Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (119.1 KB).
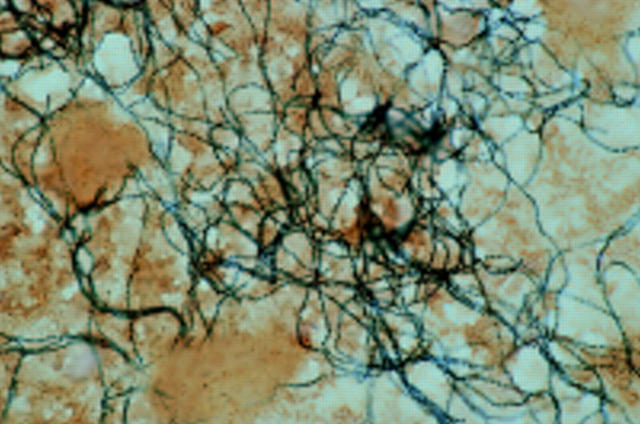
Figure 1: .
Gram stained smear from blood culture bottle showing viridans streptococci from patient with native valve endocarditis.
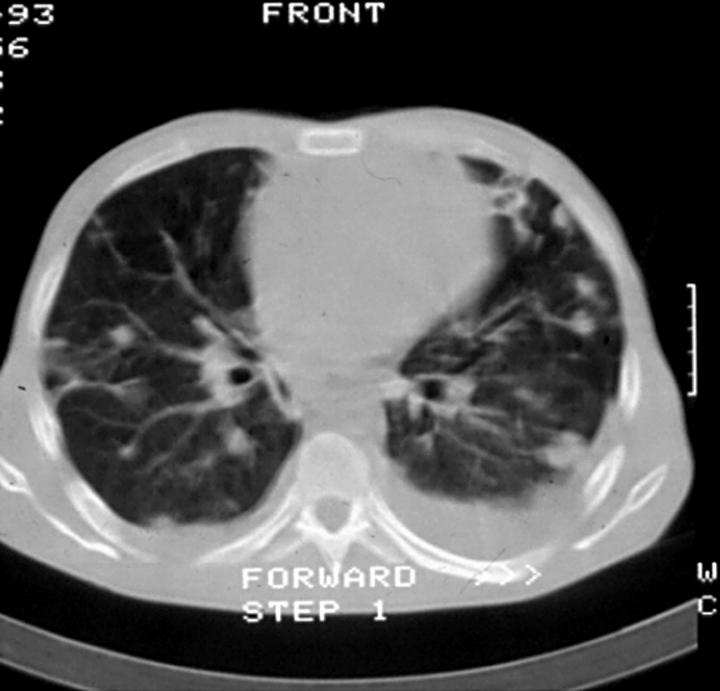
Figure 2: .
Computed tomographic chest scan from intravenous drug user with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis on the tricuspid valve. Multiple cavitating lesions are evident.
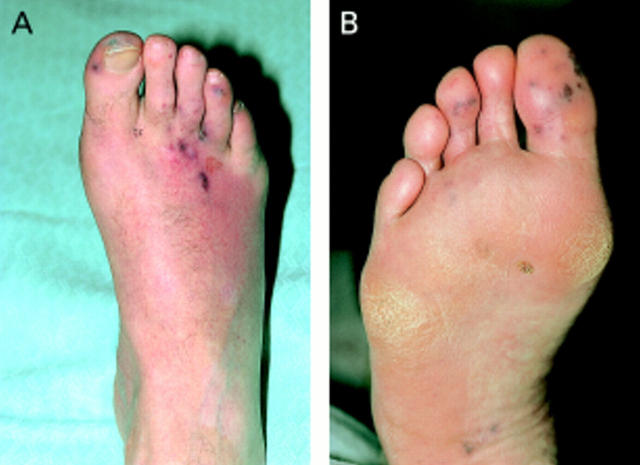
Figure 3: .
Embolic lesions on the feet of a patient with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Douglas A., Moore-Gillon J., Eykyn S. Fever during treatment of infective endocarditis. Lancet. 1986 Jun 14;1(8494):1341–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91661-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Lukes A. S., Bright D. K. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med. 1994 Mar;96(3):200–209. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniowski O., Sande M. A. Combination antimicrobial therapy for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in patients addicted to parenteral drugs and in nonaddicts: A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):496–503. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas C. C., Eykyn S. J. Suggested modifications to the Duke criteria for the clinical diagnosis of native valve and prosthetic valve endocarditis: analysis of 118 pathologically proven cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1997 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1086/513765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour R. A., Lowry R., Whitworth J. M., Martin M. V. Infective endocarditis, dentistry and antibiotic prophylaxis; time for a rethink? Br Dent J. 2000 Dec 9;189(11):610–616. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4800845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom B. L., Abrutyn E., Berlin J. A., Kinman J. L., Feldman R. S., Stolley P. D., Levison M. E., Korzeniowski O. M., Kaye D. Dental and cardiac risk factors for infective endocarditis. A population-based, case-control study. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Nov 15;129(10):761–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-129-10-199811150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Thompson R. L., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Giuliani E. R., Geraci J. E. Short-term therapy for streptococcal infective endocarditis. Combined intramuscular administration of penicillin and streptomycin. JAMA. 1981 Jan 23;245(4):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]