Abstract
Aim—To study the distribution of Hodgkin's lymphoma in South African children and report the incidence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) as regards age, race, sex, and histological subtype; to investigate whether EBV is relevant to survival.
Methods—Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridisation (ISH) to detect EBV were performed on 47 South African children with classical Hodgkin's lymphoma, ranging in age from 3 to 14 years and coming from different ethnic backgrounds. The correlation between the presence of the virus and clinical outcome was assessed.
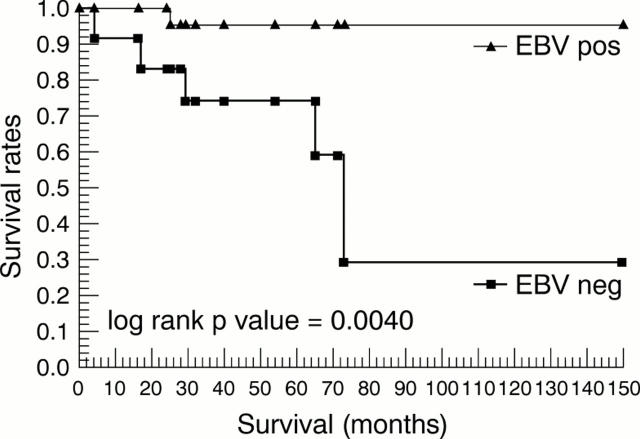
Results—The nodular sclerosing subtype predominated, comprising 89% of cases; the remaining 11% were of the mixed cellularity subtype. EBV was present in 68%. Full clinical data were available for 36 cases; EBV positive patients presented with less aggressive symptoms at diagnosis and had a significantly longer median survival than EBV negative patients.
Conclusions—The distribution of EBV in South African childhood Hodgkin's lymphoma follows a pattern intermediate to that of industrialised and non-industrialised countries. Furthermore, our data suggest that there is an association between poor prognosis and the non-detection of EBV products in South African childhood Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Key Words: children • Epstein-Barr virus • Hodgkin's lymphoma
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (127.6 KB).
Figure 1 Survival rates in South African children with Hodgkin's lymphoma according to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Browning P. J., Lorenzana I., Leventhal B. G., Cosenza H., Mann R. B., MacMahon E. M., Medina R., Cardona V., Grufferman S. Epstein-Barr virus and childhood Hodgkin's disease in Honduras and the United States. Blood. 1993 Jan 15;81(2):462–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos I., Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Stein H. Demonstration of monoclonal EBV genomes in Hodgkin's disease and Ki-1-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma by combined Southern blot and in situ hybridization. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):810–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andriko J. A., Aguilera N. S., Nandedkar M. A., Abbondanzo S. L. Childhood Hodgkin's disease in the United States: an analysis of histologic subtypes and association with Epstein-Barr virus. Mod Pathol. 1997 Apr;10(4):366–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong A. A., Alexander F. E., Paes R. P., Morad N. A., Gallagher A., Krajewski A. S., Jones D. B., Angus B., Adams J., Cartwright R. A. Association of Epstein-Barr virus with pediatric Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1683–1688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brousset P., Schlaifer D., Meggetto F., Bachmann E., Rothenberger S., Pris J., Delsol G., Knecht H. Persistence of the same viral strain in early and late relapses of Epstein-Barr virus-associated Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Oct 15;84(8):2447–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. L., Albújar P. F., Chen Y. Y., Johnson R. M., Weiss L. M. High prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus in the Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease occurring in Peru. Blood. 1993 Jan 15;81(2):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby T. V., Hoppe R. T., Warnke R. A. Hodgkin's disease: a clinicopathologic study of 659 cases. Cancer. 1982 May 1;49(9):1848–1858. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820501)49:9<1848::aid-cncr2820490918>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas E. C., Bateman A. C., Wilkins B. S., Johnson P. A., Williams J. H., Lee A. H., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Microwave antigen retrieval in immunocytochemistry: a study of 80 antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;47(5):448–452. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellbaum C., Hansmann M. L., Niedermeyer H., Kraus I., Alavaikko M. J., Blanco G., Aine R., Busch R., Pütz B., Fischer R. Influence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes on patient survival in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Sep;98(3):319–323. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/98.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser S. L., Lin R. J., Stewart S. L., Ambinder R. F., Jarrett R. F., Brousset P., Pallesen G., Gulley M. L., Khan G., O'Grady J. Epstein-Barr virus-associated Hodgkin's disease: epidemiologic characteristics in international data. Int J Cancer. 1997 Feb 7;70(4):375–382. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970207)70:4<375::aid-ijc1>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutensohn N., Cole P. Childhood social environment and Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 15;304(3):135–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101153040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutensohn N., Cole P. Epidemiology of hodgkin's disease in the young. Int J Cancer. 1977 May 15;19(5):595–604. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs in routine paraffin sections using non-isotopic RNA/RNA in situ hybridization. Histopathology. 1994 Aug;25(2):101–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb01565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. F., Gallagher A., Jones D. B., Alexander F. E., Krajewski A. S., Kelsey A., Adams J., Angus B., Gledhill S., Wright D. H. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Hodgkin's disease: relation to age. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Oct;44(10):844–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.10.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan G., Coates P. J., Kangro H. O., Slavin G. Epstein Barr virus (EBV) encoded small RNAs: targets for detection by in situ hybridisation with oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Jul;45(7):616–620. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.7.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan G., Norton A. J., Slavin G. Epstein-Barr virus in Hodgkin disease. Relation to age and subtype. Cancer. 1993 May 15;71(10):3124–3129. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930515)71:10<3124::aid-cncr2820711038>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht H., Bachmann E., Brousset P., Sandvej K., Nadal D., Bachmann F., Odermatt B. F., Delsol G., Pallesen G. Deletions within the LMP1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus are clustered in Hodgkin's disease and identical to those observed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Blood. 1993 Nov 15;82(10):2937–2942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange B., Arbeter A., Hewetson J., Henle W. Longitudinal study of Epstein-Barr virus antibody titers and excretion in pediatric patients with Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1978 Nov 15;22(5):521–527. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libetta C. M., Pringle J. H., Angel C. A., Craft A. W., Malcolm A. J., Lauder I. Demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral DNA in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples of Hodgkin's disease. J Pathol. 1990 Jul;161(3):255–260. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D. Epstein-Barr virus and a cellular signaling pathway in lymphomas from immunosuppressed patients. N Engl J Med. 1998 May 14;338(20):1413–1421. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199805143382003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morente M. M., Piris M. A., Abraira V., Acevedo A., Aguilera B., Bellas C., Fraga M., Garcia-Del-Moral R., Gomez-Marcos F., Menarguez J. Adverse clinical outcome in Hodgkin's disease is associated with loss of retinoblastoma protein expression, high Ki67 proliferation index, and absence of Epstein-Barr virus-latent membrane protein 1 expression. Blood. 1997 Sep 15;90(6):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Birkenbach M., Yalamanchili R., VanArsdale T., Ware C., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., Jiwa N. M., Kummer J. A., Horstman A., Vos W., Baak J. P., Kluin P. M., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Analysis of major histocompatibility complex class I expression on Reed-Sternberg cells in relation to the cytotoxic T-cell response in Epstein-Barr virus-positive and -negative Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1996 May 1;87(9):3844–3851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., Jiwa N. M., Meijer C. J. Epstein-Barr virus in Hodgkin's disease: more than just an innocent bystander. J Pathol. 1997 Apr;181(4):353–356. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199704)181:4<353::AID-PATH782>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90943-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Zhou X. The association of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) with T cell lymphoproliferations and Hodgkin's disease: two new developments in the EBV field. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;62:179–239. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peh S. C., Looi L. M., Pallesen G. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Hodgkin's disease in a multi-ethnic population in Malaysia. Histopathology. 1997 Mar;30(3):227–233. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1997.d01-594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preciado M. V., De Matteo E., Diez B., Grinstein S. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein (LMP) in tumor cells of Hodgkin's disease in pediatric patients. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1995 Jan;24(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950240102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou G., Favre M., Jeannel D., Bourhis J., Le Doussal V., Orth G. Association between poor prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical carcinomas and non-detection of HPV DNA. Lancet. 1990 May 19;335(8699):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92693-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Evans H. S., Young L. S., Hennessy K., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus reveal heterogeneity of the protein and inducible expression in virus-transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1575–1586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trovato R., Di Lollo S., Calzolari A., Torelli G., Ceccherini-Nelli L. Detection of human herpesvirus-6 and Epstein-Barr virus genome in childhood Hodgkin's disease. Pathologica. 1994 Oct;86(5):500–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasef M. A., Kamel O. W., Chen Y. Y., Medeiros L. J., Weiss L. M. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sites involved by Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1995 Nov;147(5):1408–1415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestlev P. M., Pallesen G., Sandvej K., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Bendtzen S. M. Prognosis of Hodgkin's disease is not influenced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein. Int J Cancer. 1992 Feb 20;50(4):670–671. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb M., Day P. J., Murray P. G., Raafat F., Crocker J., Parkes S. E., Coad N. A., Jones J. T., Mann J. R. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Hodgkin's disease in children: incidence of EBV latent membrane protein in malignant cells. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):365–369. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb M., Day P. J., Niggli F., Green E. K., Nyong'o A. O., Othieno-Abinya N. A., Riyat M. S., Raafat F., Mann J. R. The consistent association between Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease in children in Kenya. Blood. 1996 May 1;87(9):3828–3836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb M., Day P. J., Niggli F., Powell J. E., Raafat F., Hesseling P. B., Schneider J. W., Hartley P. S., Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou F., Khalek E. R. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in Hodgkin's disease from different geographical areas. Arch Dis Child. 1996 Jan;74(1):27–31. doi: 10.1136/adc.74.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Chen Y. Y., Liu X. F., Shibata D. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease. A correlative in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction study. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1259–1265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 23;320(8):502–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902233200806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Strickler J. G., Warnke R. A., Purtilo D. T., Sklar J. Epstein-Barr viral DNA in tissues of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):86–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarate-Osorno A., Roman L. N., Kingma D. W., Meneses-Garcia A., Jaffe E. S. Hodgkin's disease in Mexico. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus sequences and correlations with histologic subtype. Cancer. 1995 Mar 15;75(6):1360–1366. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950315)75:6<1360::aid-cncr2820750619>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Yan Q. H., Pallesen G. The association between Epstein-Barr virus and Chinese Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1993 Sep 30;55(3):359–363. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]