Abstract
Neutrophil disorders are an uncommon yet important cause of morbidity and mortality in infants and children. This article is an overview of these conditions, with emphasis on clinical recognition, rational investigation, and treatment. A comprehensive list of references is provided for further reading.
Key Words: neutrophil disorders • chronic granulomatous disease • neutrophil chemotaxis • phagocytosis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (174.5 KB).
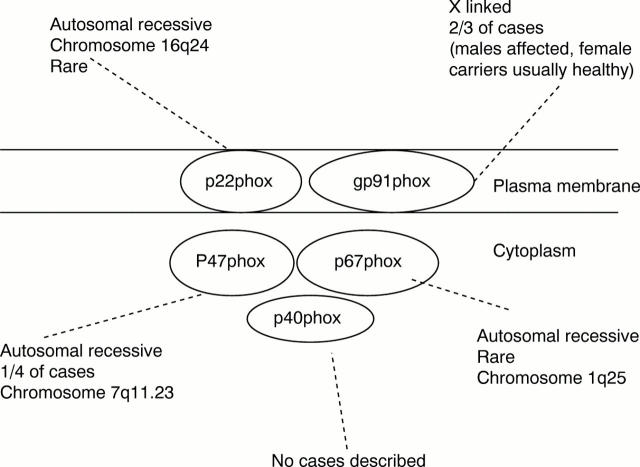
Figure 1 Components of NADPH oxidase and subgroups of chronic granulomatous disease.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A controlled trial of interferon gamma to prevent infection in chronic granulomatous disease. The International Chronic Granulomatous Disease Cooperative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 21;324(8):509–516. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102213240801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson J. S., Mills E. L., Sawyer M. K., Regelmann W. R., Nelson J. D., Quie P. G. Recurrent infections and delayed separation of the umbilical cord in an infant with abnormal phagocytic cell locomotion and oxidative response during particle phagocytosis. J Pediatr. 1981 Dec;99(6):887–894. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adès L. C., Gedeon A. K., Wilson M. J., Latham M., Partington M. W., Mulley J. C., Nelson J., Lui K., Sillence D. O. Barth syndrome: clinical features and confirmation of gene localisation to distal Xq28. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 1;45(3):327–334. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlin A., Lärfars G., Elinder G., Palmblad J., Gyllenhammar H. Gamma interferon treatment of patients with chronic granulomatous disease is associated with augmented production of nitric oxide by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999 May;6(3):420–424. doi: 10.1128/cdli.6.3.420-424.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso K., Dew J. M., Starke W. R. Thymic alymphoplasia and congenital aleukocytosis (reticular dysgenesia). Arch Pathol. 1972 Aug;94(2):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., McCabe E. R., Anderson D., Beaudet A., Ballas L. M., Brandt I. K., Brown B., Coleman R., Dunger D. B., Falletta J. M. Infectious and bleeding complications in patients with glycogenosis Ib. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Jul;139(7):691–697. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140090053027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews F. J., Katz F., Jones A., Smith S., Finn A. CD40 ligand deficiency presenting as unresponsive neutropenia. Arch Dis Child. 1996 May;74(5):458–459. doi: 10.1136/adc.74.5.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Moser B. Human chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Joseph G., Halberthal M., Sweed Y., Bialik V., Shoshani O., Etzioni A. Clostridium septicum infection in children with cyclic neutropenia. J Pediatr. 1997 Aug;131(2):317–319. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrat F. J., Auloge L., Pastural E., Lagelouse R. D., Vilmer E., Cant A. J., Weissenbach J., Le Paslier D., Fischer A., de Saint Basile G. Genetic and physical mapping of the Chediak-Higashi syndrome on chromosome 1q42-43. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Sep;59(3):625–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. G., Wanders R. J., Vreken P., Janssen E. A., Lam J., Baas F. X-linked cardioskeletal myopathy and neutropenia (Barth syndrome) (MIM 302060). J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999 Jun;22(4):555–567. doi: 10.1023/a:1005568609936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. G., Wanders R. J., Vreken P. X-linked cardioskeletal myopathy and neutropenia (Barth syndrome)-MIM 302060. J Pediatr. 1999 Sep;135(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedlow A. J., Davies E. G., Moss A. L., Rebuck N., Finn A., Marsden R. A. Pyoderma gangrenosum in a child with congenital partial deficiency of leucocyte adherence glycoproteins. Br J Dermatol. 1998 Dec;139(6):1064–1067. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.02567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard T., Gale R. E., Evans J. P., Linch D. C. Mutations of the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor receptor in patients with severe congenital neutropenia are not required for transformation to acute myeloid leukaemia and may be a bystander phenomenon. Br J Haematol. 1998 Apr;101(1):141–149. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernini J. C. Diagnosis and management of chronic neutropenia during childhood. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1996 Jun;43(3):773–792. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70432-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla M. A., Dale D., Zeidler C., Last L., Reiter A., Ruggeiro M., Davis M., Koci B., Hammond W., Gillio A. Long-term safety of treatment with recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (r-metHuG-CSF) in patients with severe congenital neutropenias. Br J Haematol. 1994 Dec;88(4):723–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla M. A., Gillio A. P., Ruggeiro M., Kernan N. A., Brochstein J. A., Abboud M., Fumagalli L., Vincent M., Gabrilove J. L., Welte K. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on neutropenia in patients with congenital agranulocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1574–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges W. G., Augustine N. H., Hill H. R. Defective interleukin-12/interferon-gamma pathway in patients with hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome. J Pediatr. 2000 Feb;136(2):176–180. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(00)70098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Greenberg M. S., Boxer G. J., Stossel T. P. Autoimmune neutropenia. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 9;293(15):748–753. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510092931505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Hutchinson R., Emerson S. Recombinant human granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in the treatment of patients with neutropenia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Jan;62(1 Pt 2):S39–S46. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90039-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredius R. G., Derkx B. H., Fijen C. A., de Wit T. P., de Haas M., Weening R. S., van de Winkel J. G., Out T. A. Fc gamma receptor IIa (CD32) polymorphism in fulminant meningococcal septic shock in children. J Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;170(4):848–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briars G. L., Parry H. F., Ansari B. M. Dominantly inherited severe congenital neutropenia. J Infect. 1996 Sep;33(2):123–126. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(96)93081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruin M. C., von dem Borne A. E., Tamminga R. Y., Kleijer M., Buddelmeijer L., de Haas M. Neutrophil antibody specificity in different types of childhood autoimmune neutropenia. Blood. 1999 Sep 1;94(5):1797–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel J., Lalezari P., Hilgartner M., Partin J., Fikrig S., O'Malley J., Barandun S. Reversal of neutropenia with intravenous gammaglobulin in autoimmune neutropenia of infancy. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):398–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bux J., Behrens G., Jaeger G., Welte K. Diagnosis and clinical course of autoimmune neutropenia in infancy: analysis of 240 cases. Blood. 1998 Jan 1;91(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bux J., Chapman J. Report on the second international granulocyte serology workshop. Transfusion. 1997 Sep;37(9):977–983. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1997.37997454028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bux J., Jung K. D., Kauth T., Mueller-Eckhardt C. Serological and clinical aspects of granulocyte antibodies leading to alloimmune neonatal neutropenia. Transfus Med. 1992 Jun;2(2):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.1992.tb00148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin T. W., Stiehm E. R., Falloon J., Gallin J. I. Corticosteroids in treatment of obstructive lesions of chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1987 Sep;111(3):349–352. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Casper J. T., Camitta B. M., McCreadie S. R. Cyclic neutropenia in identical twins. Am J Med. 1986 May;80(5):994–996. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90651-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L. T., Clay M. E., Kline W. E., Ramsay N. K., Krivit W., McCullough J. Natural history of primary autoimmune neutropenia in infancy. Pediatrics. 1987 May;79(5):728–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáp J., Mikulecky M. Cyclic neutropenia in a family with evidence of monocytes, lymphocytes, plasmocytes, eosinophils and basophils cycling. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Aug;43(2):188–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale D. C., Hammond W. P., 4th Cyclic neutropenia: a clinical review. Blood Rev. 1988 Sep;2(3):178–185. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(88)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson L., Harmenberg J. Intermittent rG-CSF treatment in cyclic neutropenia. Eur J Haematol. 1992 Feb;48(2):123–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1992.tb00581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danziger R. N., Goren A. T., Becker J., Greene J. M., Douglas S. D. Outpatient management with oral corticosteroid therapy for obstructive conditions in chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1993 Feb;122(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(06)80138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong F., Brynes R. K., Tidow N., Welte K., Löwenberg B., Touw I. P. Mutations in the gene for the granulocyte colony-stimulating-factor receptor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia preceded by severe congenital neutropenia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Aug 24;333(8):487–493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199508243330804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong F., Dale D. C., Bonilla M. A., Freedman M., Fasth A., Neijens H. J., Palmblad J., Briars G. L., Carlsson G., Veerman A. J. Mutations in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor gene in patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Leukemia. 1997 Jan;11(1):120–125. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong F., van Buitenen C., Pouwels K., Hoefsloot L. H., Löwenberg B., Touw I. P. Distinct cytoplasmic regions of the human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor involved in induction of proliferation and maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7774–7781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkel I. J., Bussel J. B. New developments in the treatment of neutropenia. Am J Dis Child. 1993 Sep;147(9):994–1000. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1993.02160330084026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. E., Rohrer J., Conley M. E. Neutropenia in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Dec;81(3):271–276. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.0188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A., Hadzić N., Morgan G., Strobel S., Levinsky R. J. Prognosis of chronic granulomatous disease. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Sep;65(9):942–945. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.9.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A., Rebuck N. Measurement of adhesion molecule expression on neutrophils and fixation. J Immunol Methods. 1994 May 16;171(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Segal A. W., Seger R., Weening R. S. The management of chronic granulomatous disease. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Nov;152(11):896–899. doi: 10.1007/BF01957525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch B. K., Bauer F., Neppert J. Rapid typing of the human Fc gamma receptor IIA polymorphism by polymerase chain reaction amplification with allele-specific primers. Transfusion. 1998 Feb;38(2):174–176. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1998.38298193100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest C. B., Forehand J. R., Axtell R. A., Roberts R. L., Johnston R. B., Jr Clinical features and current management of chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):253–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Bonilla M. A., Fier C., Bolyard A. A., Scarlata D., Boxer L. A., Brown S., Cham B., Kannourakis G., Kinsey S. E. Myelodysplasia syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia in patients with congenital neutropenia receiving G-CSF therapy. Blood. 2000 Jul 15;96(2):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Elin R. J., Hubert R. T., Fauci A. S., Kaliner M. A., Wolff S. M. Efficacy of ascorbic acid in Chediak-Higashi syndrome (CHS): studies in humans and mice. Blood. 1979 Feb;53(2):226–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman P. A., Jackson D. P., Guild H. G. Congenital agranulocytosis: prolonged survival and terminal acute leukemia. Blood. 1970 Nov;36(5):576–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimbacher B., Holland S. M., Gallin J. I., Greenberg F., Hill S. C., Malech H. L., Miller J. A., O'Connell A. C., Puck J. M. Hyper-IgE syndrome with recurrent infections--an autosomal dominant multisystem disorder. N Engl J Med. 1999 Mar 4;340(9):692–702. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199903043400904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry D., 4th, Dale D. C., Omine M., Perry S., Wolff S. M. Periodic hematopoiesis in human cyclic neutropenia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3220–3230. doi: 10.1172/JCI107522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad E., Le Deist F., Blanche S., Benkerrou M., Rohrlich P., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Fischer A. Treatment of Chediak-Higashi syndrome by allogenic bone marrow transplantation: report of 10 cases. Blood. 1995 Jun 1;85(11):3328–3333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond W. P., 4th, Price T. H., Souza L. M., Dale D. C. Treatment of cyclic neutropenia with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 18;320(20):1306–1311. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905183202003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada T., Ono I., Nagasawa T. Childhood cyclic neutropenia treated with recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Br J Haematol. 1990 May;75(1):135–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon D. C., Weitzman S. A., Stossel T. P. The severity of immune neutropenia correlates with the maturational specificity of antineutrophil antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1984 Oct;58(2):209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb06078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández A., Olivares F., Cantú J. M. Autosomal recessive onychotrichodysplasia, chronic neutropenia and mild mental retardation. Delineation of the syndrome. Clin Genet. 1979 Feb;15(2):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestdal K., Welte K., Lie S. O., Keller J. R., Ruscetti F. W., Abrahamsen T. G. Severe congenital neutropenia: abnormal growth and differentiation of myeloid progenitors to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) but normal response to G-CSF plus stem cell factor. Blood. 1993 Nov 15;82(10):2991–2997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussner P., Haase D., Kanz L., Fonatsch C., Welte K., Freund M. G-CSF in the long-term treatment of cyclic neutropenia and chronic idiopathic neutropenia in adult patients. Int J Hematol. 1995 Dec;62(4):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgartner M. W., Bussel J. Use of intravenous gamma globulin for the treatment of autoimmune neutropenia of childhood and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Am J Med. 1987 Oct 23;83(4A):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90547-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima K., Yoshida Y., Asano S., Takaku F., Omine M., Furusawa S., Abe T., Abe T., Dohy H., Tajiri M. Clinical effect of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) on various types of neutropenia including cyclic neutropenia. Biotherapy. 1991;3(4):297–307. doi: 10.1007/BF02221322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Stewart M. P., Scarth S. L., Newton R., Shaw J. M., Law S. K., Klein N. A novel leukocyte adhesion deficiency caused by expressed but nonfunctional beta2 integrins Mac-1 and LFA-1. J Clin Invest. 1999 Jan;103(1):97–106. doi: 10.1172/JCI3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M., Benson K. F., Person R. E., Aprikyan A. G., Dale D. C. Mutations in ELA2, encoding neutrophil elastase, define a 21-day biological clock in cyclic haematopoiesis. Nat Genet. 1999 Dec;23(4):433–436. doi: 10.1038/70544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. J., Hollers J. C., Crockett-Torabi E., Smith C. W. Recruitment of CD11b/CD18 to the neutrophil surface and adherence-dependent cell locomotion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1172/JCI116041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. G., Avalos B. R. Deletion of a critical internalization domain in the G-CSFR in acute myelogenous leukemia preceded by severe congenital neutropenia. Blood. 1999 Jan 15;93(2):440–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imashuku S., Tsuchida M., Sasaki M., Shimokawa T., Nakamura H., Matsuyama T., Taniguchi N., Oda M., Higuchi S., Ishimoto K. Recombinant human granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in the treatment of patients with chronic benign granulocytopenia and congenital agranulocytosis (Kostmann's syndrome). Acta Paediatr. 1992 Feb;81(2):133–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen N., Broxmeyer H. E. Oscillations of granulocytic and megakaryocytic progenitor cell populations in cyclic neutropenia in man. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Jul;23(1):33–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb02850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayabose S., Tugal O., Sandoval C., Li K. Recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor in cyclic neutropenia: use of a new 3-day-a-week regimen. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1994 Nov;16(4):338–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppson J. D., Jaffe H. S., Hill H. R. Use of recombinant human interferon gamma to enhance neutrophil chemotactic responses in Job syndrome of hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and recurrent infections. J Pediatr. 1991 Mar;118(3):383–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Newman S. L. Chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1977 May;24(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson O. G., Buchanan G. R. Chronic neutropenia during childhood. A 13-year experience in a single institution. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Feb;145(2):232–235. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160020126032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karayalcin G., Rosner F., Sawitsky A. Pseudoneutropenia in Negroes: a normal phenomenon. N Y State J Med. 1972 Jul 15;72(14):1815–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keel M., Ungethüm U., Steckholzer U., Niederer E., Hartung T., Trentz O., Ertel W. Interleukin-10 counterregulates proinflammatory cytokine-induced inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis during severe sepsis. Blood. 1997 Nov 1;90(9):3356–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama A., Ishiguro A., Kubo T., Matsuoka T., Yasukohchi S., Yasui K., Yanagisawa M., Yamada S., Yamazaki M., Akabane T. Increases in neutrophil counts by purified human urinary colony-stimulating factor in chronic neutropenia of childhood. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostman R. Infantile genetic agranulocytosis. A review with presentation of ten new cases. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Mar;64(2):362–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krance R. A., Spruce W. E., Forman S. J., Rosen R. B., Hecht T., Hammond W. P., Blume K. G. Human cyclic neutropenia transferred by allogeneic bone marrow grafting. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1263–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan K., Ross C. W., Bockenstedt P. L., Adams P. T. Successful treatment of autoimmune neutropenia with recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (R-metHuG-CSF). Clin Lab Haematol. 1997 Jun;19(2):105–109. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2257.1997.d01-275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers T. W., Van Lier R. A., Hamann D., de Boer M., Thung L. Y., Weening R. S., Verhoeven A. J., Roos D. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD-1)/variant. A novel immunodeficiency syndrome characterized by dysfunctional beta2 integrins. J Clin Invest. 1997 Oct 1;100(7):1725–1733. doi: 10.1172/JCI119697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers T. W., de Haas M., de Groot C. J., von dem Borne A. E., Weening R. S. The use of rhG-CSF in chronic autoimmune neutropenia: reversal of autoimmune phenomena, a case history. Br J Haematol. 1996 Sep;94(3):464–469. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.d01-1823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzberg J., Friedman H. S., Chaffee S., Falletta J. M., Kinney T. R., Kurlander R., Matthews T. J., Schwartz R. S. Efficacy of intravenous gamma globulin in autoimmune-mediated pediatric blood dyscrasias. Am J Med. 1987 Oct 23;83(4A):4–9. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90544-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R. D., Crowder C. G., Cruz P., Hawkinson S. W., Lozzio C. B., Machado E., Painter P., Terry W., Jones J. B. Cyclic neutropenia. A tale of two brothers and their family. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1981 Summer;3(2):127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R. D. Cyclic hematopoiesis: human cyclic neutropenia. Exp Hematol. 1983 Jul;11(6):435–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. C., Papa M. Z., Hoffman M. A., Loeff D. S., Pearl R. H., Filler R. M. Cyclic neutropenia with colonic perforation and nonhealing colocutaneous fistula. J Pediatr Surg. 1990 Mar;25(3):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(90)90084-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky R. J., Tiedeman K. Successful bone-marrow transplantation for reticular dysgenesis. Lancet. 1983 Mar 26;1(8326 Pt 1):671–672. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91968-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Espanol-Boren T., Thomas C., Fischer A., Tovo P., Bordigoni P., Resnick I., Fasth A., Baer M., Gomez L. Clinical spectrum of X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. J Pediatr. 1997 Jul;131(1 Pt 1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli F., Pedrazzoli P., Zecca M., Maccario R., Giorgiani G., Prete L., Nespoli L., Severi F. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (rHuGM-CSF) in cyclic neutropenia. Haematologica. 1991 May-Jun;76(3):238–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis D. M., Melnick D. A., Alling D. W., Gallin J. I. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis in the management of chronic granulomatous disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):723–726. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Morton C. C., Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. LFA-1 immunodeficiency disease. Definition of the genetic defect and chromosomal mapping of alpha and beta subunits of the lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) by complementation in hybrid cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):855–867. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt T., Brune T., Lühn K., Zimmer K. P., Körner C., Fabritz L., van der Werft N., Vormoor J., Freeze H. H., Louwen F. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency II syndrome, a generalized defect in fucose metabolism. J Pediatr. 1999 Jun;134(6):681–688. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(99)70281-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton J., Neil S., Wintle J., Clark-Lewis I., Moore H., Lam C., Auer M., Hub E., Rot A. Transcytosis and surface presentation of IL-8 by venular endothelial cells. Cell. 1997 Oct 31;91(3):385–395. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Borregaard N., Boxer L. A. Novel trends in neutrophil structure, function and development. Immunol Today. 1999 Dec;20(12):535–537. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01500-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley A. A., Carew J. P., Baikie A. G. Familial cyclical neutropenia. Br J Haematol. 1967 Sep;13(5):719–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouy R., Seger R., Bourquin J. P., Veber F., Blanche S., Griscelli C., Fischer A. Interferon gamma for chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 21;325(21):1516–1517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111213252115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouy R., Veber F., Blanche S., Donadieu J., Brauner R., Levron J. C., Griscelli C., Fischer A. Long-term itraconazole prophylaxis against Aspergillus infections in thirty-two patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1994 Dec;125(6 Pt 1):998–1003. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanrahan T., Dark P., Irving M. H. Cyclic neutropenia--unusual cause of acute abdomen. Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991 Dec;34(12):1125–1127. doi: 10.1007/BF02050076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozsahin H., von Planta M., Müller I., Steinert H. C., Nadal D., Lauener R., Tuchschmid P., Willi U. V., Ozsahin M., Crompton N. E. Successful treatment of invasive aspergillosis in chronic granulomatous disease by bone marrow transplantation, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized granulocytes, and liposomal amphotericin-B. Blood. 1998 Oct 15;92(8):2719–2724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Root R. K., Metcalf J. A., Delaney K. K., Kaplow L. S., Richar W. J. Myeloperoxidase deficiency: prevalence and clinical significance. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):293–301. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham A., O'Reilly M. A., Malcolm S., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C. RFLP and deletion analysis for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease using the cDNA probe: potential for improved prenatal diagnosis and carrier determination. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):820–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. D., Parkar M. H., Collins M. K., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C. Superoxide production by normal and chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patient-derived EBV-transformed B cell lines measured by chemiluminescence-based assays. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Nov 5;155(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90281-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price T. H., Ochs H. D., Gershoni-Baruch R., Harlan J. M., Etzioni A. In vivo neutrophil and lymphocyte function studies in a patient with leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1635–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck N., Finn A. Polymorphonuclear granulocyte expression of CD11a/CD18, CD11b/CD18 and L-selectin in normal individuals. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1994 Mar;8(3):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1994.tb00442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell R. L., Gray P. H., Taylor K. M., Minchinton R. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor treatment for alloimmune neonatal neutropenia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996 Jul;75(1):F57–F58. doi: 10.1136/fn.75.1.f57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler J., Hecht M., Freihorst J., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Emmendörffer A. Diagnosis of chronic granulomatous disease and of its mode of inheritance by dihydrorhodamine 123 and flow microcytofluorometry. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Jan;150(3):161–165. doi: 10.1007/BF01963557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen R. B., Kang S. J. Congenital agranulocytosis terminating in acute myelomonocytic leukemia. J Pediatr. 1979 Mar;94(3):406–408. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80581-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. R., Davies E. G., Ball S. E., Gordon-Smith E. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor treatment for neonatal neutropenia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1995 Jan;72(1):F53–F54. doi: 10.1136/fn.72.1.f53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M., Will A. M., Testa N., Hayworth C., Darbyshire P. J. Severe congenital neutropenia unresponsive to G-CSF. Br J Haematol. 1995 Sep;91(1):43–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb05242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders L. A., Feldman R. G., Voorhorst-Ogink M. M., de Haas M., Rijkers G. T., Capel P. J., Zegers B. J., van de Winkel J. G. Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fc receptor IIA (CD32) polymorphism and IgG2-mediated bacterial phagocytosis by neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1995 Jan;63(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.1.73-81.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders L. A., van de Winkel J. G., Rijkers G. T., Voorhorst-Ogink M. M., de Haas M., Capel P. J., Zegers B. J. Fc gamma receptor IIa (CD32) heterogeneity in patients with recurrent bacterial respiratory tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;170(4):854–861. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz S., Franke H., Wichmann H. E., Diehl V. The effect of continuous G-CSF application in human cyclic neutropenia: a model analysis. Br J Haematol. 1995 May;90(1):41–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb03378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroten H., Roesler J., Breidenbach T., Wendel U., Elsner J., Schweitzer S., Zeidler C., Burdach S., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Wahn V. Granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors for treatment of neutropenia in glycogen storage disease type Ib. J Pediatr. 1991 Nov;119(5):748–754. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri K. A., Logue G. L. Autoimmune neutropenia. Blood. 1993 Apr 15;81(8):1984–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Finn A. Antimicrobial prophylaxis. Arch Dis Child. 1999 Apr;80(4):388–392. doi: 10.1136/adc.80.4.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith O. P., Hann I. M., Chessells J. M., Reeves B. R., Milla P. Haematological abnormalities in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1996 Aug;94(2):279–284. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.d01-1788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield J. A., Sumiya M., Levin M., Turner M. W. Association of mutations in mannose binding protein gene with childhood infection in consecutive hospital series. BMJ. 1997 Apr 26;314(7089):1229–1232. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7089.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Super M., Thiel S., Lu J., Levinsky R. J., Turner M. W. Association of low levels of mannan-binding protein with a common defect of opsonisation. Lancet. 1989 Nov 25;2(8674):1236–1239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C., Le Deist F., Cavazzana-Calvo M., Benkerrou M., Haddad E., Blanche S., Hartmann W., Friedrich W., Fischer A. Results of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in patients with leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1629–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw I. P., Dong F. Severe congenital neutropenia terminating in acute myeloid leukemia: disease progression associated with mutations in the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor receptor gene. Leuk Res. 1996 Aug;20(8):629–631. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(96)00017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunogake S., Nagashima S., Maekawa R., Takano N., Kajitani H., Saito K., Enokihara H., Furusawa S., Shishido H. Myeloid progenitor cell growth characteristics and effect of G-CSF in a patient with congenital cyclic neutropenia. Int J Hematol. 1991 Jun;54(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. C., van Aesch Y. M., Gits J., Schelen A. M., de Koning J. P., van Leeuwen D., Freedman M. H., Touw I. P. Novel point mutation in the extracellular domain of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor in a case of severe congenital neutropenia hyporesponsive to G-CSF treatment. J Exp Med. 1999 Aug 16;190(4):497–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Adriaansz L. H., Weemaes C. M., Lutter R., Roos D. Clinical differences in chronic granulomatous disease in patients with cytochrome b-negative or cytochrome b-positive neutrophils. J Pediatr. 1985 Jul;107(1):102–104. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Leitz G. J., Seger R. A. Recombinant human interferon-gamma in patients with chronic granulomatous disease--European follow up study. Eur J Pediatr. 1995 Apr;154(4):295–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01957365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Dale D. Pathophysiology and treatment of severe chronic neutropenia. Ann Hematol. 1996 Apr;72(4):158–165. doi: 10.1007/s002770050156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston B., Todd R. F., 3rd, Axtell R., Balazovich K., Stewart J., Locey B. J., Mayo-Bond L., Loos P., Hutchinson R., Boxer L. A. Severe congenital neutropenia: clinical effects and neutrophil function during treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Apr;117(4):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Schie R. C., Wilson M. E. Saliva: a convenient source of DNA for analysis of bi-allelic polymorphisms of Fc gamma receptor IIA (CD32) and Fc gamma receptor IIIB (CD16). J Immunol Methods. 1997 Oct 13;208(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)00132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen J. P., Hack C. E., Engelfriet C. P., Pegels J. G., von dem Borne A. E. Chronic idiopathic and secondary neutropenia: clinical and serological investigations. Br J Haematol. 1986 May;63(1):161–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb07506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]