Abstract
Aims—To investigate the role of CD34 positive stromal cells, namely dendritic interstitial cells, in gastric carcinomas, the distribution of CD34 positive stromal cells in gastric adenocarcinomas (GCs), with special reference to two histological types (diffuse (D-type) and intestinal (I-type)), was examined.
Methods—In total, 55 surgically resected GCs (15 D-type and 40 I-type) and their normal tissues were examined. To distinguish CD34 positive stromal cells from vascular endothelial cells and to recognise the tumour border, immunostaining for CD34, CD31, and low molecular weight cytokeratins was performed.
Results—In the 15 D-type GCs, eight of the nine D-type GCs invading the muscularis propria and subserosa had a large number of CD34 positive stromal cells in the tumour stroma, whereas all six D-type GCs confined to the submucosa had no CD34 positive stromal cells in the tumour stroma. All of the 40 I-type GCs had no CD34 positive stromal cells, regardless of tumour depth.
Conclusions—These results suggest that CD34 expression in stromal cells is associated with progression of D-type GCs, and that absence of expression is also seen in I-type GCs that are progressing.
Key Words: CD34 • stromal cell • diffuse type • intestinal type • gastric adenocarcinoma
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (130.9 KB).
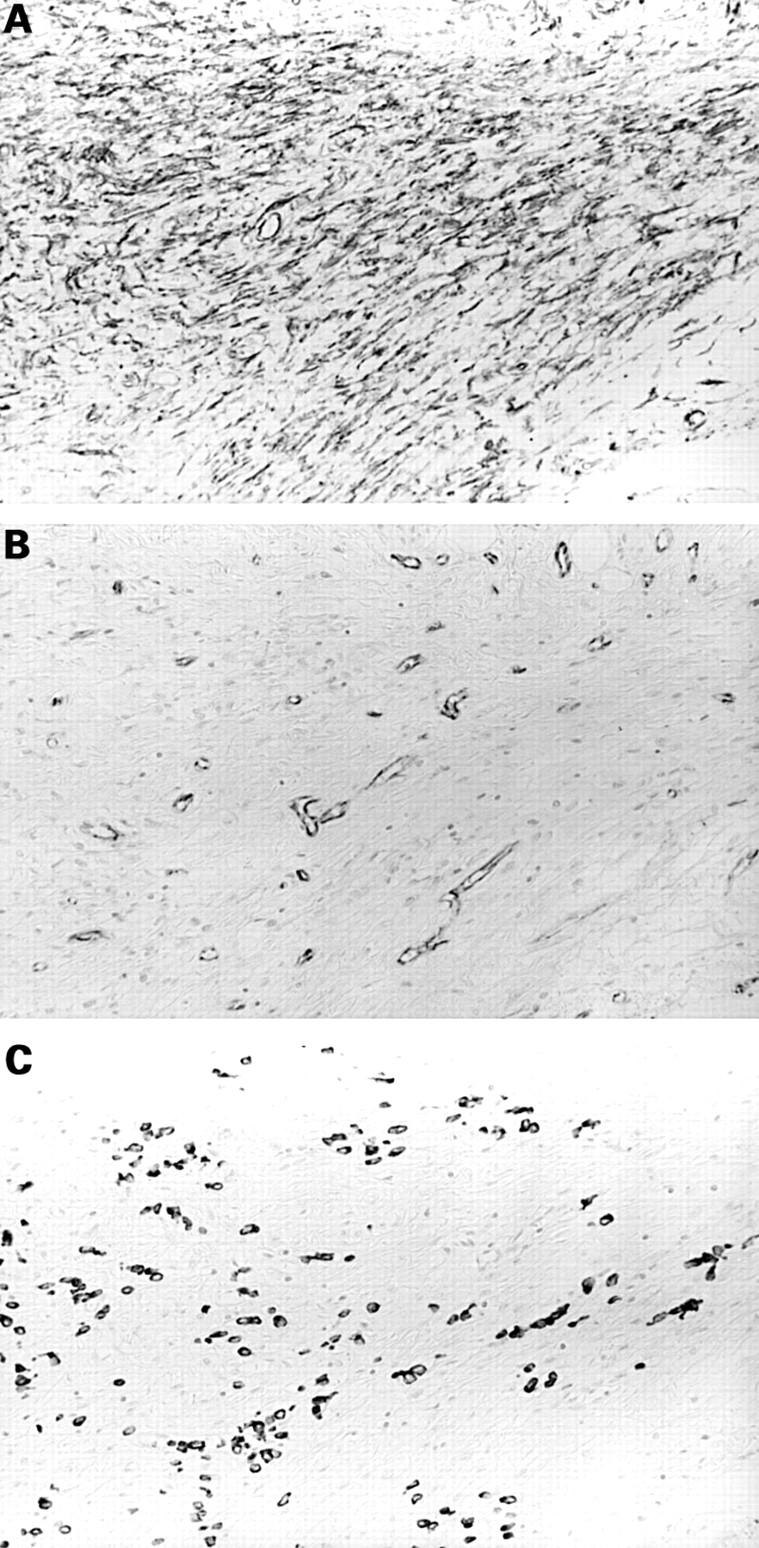
Figure 1 CD34 positive stromal cells in diffuse-type advanced gastric adenocarcinoma tissue. Staining for (A) CD34, (B) CD31, and (C) low molecular weight cytokeratins (LMW-CKs). Large numbers of CD34 positive stromal cells are detected in the tumour stroma. Immunoreactivity for CD31 is shown to distinguish CD34 positive stromal cells from vascular endothelial cells. Immunoreactivity for LMW-CKs is shown to recognise the diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinoma cells.
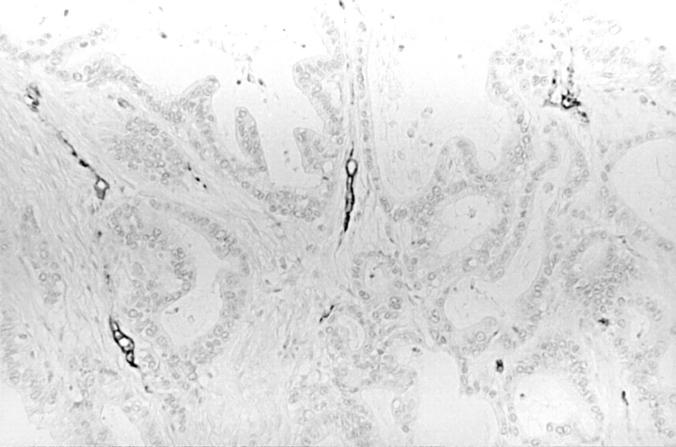
Figure 2 CD34 immunostaining in intestinal-type advanced gastric adenocarcinoma tissue. CD34 is positive in vascular endothelial cells; no CD34 positive stromal cells are seen.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Civin C. I., Strauss L. C., Brovall C., Fackler M. J., Schwartz J. F., Shaper J. H. Antigenic analysis of hematopoiesis. III. A hematopoietic progenitor cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody raised against KG-1a cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown J., Molgaard H. V., Spurr N. K., Robertson D., Delia D., Sutherland D. R. Molecular features of CD34: a hemopoietic progenitor cell-associated molecule. Leukemia. 1992;6 (Suppl 1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. K., Higgins J., Cho E. Y., Ko Y. H., Oh Y. L. Expression of CD34, bcl-2, and kit in inflammatory fibroid polyps of the gastrointestinal tract. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2000 Jun;8(2):147–153. doi: 10.1097/00129039-200006000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUREN P. THE TWO HISTOLOGICAL MAIN TYPES OF GASTRIC CARCINOMA: DIFFUSE AND SO-CALLED INTESTINAL-TYPE CARCINOMA. AN ATTEMPT AT A HISTO-CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer A. E., Miettinen M. Immunophenotypic features of uterine stromal cells. CD34 expression in endocervical stroma. Virchows Arch. 1995;426(5):457–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00193168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lindenmayer A. E., Chaubal A. Endothelial cell markers CD31, CD34, and BNH9 antibody to H- and Y-antigens--evaluation of their specificity and sensitivity in the diagnosis of vascular tumors and comparison with von Willebrand factor. Mod Pathol. 1994 Jan;7(1):82–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Enzan H., Miyazaki E., Kuroda N., Naruse K., Hiroi M. Differential expression of CD34 in normal colorectal tissue, peritumoral inflammatory tissue, and tumour stroma. J Clin Pathol. 2000 Aug;53(8):626–629. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.8.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Enzan H., Miyazaki E., Kuroda N., Naruse K., Kiyoku H., Hiroi M. Myofibroblasts at the tumor border of invasive gastric carcinomas: with special reference to histological type and tumor depth. Oncol Rep. 2000 Sep-Oct;7(5):1011–1015. doi: 10.3892/or.7.5.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narvaez D., Kanitakis J., Faure M., Claudy A. Immunohistochemical study of CD34-positive dendritic cells of human dermis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996 Jun;18(3):283–288. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199606000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J. The human progenitor cell antigen (CD34) is localized on endothelial cells, dermal dendritic cells, and perifollicular cells in formalin-fixed normal skin, and on proliferating endothelial cells and stromal spindle-shaped cells in Kaposi's sarcoma. Arch Dermatol. 1991 Apr;127(4):523–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Satterthwaite A. B., Tenen D. G., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding CD34, a sialomucin of human hematopoietic stem cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizer J. S., Frederick P. L., Osborne M. P. Primary linitis plastica of the colon: report of a case and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1967 Sep-Oct;10(5):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF02617014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinden J. M., Rumessen J. J., De Laet M. H., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Schiffmann S. N. CD34 immunoreactivity and interstitial cells of Cajal in the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 2000 Nov;302(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/s004410000264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinden J. M., Rumessen J. J., De Laet M. H., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Schiffmann S. N. CD34+ cells in human intestine are fibroblasts adjacent to, but distinct from, interstitial cells of Cajal. Lab Invest. 1999 Jan;79(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Eyden B. P. Interfollicular fibroblasts in the human thyroid gland: recognition of a CD34 positive stromal cell network communicated by gap junctions and terminated by autonomic nerve endings. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1997 Oct;29(4):461–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Eyden B. P. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical observations on intralobular fibroblasts of human breast, with observations on the CD34 antigen. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1995 Jul;27(3):309–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Eyden B. P. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies of intralobular fibroblasts in human submandibular gland: the recognition of a 'CD34 positive reticular network' connected by gap junctions. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1996 Oct;28(4):471–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]