Abstract
How providers of external quality assessment (EQA) programmes relate to and interact with the monitors and watchdog of clinical laboratory performance in the UK is described. With regard to the quality of antibiotic assays, the changes in methodologies and in performance quality between 1971 (when the UK NEQAS for Antibiotic Assays began) and 1999 is reviewed. How improvements in performance and changes of methodology are related is discussed. The findings and conclusions of two experimental pilot EQA distributions (the teicoplanin assay and serum bactericidal test) are also discussed.
Key Words: external quality assessment • antibiotic assays • United Kingdom National Quality Assessment Schemes
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (129.8 KB).
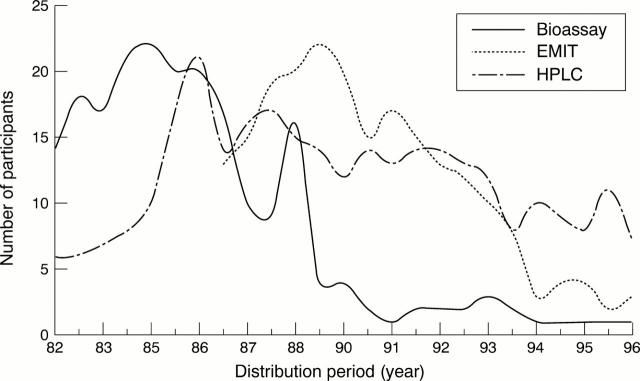
Figure 1 Trends in the numbers of participants in the UK NEQAS for chloramphenicol assay by method.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burd J. F., Wong R. C., Feeney J. E., Carrico R. J., Boguslaski R. C. Homogeneous reactant-labeled fluorescent immunoassay for therapeutic drugs exemplified by gentamicin determination in human serum. Clin Chem. 1977 Aug;23(8):1402–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGowan A., McMullin C., James P., Bowker K., Reeves D., White L. External quality assessment of the serum bactericidal test: results of a methodology/interpretation questionnaire. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997 Feb;39(2):277–284. doi: 10.1093/jac/39.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J. Quality control of serum gentamicin assays--experience of national surveys. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Mar;1(1):103–116. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., MacGowan A. P., Holt H. A., Lovering A. M., Warnock D. W., White L. O. Therapeutic monitoring of antimicrobials: a summary of the information presented at the UK NEQAS for antibiotic Assays meeting for participants, October 1993. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1995 Jan;35(1):213–226. doi: 10.1093/jac/35.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw E. J., Watson R. A., Landon J., Smith D. S. Estimation of serum gentamicin by quenching fluoroimmunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;30(6):526–531. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.6.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K. K., Hardin T. C., Gore S. J., Graybill J. R. Therapeutic drug monitoring of systemic antifungal therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997 Dec;40(6):753–764. doi: 10.1093/jac/40.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White L. O. Assays for therapeutic monitoring and pharmacokinetic investigations of aminoglycosides: quality aspects. Ther Drug Monit. 1998 Oct;20(5):464–468. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199810000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White L. O., McMullin C., Davis A. J., MacGowan A. P., Harding I., Reeves D. S. The quality of clinical serum teicoplanin assays: an experimental European EQA distribution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996 Oct;38(4):701–706. doi: 10.1093/jac/38.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. P., Browning D. M., Gregory A. A comparative survey of the results of analyses of blood serum in clinical chemistry laboratories in the United Kingdom. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jun;26(6):435–445. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]