Abstract
Aims—To investigate the prognostic value of recently proposed flow cytometric S-phase fraction (SPF) variables (average SPF and SPF tertiles) compared with conventional SPF, and to compare the one with the best predictive value with the immunohistochemical Ki-67 index in breast carcinoma.
Methods—A short term follow up study (median, 39.6 months) of a large series of patients (n = 306) was conducted. DNA ploidy was analysed on fresh/frozen tumour samples by flow cytometry, and the SPF was calculated from the DNA histogram using an algorithm. The Ki-67 index was assessed on paraffin wax embedded material by immunohistochemistry (cut off point, 10%). The two methods were compared by means of κ statistics, and the prognostic significance of both in relation to disease free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) was determined.
Results—SPF and Ki-67 analysis was performed on 234 (76.5%) and 295 (96.4%) tumours, respectively. The two assessments were simultaneously available in 230 cases. All SPF variables analysed in the whole series significantly correlated with disease evolution, with the conventional median SPF (cut off point, 6.1%) showing the highest predictive value in relation to both DFS (p = 0.0001) and OS (p = 0.0003). SPF tertiles and median SPF evaluated according to DNA ploidy status had no prognostic significance. The Ki-67 index showed a trend in relation to DFS (p = 0.086) that did not reach significance, and no correlation with OS was found (p = 0.264). The comparative analysis of SPF and Ki-67 revealed some agreement between the two methods (agreement, 69.13%; κ statistic, 0.3844; p < 0.001), especially in the subgroup of diploid tumours.
Conclusions—Flow cytometric SPF is a better prognosticator than the Ki-67 index, but only SPF variables applied in the whole series show potential clinical usefulness.
Key Words: breast carcinoma • DNA flow cytometry • immunohistochemistry • S-phase fraction • Ki-67 • prognosis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (186.0 KB).
Figure 1 Flow cytometric DNA histogram showing a multiploid tumour with overlapping cell populations. Only "average S-phase fraction (SPF)" was determined (15.7%), and the tumour was classified as highly proliferative by flow cytometry and histochemistry methods.
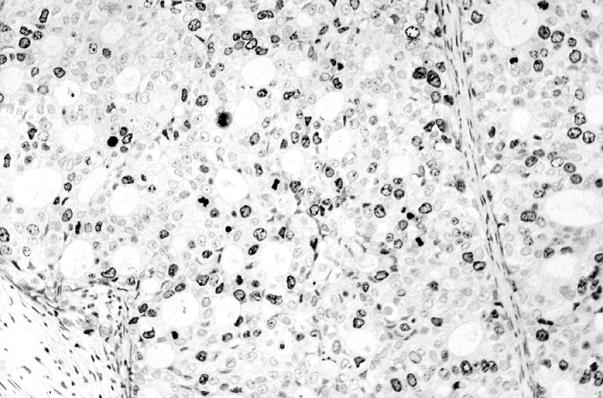
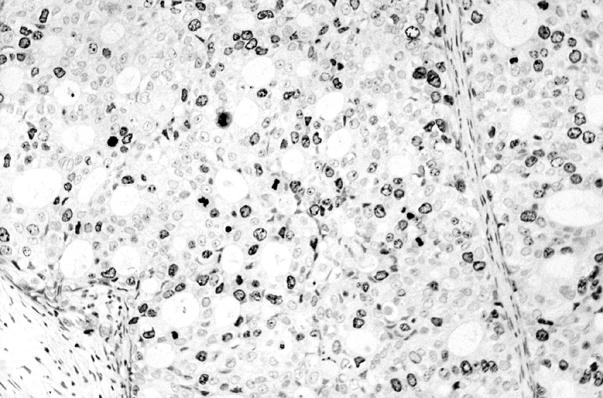
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining (anti-Ki-67 antibody) of the same ductal invasive carcinoma shown in fig 1.
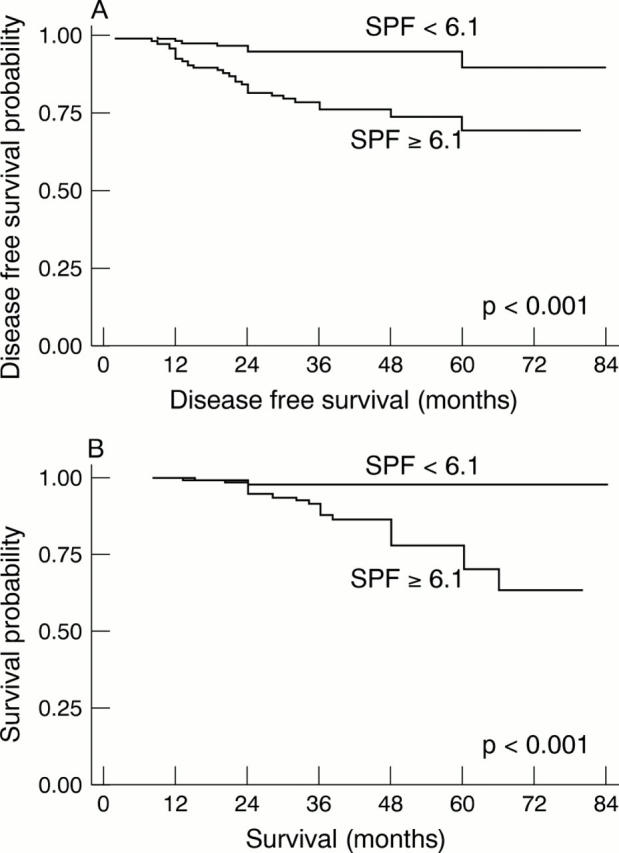
Figure 3 (A) Probability of disease free survival and (B) overall survival according to S-phase fraction (SPF) (cut off point, 6.1%) in breast carcinoma (n = 234). Low SPF groups have a more favourable outcome (p < 0.001).
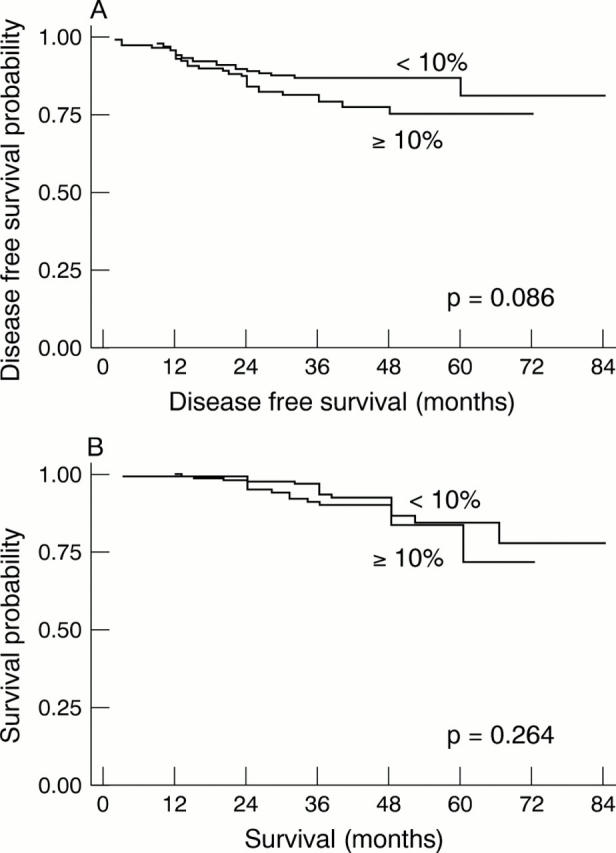
Figure 4 (A) Probability of disease free survival (DFS) and (B) overall survival (OS) according to Ki-67 index (cut off point, 10%) in breast carcinoma (n = 294). Weak differences between survival curves in relation to DFS (not significant; p = 0.086) were verified. No differences in relation to OS were found (p = 0.264).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldetorp B., Bendahl P. O., Fernö M., Alanen K., Delle U., Falkmer U., Hansson-Aggesjö B., Höckenström T., Lindgren A., Mossberg L. Reproducibility in DNA flow cytometric analysis of breast cancer: comparison of 12 laboratories' results for 67 sample homogenates. Cytometry. 1995 Jun 15;22(2):115–127. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990220207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers E., Baak J. P., van Diest P. J., van Gorp L. H., Kwee W. S., Los J., Peterse H. L., Ruitenberg H. M., Schapers R. F., Somsen J. G. Prognostic implications of different cell cycle analysis models of flow cytometric DNA histograms of 1,301 breast cancer patients: results from the Multicenter Morphometric Mammary Carcinoma Project (MMMCP). Int J Cancer. 1997 Jun 20;74(3):260–269. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970620)74:3<260::aid-ijc5>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers E., Montironi R., van Diest P. J., Prete E., Baak J. P. Interlaboratory reproducibility of semiautomated cell cycle analysis of flow cytometry DNA-histograms obtained from fresh material of 1,295 breast cancer cases. Hum Pathol. 1996 Jun;27(6):553–560. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers E., van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. Tumour heterogeneity of DNA cell cycle variables in breast cancer measured by flow cytometry. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Nov;49(11):931–937. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.11.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzetti C., Nizzoli R., Camisa R., Guazzi A., Ceci G., Cocconi G., Mazzini G., Naldi N. Comparison between Ki-67 index and S-phase fraction on fine-needle aspiration samples from breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1997 Oct 25;81(5):287–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. C., Gatter K. C. Monoclonal antibody Ki-67: its use in histopathology. Histopathology. 1990 Dec;17(6):489–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. W., Allred C. D., Clark G. M., Osborne C. K., Hilsenbeck S. G. Prognostic value of Ki-67 compared to S-phase fraction in axillary node-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1996 Mar;2(3):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. N., Jett J. H. Mathematical analysis of DNA distributions derived from flow microfluorometry. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):523–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettmar P., Harbeck N., Thomssen C., Pache L., Ziffer P., Fizi K., Jänicke F., Nathrath W., Schmitt M., Graeff H. Prognostic impact of proliferation-associated factors MIB1 (Ki-67) and S-phase in node-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(10):1525–1533. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duque R. E., Andreeff M., Braylan R. C., Diamond L. W., Peiper S. C. Consensus review of the clinical utility of DNA flow cytometry in neoplastic hematopathology. Cytometry. 1993;14(5):492–496. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990140507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Boracchi P., Verderio P., Bevilacqua P. Cell kinetics in human breast cancer: comparison between the prognostic value of the cytofluorimetric S-phase fraction and that of the antibodies to Ki-67 and PCNA antigens detected by immunocytochemistry. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 15;57(6):822–829. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Coates P. J. Assessment of cell proliferation in pathology--what next? Histopathology. 1995 Feb;26(2):105–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1995.tb00639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Clark G. M., Cornelisse C. J., Killander D., Kute T., Merkel D. Consensus review of the clinical utility of DNA cytometry in carcinoma of the breast. Report of the DNA Cytometry Consensus Conference. Cytometry. 1993;14(5):482–485. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990140505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. The use of antiavidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex in immunoperoxidase technics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jun;75(6):816–821. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. L., Hupperets P. S., Arends J. W., Joosten-Achjanie S. R., Volovics A., Schouten H. C., Hillen H. F. MIB-1 labelling index is an independent prognostic marker in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1998 Aug;78(4):460–465. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshgegian A. A., Cnaan A. Proliferation markers in breast carcinoma. Mitotic figure count, S-phase fraction, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki-67 and MIB-1. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jul;104(1):42–49. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/104.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis J. R., Koch G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977 Mar;33(1):159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood C. A., Ricciardelli C., Raymond W. A., Seshadri R., McCaul K., Horsfall D. J. A simple index using video image analysis to predict disease outcome in primary breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1999 Jun 21;84(3):203–208. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990621)84:3<203::aid-ijc1>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGrogan G., Jollet I., Huet S., Sierankowski G., Picot V., Bonichon F., Coindre J. M. Comparison of quantitative and semiquantitative methods of assessing MIB-1 with the S-phase fraction in breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 1997 Aug;10(8):769–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966 Mar;50(3):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molino A., Micciolo R., Turazza M., Bonetti F., Piubello Q., Bonetti A., Nortilli R., Pelosi G., Cetto G. L. Ki-67 immunostaining in 322 primary breast cancers: associations with clinical and pathological variables and prognosis. Int J Cancer. 1997 Aug 22;74(4):433–437. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970822)74:4<433::aid-ijc12>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton A. J., Jordan S., Yeomans P. Brief, high-temperature heat denaturation (pressure cooking): a simple and effective method of antigen retrieval for routinely processed tissues. J Pathol. 1994 Aug;173(4):371–379. doi: 10.1002/path.1711730413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A. E., André S., Soares J. Short-term significance of DNA ploidy and cell proliferation in breast carcinoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic markers in a series of 308 patients. J Clin Pathol. 1999 Aug;52(8):604–611. doi: 10.1136/jcp.52.8.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querzoli P., Albonico G., Ferretti S., Rinaldi R., Magri E., Indelli M., Nenci I. MIB-1 proliferative activity in invasive breast cancer measured by image analysis. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Nov;49(11):926–930. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.11.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Railo M., Lundin J., Haglund C., von Smitten K., von Boguslawsky K., Nordling S. Ki-67, p53, Er-receptors, ploidy and S-phase as prognostic factors in T1 node negative breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 1997;36(4):369–374. doi: 10.3109/02841869709001282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin A. A., Ro J., Ro J. Y., Blick M. B., el-Naggar A. K., Ordonez N. G., Fritsche H. A., Smith T. L., Hortobagyi G. N., Ayala A. G. Ki-67 immunostaining in node-negative stage I/II breast carcinoma. Significant correlation with prognosis. Cancer. 1991 Aug 1;68(3):549–557. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910801)68:3<549::aid-cncr2820680318>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankey T. V., Rabinovitch P. S., Bagwell B., Bauer K. D., Duque R. E., Hedley D. W., Mayall B. H., Wheeless L., Cox C. Guidelines for implementation of clinical DNA cytometry. International Society for Analytical Cytology. Cytometry. 1993;14(5):472–477. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson H., Baldetorp B., Borg A., Dalberg M., Fernö M., Killander D., Olsson H., Ranstam J. Flow cytometry in primary breast cancer: improving the prognostic value of the fraction of cells in the S-phase by optimal categorisation of cut-off levels. Br J Cancer. 1990 Nov;62(5):786–790. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H. J., van Driel R., Beck J. L., van Dierendonck J. H., Brakenhoff G. J., Ramaekers F. C. Ki-67 detects a nuclear matrix-associated proliferation-related antigen. II. Localization in mitotic cells and association with chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92(Pt 4):531–540. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese S. M., Gambacorta M., Gottardi O., Scanzi F., Ferrari M., Lampertico P. Proliferation index as a prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer. 1993 Jun 15;71(12):3926–3931. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930615)71:12<3926::aid-cncr2820711221>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vielh P., Chevillard S., Mosseri V., Donatini B., Magdelenat H. Ki67 index and S-phase fraction in human breast carcinomas. Comparison and correlations with prognostic factors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Dec;94(6):681–686. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/94.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintzer H. O., Zipfel I., Schulte-Mönting J., Hellerich U., von Kleist S. Ki-67 immunostaining in human breast tumors and its relationship to prognosis. Cancer. 1991 Jan 15;67(2):421–428. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910115)67:2<421::aid-cncr2820670217>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dierendonck J. H., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J. Nuclear distribution of the Ki-67 antigen during the cell cycle: comparison with growth fraction in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2999–3006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diest P. J., Baak J. P., Matze-Cok P., Wisse-Brekelmans E. C., van Galen C. M., Kurver P. H., Bellot S. M., Fijnheer J., van Gorp L. H., Kwee W. S. Reproducibility of mitosis counting in 2,469 breast cancer specimens: results from the Multicenter Morphometric Mammary Carcinoma Project. Hum Pathol. 1992 Jun;23(6):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90313-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diest P. J., Brugal G., Baak J. P. Proliferation markers in tumours: interpretation and clinical value. J Clin Pathol. 1998 Oct;51(10):716–724. doi: 10.1136/jcp.51.10.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]