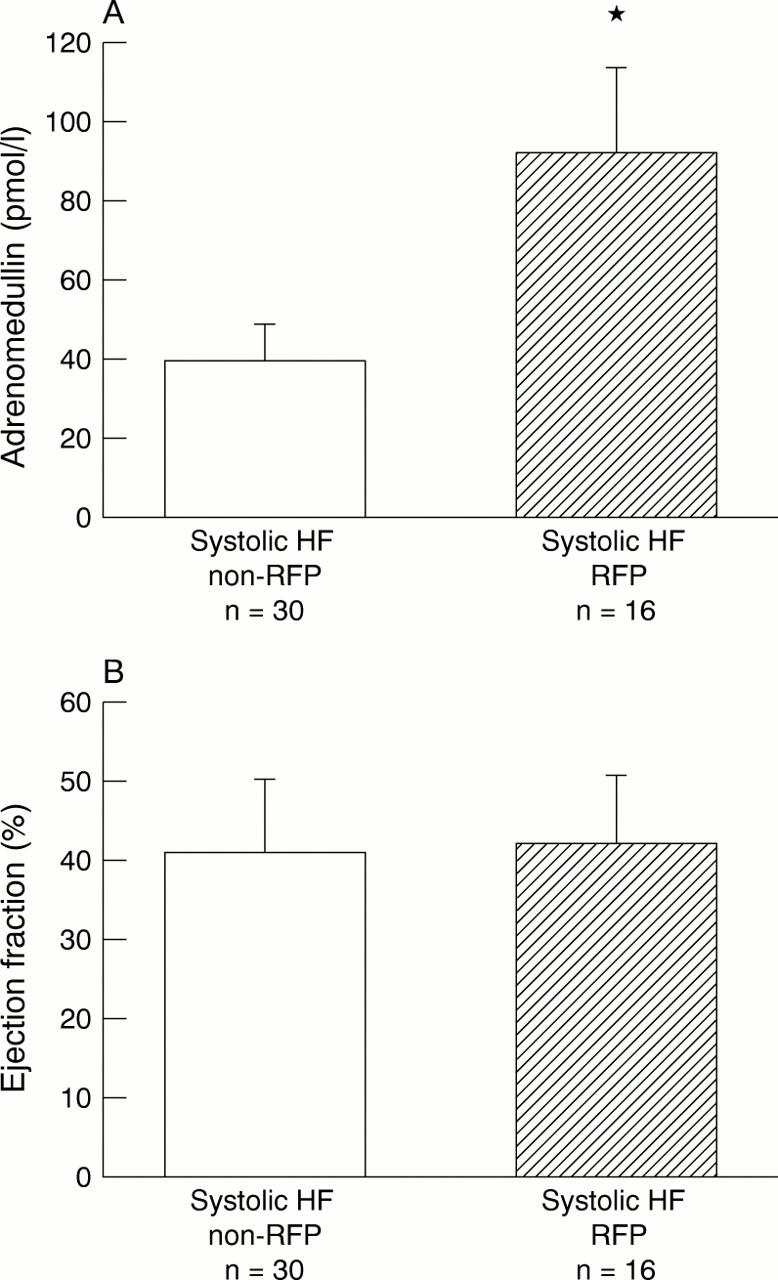
Effect of diastolic dysfunction with restrictive filling pattern (RFP) on plasma adrenomedullin concentrations in patients with systolic heart failure (HF). (A) Patients with RFP (hatched bar) had significantly higher plasma adrenomedullin that those with a non-restrictive pattern (non-RFP) (white bar). *p < 0.05, RFP v non-RFP groups. (B) There was no difference in the left ventricular ejection fraction between RFP and non-RFP groups.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleton C. P., Hatle L. K., Popp R. L. Relation of transmitral flow velocity patterns to left ventricular diastolic function: new insights from a combined hemodynamic and Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Aug;12(2):426–440. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung B., Leung R. Elevated plasma levels of human adrenomedullin in cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic and renal disorders. Clin Sci (Lond) 1997 Jan;92(1):59–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0920059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. I., Pietrolungo J. F., Thomas J. D., Klein A. L. A practical guide to assessment of ventricular diastolic function using Doppler echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Jun;27(7):1753–1760. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(96)00088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki Y., Kitamura K., Kangawa K., Kawamoto M., Matsuo H., Eto T. Distribution and characterization of immunoreactive adrenomedullin in human tissue and plasma. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 24;338(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama Y., Kitamura K., Ichiki Y., Nakamura S., Kida O., Kangawa K., Eto T. Hemodynamic effects of a novel hypotensive peptide, human adrenomedullin, in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 14;241(2-3):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jougasaki M., Wei C. M., McKinley L. J., Burnett J. C., Jr Elevation of circulating and ventricular adrenomedullin in human congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1995 Aug 1;92(3):286–289. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Kobayashi K., Etoh T., Tanaka M., Kitamura K., Imamura T., Koiwaya Y., Kangawa K., Eto T. Plasma adrenomedullin concentration in patients with heart failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Jan;81(1):180–183. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.1.8550749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh F., Niina H., Kitamura K., Ichiki Y., Yamamoto Y., Kangawa K., Eto T., Wada A. Ca(2+)-dependent cosecretion of adrenomedullin and catecholamines mediated by nicotinic receptors in bovine cultured adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jul 4;348(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kangawa K., Kawamoto M., Ichiki Y., Nakamura S., Matsuo H., Eto T. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):553–560. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang C. C., Prasad N., McAlpine H. M., Macleod C., Lipworth B. J., MacDonald T. M., Struthers A. D. Increased plasma levels of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with isolated diastolic dysfunction. Am Heart J. 1994 Jun;127(6):1635–1636. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(94)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. K., Smith M. W., Yandle T. G., Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G. Adrenomedullin(1-52) measured in human plasma by radioimmunoassay: plasma concentration, adsorption, and storage. Clin Chem. 1998 Mar;44(3):571–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi T., Kitamura K., Saito Y., Shimada K., Ishimitsu T., Takamiya M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Eto T., Omae T. Clinical studies on the sites of production and clearance of circulating adrenomedullin in human subjects. Hypertension. 1994 Nov;24(5):600–604. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.24.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi T., Saito Y., Kitamura K., Ishimitsu T., Eto T., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Omae T., Matsuoka H. Increased plasma levels of adrenomedullin in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 15;26(6):1424–1431. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00338-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinamonti B., Di Lenarda A., Sinagra G., Camerini F. Restrictive left ventricular filling pattern in dilated cardiomyopathy assessed by Doppler echocardiography: clinical, echocardiographic and hemodynamic correlations and prognostic implications. Heart Muscle Disease Study Group. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Sep;22(3):808–815. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossvoll O., Hatle L. K. Pulmonary venous flow velocities recorded by transthoracic Doppler ultrasound: relation to left ventricular diastolic pressures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Jun;21(7):1687–1696. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90388-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahn D. J., DeMaria A., Kisslo J., Weyman A. Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation. 1978 Dec;58(6):1072–1083. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.6.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo S., Minamino N., Shoji H., Kangawa K., Kitamura K., Eto T., Matsuo H. Interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor and lipopolysaccharide additively stimulate production of adrenomedullin in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 6;207(1):25–32. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Heublein D. M., Perrella M. A., Lerman A., Rodeheffer R. J., McGregor C. G., Edwards W. D., Schaff H. V., Burnett J. C., Jr Natriuretic peptide system in human heart failure. Circulation. 1993 Sep;88(3):1004–1009. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.3.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie G. Y., Berk M. R., Smith M. D., Gurley J. C., DeMaria A. N. Prognostic value of Doppler transmitral flow patterns in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Jul;24(1):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue H., Yoshimura M., Sumida H., Kikuta K., Kugiyama K., Jougasaki M., Ogawa H., Okumura K., Mukoyama M., Nakao K. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1994 Jul;90(1):195–203. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara F., Nishikimi T., Horio T., Yutani C., Nagaya N., Matsuo H., Ohe T., Kangawa K. Ventricular adrenomedullin concentration is a sensitive biochemical marker for volume and pressure overload in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000 Feb;278(2):H633–H642. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2000.278.2.H633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. M., Sanderson J. E., Chan S., Yeung L., Hung Y. T., Woo K. S. Right ventricular diastolic dysfunction in heart failure. Circulation. 1996 Apr 15;93(8):1509–1514. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.8.1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. M., Sanderson J. E., Shum I. O., Chan S., Yeung L. Y., Hung Y. T., Cockram C. S., Woo K. S. Diastolic dysfunction and natriuretic peptides in systolic heart failure. Higher ANP and BNP levels are associated with the restrictive filling pattern. Eur Heart J. 1996 Nov;17(11):1694–1702. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H. C., Sanderson J. E. Different prognostic significance of right and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in heart failure. Clin Cardiol. 1999 Aug;22(8):504–512. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960220804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]