Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (147.5 KB).
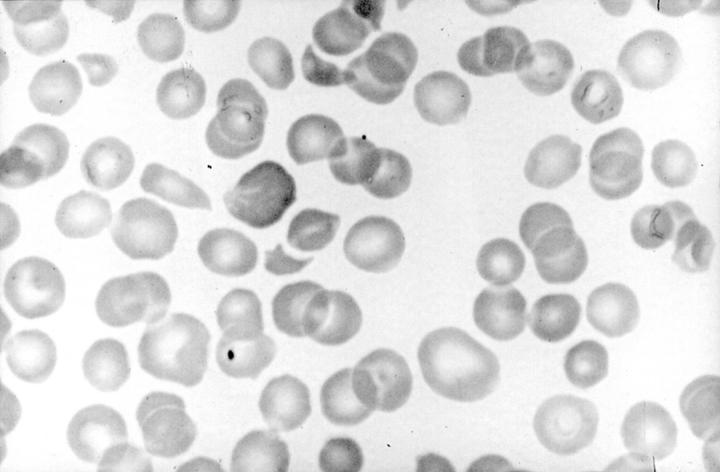
Figure 1 Peripheral blood film of patient with intermittent thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Severe thrombocytopenia and red cell fragmentation are prominent features. Circulating normoblasts and neutrophilia may also be seen.
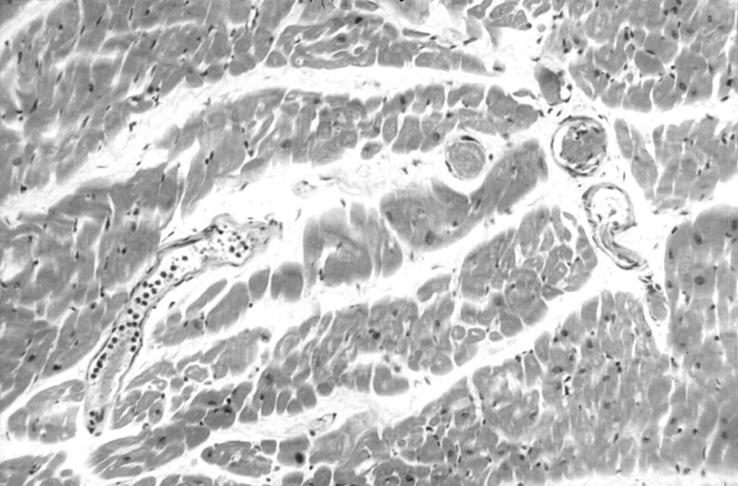
Figure 2 Typical histological findings of acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) (cardiac muscle). There is florid thrombosis within the microvasculature. Immunohistochemistry shows these thrombi to be composed predominantly of von Willebrand factor (vWF) and platelets, with only small amounts of fibrin and fibrinogen.
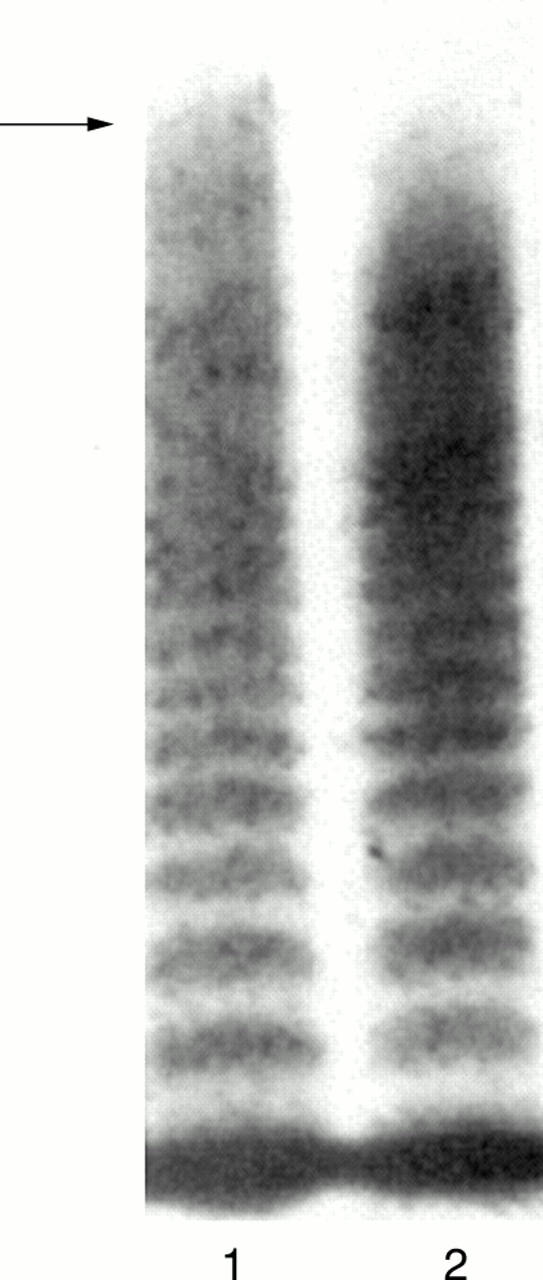
Figure 3 von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimeric analysis demonstrating unusually large forms of vWF (ULvWF) in patient plasma obtained during an episode of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) (lane 1, marked with an arrow). By comparison, lane 2 shows the series of vWF multimeric bands present in normal pooled platelet poor plasma: ULvWF are not a feature.
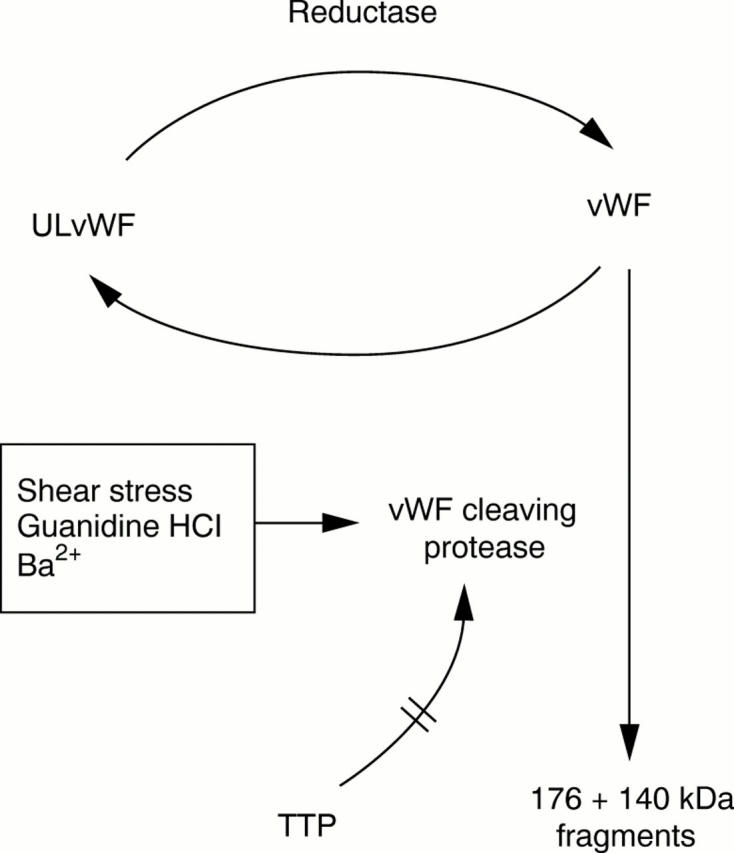
Figure 4 Proposed mechanism for proteolytic breakdown of von Willebrand factor (vWF). Ultra large forms of vWF (ULvWF) are reversibly converted in vitro to those forms normally found circulating in plasma by an activity in the cryosupernatant fraction of normal plasma with properties of a limited disulphide bond reductase. Under the conditions shown, a metalloproteinase further cleaves vWF forms into circulating 140 kDa and 176 kDa fragments, thus preventing reversible re-formation of ULvWF. This metalloproteinase activity has been reported to be absent in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), whereas it appears to be inhibited in single episode or intermittent adult TTP.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony M. T., Zeigler Z. R., Lister J., Raymond J. M., Shadduck R. K., Kramer R. E., Gryn J. F., Rintels P. B., Besa E. C., George J. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) antigen levels in primary TTP and secondary TTP post-bone marrow transplantation. Am J Hematol. 1998 Sep;59(1):9–14. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8652(199809)59:1<9::aid-ajh3>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asada Y., Sumiyoshi A., Hayashi T., Suzumiya J., Kaketani K. Immunohistochemistry of vascular lesion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, with special reference to factor VIII related antigen. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 1;38(5):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. L., Weinberg P. D., Rozenberg-Ben-Dror K., Yarnold P. R., Kwaan H. C., Green D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with ticlopidine. A review of 60 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Apr 1;128(7):541–544. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-7-199804010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chintagumpala M. M., Hurwitz R. L., Moake J. L., Mahoney D. H., Steuber C. P. Chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in infants with large von Willebrand factor multimers during remission. J Pediatr. 1992 Jan;120(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80596-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong B. H., Murray B., Berndt M. C., Dunlop L. C., Brighton T., Chesterman C. N. Plasma P-selectin is increased in thrombotic consumptive platelet disorders. Blood. 1994 Mar 15;83(6):1535–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T. W., Turner N. A., Chintagumpala M., McPherson P. D., Nolasco L. H., Rice L., Hellums J. D., Moake J. L. Increased von Willebrand factor binding to platelets in single episode and recurrent types of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol. 1998 Apr;57(4):293–302. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8652(199804)57:4<293::aid-ajh5>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Galbusera M., Ruggeri Z. M. Heterogeneity of plasma von Willebrand factor multimers resulting from proteolysis of the constituent subunit. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):774–782. doi: 10.1172/JCI115376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Galbusera M., Remuzzi G., Kyrle P. A., Brenner B., Krause M., Scharrer I., Aumann V., Mittler U. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1998 Nov 26;339(22):1578–1584. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811263392202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Lämmle B. Partial purification and characterization of a protease from human plasma cleaving von Willebrand factor to fragments produced by in vivo proteolysis. Blood. 1996 May 15;87(10):4223–4234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Morselli B., Sandoz P., Lämmle B. Recovery and half-life of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease after plasma therapy in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost. 1999 Jan;81(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Solenthaler M., Wassmer M., Sandoz P., Lämmle B. Deficient activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1997 May 1;89(9):3097–3103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness D. R., Byrnes J. J., Lian E. C., Williams W. D., Hensley G. T. Hazard of platelet transfusion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA. 1981 Oct 23;246(17):1931–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpman D., Lethagen S., Kristoffersson A., Isaksson C., Holmberg L. von Willebrand factor mediates increased platelet retention in recurrent thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost. 1997 Dec;78(6):1456–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama M., Handa M., Araki Y., Ambo H., Kawai Y., Watanabe K., Ikeda Y. Soluble P-selectin is present in normal circulation and its plasma level is elevated in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1993 Aug;84(4):702–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Wada H., Wakita Y., Shimura M., Nakase T., Hiyoyama K., Nagaya S., Minami N., Nakano T., Shiku H. Decreased plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jan;73(1):10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Mitra D., Steiner M., Staiano-Coico L., Jaffe E. Plasma from patients with idiopathic and human immunodeficiency virus-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura induces apoptosis in microvascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1996 Apr 15;87(8):3245–3254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra D., Jaffe E. A., Weksler B., Hajjar K. A., Soderland C., Laurence J. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and sporadic hemolytic-uremic syndrome plasmas induce apoptosis in restricted lineages of human microvascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1997 Feb 15;89(4):1224–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L. H., Hellums J. D. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI112736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L., Hellums J. D. Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released from platelets, as well as by exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1366–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J., Chintagumpala M., Turner N., McPherson P., Nolasco L., Steuber C., Santiago-Borrero P., Horowitz M., Pehta J. Solvent/detergent-treated plasma suppresses shear-induced platelet aggregation and prevents episodes of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):490–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. R., Etherington M. D. The endothelial von Willebrand factor in venous occlusion blood. Thromb Haemost. 1997 Dec;78(6):1528–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. M., Stathopoulos N. A., Giorgio T. D., Hellums J. D., Moake J. L. Shear-induced platelet aggregation requires von Willebrand factor and platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and IIb-IIIa. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):625–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumak K. H., Rock G. A., Nair R. C. Late relapses in patients successfully treated for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Group. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Apr 15;122(8):569–572. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-8-199504150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarantolo S. R., Landmark J. D., Iwen P. C., Kessinger A., Chan W. C., Hinrichs S. H. Bartonella-like erythrocyte inclusions in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Lancet. 1997 Nov 29;350(9091):1602–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)64019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Lian E. C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1998 Nov 26;339(22):1585–1594. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811263392203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Nagel R. L., Hatcher V. B., Seaton A. C., Sussman I. I. The high molecular weight form of endothelial cell von Willebrand factor is released by the regulated pathway. Br J Haematol. 1991 Oct;79(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Nagel R. L., Sussman I. I. Subunit composition of plasma von Willebrand factor multimers: evidence for a non-proteolytic mechanism resulting in apparent increase in proteolytic fragments. Thromb Res. 1991 Jul 1;63(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90280-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M. Physiologic cleavage of von Willebrand factor by a plasma protease is dependent on its conformation and requires calcium ion. Blood. 1996 May 15;87(10):4235–4244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Sussman I. I., Nagel R. L. Shear stress enhances the proteolysis of von Willebrand factor in normal plasma. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2171–2179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Kaneko T., Ohiwa M., Tanigawa M., Hayashi T., Tamaki S., Minami N., Deguchi K., Suzuki K., Nakano T. Increased levels of vascular endothelial cell markers in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol. 1993 Oct;44(2):101–105. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830440206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Mori Y., Shimura M., Hiyoyama K., Ioka M., Nakasaki T., Nishikawa M., Nakano M., Kumeda K., Kaneko T. Poor outcome in disseminated intravascular coagulation or thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura patients with severe vascular endothelial cell injuries. Am J Hematol. 1998 Jul;58(3):189–194. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8652(199807)58:3<189::aid-ajh5>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Dent J. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Nannini L. H. Subunit composition of plasma von Willebrand factor. Cleavage is present in normal individuals, increased in IIA and IIB von Willebrand disease, but minimal in variants with aberrant structure of individual oligomers (types IIC, IID, and IIE). J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):947–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI112394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plas R. M., Schiphorst M. E., Huizinga E. G., Hené R. J., Verdonck L. F., Sixma J. J., Fijnheer R. von Willebrand factor proteolysis is deficient in classic, but not in bone marrow transplantation-associated, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1999 Jun 1;93(11):3798–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]