Abstract
Seizure activity regulates gene expression for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and neurturin (NRTN), and their receptor components, the transmembrane c-Ret tyrosine kinase and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored GDNF family receptor (GFR) α1 and α2 in limbic structures. We demonstrate here that epileptogenesis, as assessed in the hippocampal kindling model, is markedly suppressed in mice lacking GFRα2. Moreover, at 6 to 8 wk after having reached the epileptic state, the hyperexcitability is lower in GFRα2 knock-out mice as compared with wild-type mice. These results provide evidence that signaling through GFRα2 is involved in mechanisms regulating the development and persistence of kindling epilepsy. Our data suggest that GDNF and NRTN may modulate seizure susceptibility by altering the function of hilar neuropeptide Y-containing interneurons and entorhinal cortical afferents at dentate granule cell synapses.
Complex partial seizures constitute the most common type of epilepsy in adult humans, but the mechanisms underlying the development and persistence of this syndrome are poorly understood (1). Kindling is a model of complex partial seizures in which repeated electrical stimulation in limbic structures triggers progressive intensification of epileptiform responses (2). When the animal has exhibited several generalized convulsions, it is said to be kindled and will retain abnormal excitability thereafter (3). Kindling-evoked seizures induce transient changes in levels of the neurotrophins, nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and neurotrophin-3 in hippocampal and cortical neurons (4–7). Reduction of neurotrophin levels in knock-out mice or blockade of neurotrophin signaling in rats retards the development of kindling (8–10). These data suggest that neurotrophins might be involved in the regulation of plastic changes underlying kindling epileptogenesis (11).
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) (12) and neurturin (NRTN) (13) have trophic effects on several neuron types (14–16). The receptor complex for these GDNF family ligands consists of two components: the transmembrane Ret tyrosine kinase and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored ligand-binding part called GDNF family receptor (GFR) α1-α4 (reviewed in refs. 17 and 18). Both GFRα1 and α2 can mediate GDNF and NRTN binding to c-Ret in vitro. GDNF interacts more efficiently with GFRα1 (19) and binds GFRα2 only if this coreceptor has formed a complex with c-Ret (20). In contrast, NRTN preferentially acts through GFRα2 (reviewed in refs. 17 and 18). The genes for GDNF, NRTN, c-Ret, GFRα1, and GFRα2 are expressed in the adult rodent forebrain (21, 22) and show differential changes in limbic structures after kindling-evoked seizures (21). This observation suggests that GDNF and NRTN signaling could be involved in the pathophysiology of kindling. We studied the development and persistence of the abnormal excitability in hippocampal kindling in wild-type and GFRα2 knock-out mice. Our data indicate that GFRα2-mediated signaling not only promotes epileptogenesis but also is important for the long-term stability of this epileptic-like syndrome.
Materials and Methods
Animals and Experimental Groups.
Studies were performed ac-cording to National Institutes of Health guidelines and approved by the local Ethical Committee. The GFRα2-deficient mice have been described previously (23). For kindling and immunocytochemistry, male adult GFRα2 −/− (n = 13) and littermate +/+ mice (n = 14) weighing 19–25 g were used. Immunocytochemistry with GFRα2 antibody and in situ hybridization were performed on sections from naive C57BL/6 mice (n = 3 for each procedure). For electrophysiology, hippocampal slices from two groups of 4- to 5-wk-old GFRα2 −/− and littermate +/+ mice were used. In the first group (n = 4 +/+ and 5 −/− mice), we studied basal properties and plasticity in Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses, and inhibitory synaptic transmission on subicular pyramidal neurons. In the second group (n = 4 +/+ and 5 −/− mice), we analyzed basal properties and plasticity in lateral perforant path (LPP)- and medial perforant path (MPP)-dentate granule cell synapses.
Kindling Procedure.
Twelve wild-type and eleven knock-out mice were anesthetized with Equithesin (3 ml/kg, i.p.), and bipolar stainless steel electrodes were implanted bilaterally in the ventral hippocampus (coordinates: tooth bar at 0; 2.9 mm caudal to bregma; 3.0 mm lateral to midline; and 3.0 mm ventral to dura) (24). Kindling stimulations (1-ms pulses, 100 Hz frequency, 1 s duration once daily in the left hippocampus) were started 10 days after electrode implantation in ten GFRα2 +/+ and nine −/− mice, and continued until the animals had experienced five grade 5 seizures. On the first day of stimulation, the threshold for eliciting focal epileptiform activity (after discharge, AD) was determined, and this current intensity was used thereafter. The electroencephalogram was recorded from both electrodes, and behavioral convulsions were scored blindly (25): grade 1, facial twitches; grade 2, chewing and nodding; grade 3, forelimb clonus; grade 4, rearing, body jerks, tail upholding; and grade 5, imbalance, hind limb clonus, vocalization. Six to eight weeks after exhibiting five grade 5 seizures, mice were test-stimulated once daily for 5 consecutive days by using the same parameters as during the kindling process. Four nonoperated and 4 electrode-implanted but nonstimulated mice (two GFRα2 +/+ and two −/− mice in each group) were used as controls for immunocytochemistry. Twenty-four hours after the last stimulus, kindled and control mice were anesthetized and perfused transcardially with paraformaldehyde.
Immunocytochemistry.
The following antibodies were used on free floating sections (26): NeuN (1:100; Chemicon), parvalbumin (1:1,000; Sigma), neuropeptide Y (NPY) (1:1,000; Incstar, Stillwater, MN; and 1:5,000; Sigma), somatostatin (1:1000; Incstar), and calretinin (1:2000; Chemicon). Briefly, coronal sections (40 μm) were rinsed in potassium PBS and treated with H2O2 and methanol, and, after preincubation with 5% serum in 0.25% Triton X-100, sections were incubated with the primary antibody. Sections were rinsed and incubated with the appropriate biotinylated secondary antibody (1:200; Vector Laboratories; horse-anti mouse for NeuN; goat anti-rabbit for parvalbumin, NPY, and somatostatin; and horse anti-goat for calretinin), rinsed, incubated in avidin-biotin complex (Elite ABC kit, Vector Laboratories), and developed with diaminobenzidine.
Immunocytochemistry by using goat anti-GFRα2 antibody (1:200; R&D Systems) was performed on glass slide-mounted 15-μm sagittal sections from 4% paraformaldehyde-perfused brains. After incubation with primary antibody, sections were treated with Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-goat secondary antibody (1:200; Jackson ImmunoResearch) in the dark. Sections were analyzed by conventional epifluorescence microscopy.
Fluoro-Jade Staining.
For visualization of degenerating neurons, Fluoro-Jade staining (27) was performed on mounted sections of all perfused kindled GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice (see ref. 28).
In Situ Hybridization.
Fifteen-micrometer-thick sagittal sections from fresh frozen brains were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and in situ hybridization by using 35S-labeled RNA probes for c-Ret, GFRα1, and GFRα2 was performed (21, 23).
Morphometric Analysis.
Neuronal numbers were quantified by using stereological procedures (see ref. 28) at three levels: 1.3, 1.8, and 2.3 mm caudal to bregma (24). The image of the section was first displayed on the computer screen by using a charge-coupled device (CCD)-IRIS color video camera attached to a microscope controlled by CAST-GRID software (Olympus, Denmark). The border of the hippocampus was marked at low magnification (×4 objective), and sampling and cell counting were performed with ×40 objective.
Relative levels of NPY immunoreactivity were measured as optical densities by computerized image analysis (IMAGE 1.57 software; W. Rasband, National Institutes of Health). For each animal, measurements were performed bilaterally in areas of the same size (0.21 mm2), and background density (in the corpus callosum) was subtracted. The mean of the three measurements per animal represented one value in the statistical analysis.
Electrophysiology.
Sectioning and electrophysiological procedures for field recordings in hippocampal slices were performed as described previously (29, 30). Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from subicular pyramidal cells visualized by video microscopy (31). Paired-pulse stimulations were delivered with interpulse intervals of 100 ms and inhibitory postsynaptic currents were recorded at holding potential of −70 mV with patch-clamp pipettes filled with solution of (in mM): 135 CsCl, 10 CsOH Hepes, 8 NaCl, 0.2 CsOH EGTA, 2 MgATP, 0.3 Na3GTP, 5 QX-314 Br, and 0.1% Lucifer Yellow (pH 7.2, osmolarity 295 mOsm). Currents were amplified and filtered at 1 and 2.9 kHz, and were sampled at 10 kHz with an EPC-9 patch-clamp amplifier (HEKA Electronics, Lambrecht/Pfalz, Germany). Excitatory synaptic transmission was blocked by NBQX (5 μM) and AP-5 (50 μM). For morphological identification of recorded subicular pyramidal neurons, slices were fixed and examined in a UV microscope.
Statistical Analysis.
Two GFRα2 −/− mice had not reached the kindled state after 60 stimulations and were not included in the statistical analysis. Differences in kindling and electrophysiological characteristics were assessed by using Student's unpaired t test, repeated-measures ANOVA, or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni/Dunn post hoc test. The number of animals in the GFRα2 +/+ and −/− groups experiencing grade 5 seizures during test stimulations was compared by χ2 test. No differences in number of cells stained with different immunocytochemical markers were observed between intact and electrode-implanted, nonstimulated GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice. Data from both types of control animals were therefore pooled for statistical comparisons by using Student's unpaired t test. Significance was at P < 0.05.
Results
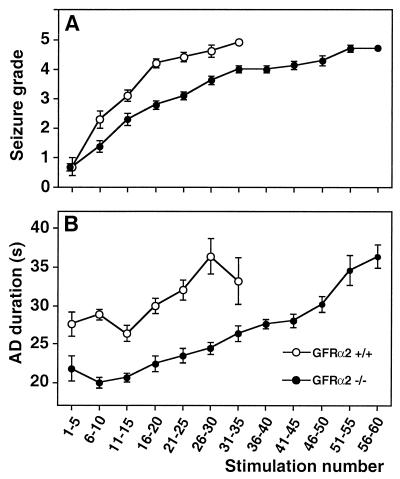
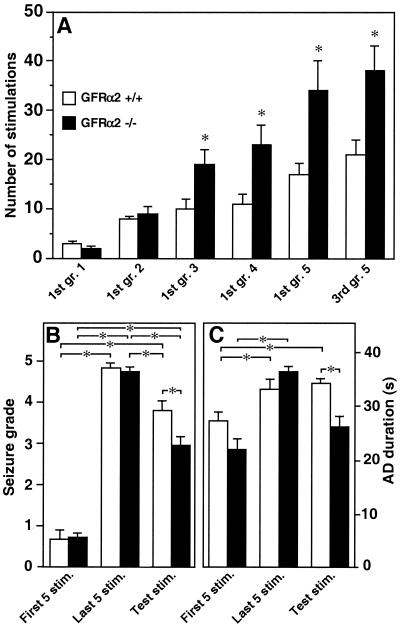
The first five stimulations did not reveal any significant differences between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice in either seizure grade (Fig. 1A and 2B) or AD duration (Fig. 1B and 2C). Also, the number of stimulations to reach grade 1 and 2 was similar for both groups (Fig. 2A). The GFRα2 −/− mice showed marked suppression of the development of generalized seizures and shorter ADs (Fig. 1) and required significantly more stimulations to exhibit the first grade 3, 4, and 5 seizures and to establish the fully kindled state (third grade 5 seizure) (Fig. 2A). The duration of ADs at different seizure grades, as well as secondary ADs (Table 1), was shorter in GFRα2 −/− mice. In contrast, the gradual increase of AD duration with progression of seizure grade occurred similarly in both groups. Other seizure characteristics (Table 1) and seizure grades and AD durations evoked by the last 5 stimulations (Fig. 2 B and C) did not differ between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice.
Figure 1.
Seizure grade and AD duration in hippocampal kindling differ between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice. Knock-out mice displayed marked retardation of kindling development as expressed by lower mean seizure grade (A) and shorter AD duration (B) (P < 0.05, repeated measures ANOVA; n = 10 for GFRα2 +/+ and n = 7 for −/− mice). Each value represents the mean of five consecutive stimulations ±SEM.
Figure 2.
GFRα2 −/− mice require more stimulations to reach higher seizure grades, and the persistence of hyperexcitability is less pronounced. (A) The number of stimulations to reach different seizure grades. (B and C) Mean seizure grade and AD duration, respectively, in response to the first and last five stimulations during kindling, and after the five test stimulations. The number of stimulations to exhibit forelimb clonus (grade 3), generalized seizures (grades 4 and 5), and the fully kindled state (third grade 5) was significantly increased in GFRα2 −/− mice (A). The mean seizure grade (B) and AD duration (C) induced by test stimulations were significantly lower and shorter, respectively, in GFRα2 −/− mice. Mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05, Student's unpaired t test (A) and one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni/Dunn post hoc test (B and C) (n = 10 for GFRα2 +/+ and n = 7 for −/− mice).
Table 1.
Seizure characteristics during development of hippocampal kindling in GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice
| Animals | Seizure threshold, μA | AD duration (s) at different
seizure grades
|
Behavioral convulsions,
s
|
Secondary AD duration, s
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Latency | Duration | Kindling stim. | Test stim. | ||
| GFRα2 +/+ (n = 10) | 30 ± 2 | 25 ± 2 | 26 ± 1 | 33 ± 4 | 34 ± 3 | 36 ± 3 | 16 ± 1 | 17 ± 1 | 48 ± 6 | 77 ± 20 |
| GFRα2 −/− (n = 7) | 27 ± 2 | 22 ± 2 | 22 ± 1 | 23 ± 1 | 28 ± 2 | 34 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | 14 ± 1 | 24 ± 8* | 41 ± 14 |
Values are means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05, Student's unpaired t test. The AD duration at different seizure grades is significantly shorter in GFRα2 −/− as compared with +/+ mice (P < 0.05, repeated measures ANOVA). n, number of animals.
Hyperexcitability was maintained in both groups at 6–8 weeks after five grade 5 seizures (Fig. 2B). However, the test stimuli gave rise to significantly lower mean seizure grade (Fig. 2B) and shorter ADs (Fig. 2C) in GFRα2 −/− mice. Significantly fewer (2 of 7) GFRα2 −/− than +/+ mice (9 of 10) experienced grade 5 seizures, and the mean number of grade 5 seizures was lower in GFRα2−/− as compared with +/+ mice (0.3 ± 0.2 and 2.8 ± 0.6, respectively).
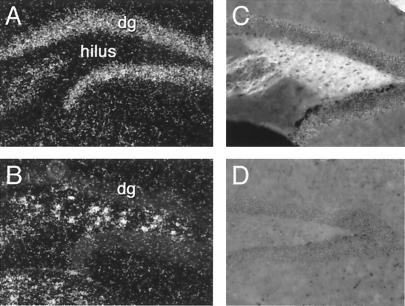
To explore mechanisms underlying the observed kindling deficit, we first analyzed expression of GFRα2 and c-Ret in wild-type mice. GFRα2 mRNA was detected in dentate granule cell layer (Fig. 3A), CA1 and CA3 pyramidal layers, stratum oriens of CA1, and subicular neurons (23). High c-Ret mRNA expression was observed in hilar interneurons and CA4 pyramidal layer (Fig. 3B), scattered neurons in the stratum radiatum and oriens of CA1, and subicular neurons. GFRα2 immunoreactivity was detected only in the dentate hilus, in a pattern resembling the distribution of mossy fibers (Fig. 3C). No GFRα2 immunoreactivity was observed in GFRα2 −/− mice (Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
Expression of c-Ret and GFRα2 mRNAs and of GFRα2 immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus. Dark-field photomicrographs showing expression of GFRα2 (A) and c-Ret (B) mRNAs in naive C57BL/6 mice. Note the high expression of GFRα2 mRNA in granule cells (A) and of c-Ret in hilar interneurons (B). Also note that hilar interneurons do not express GFRα2 mRNA (A). C and D show the high level (C) and absence (D) of GFRα2 immunoreactivity in the hilus of wild-type (C) and knock-out (D) mice.
We then studied whether lack of GFRα2 caused loss of hippocampal neurons. No Fluoro-Jade-positive-degenerating neurons were detected in kindled, wild-type, or knock-out mice. There were no differences between nonstimulated GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice in the number of parvalbumin-, somatostatin-, calretinin-, and NPY-immunoreactive hippocampal interneurons. Moreover, the animals did not differ in the layering, thickness, and cell density of the dentate gyrus and CA1 and CA3 regions.
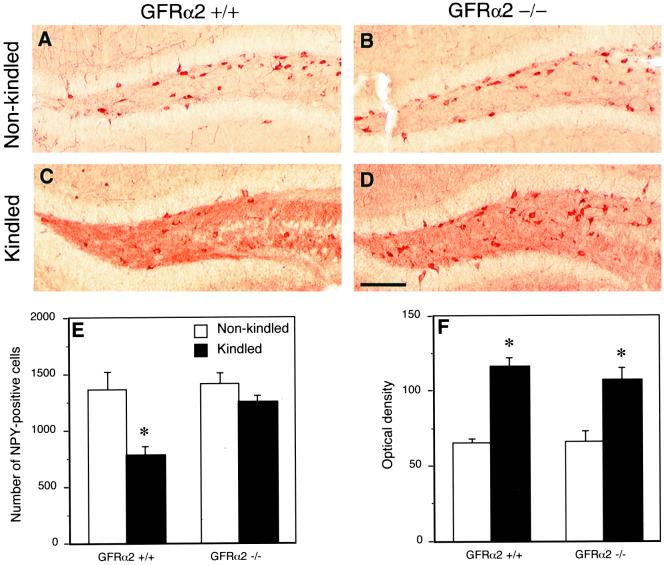
The number of NPY-positive hilar interneurons in GFRα2 +/+ mice was lower at 24 h after the last test stimulation as compared with nonstimulated animals (Fig. 4 A, C, and E). This decrease was not observed in GFRα2 −/− mice. Seizures did not change the numbers of NPY-positive neurons in stratum radiatum and oriens of CA1 and CA3 and lead to similar increase of NPY-immunoreactivity in mossy fibers in both strains (Fig. 4 C, D, and F).
Figure 4.
Down-regulation of NPY immunoreactivity in hilar interneurons after test stimulations in kindled animals is not observed in GFRα2 −/− mice. Color photomicrographs showing NPY immunoreactivity in the dentate hilus of non-kindled (A and B) and kindled animals (C and D). (E) The number of NPY-positive neurons; (F) the optical density of NPY immunoreactivity in the hilus of nonstimulated or kindled GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice. Note the decrease of NPY-positive neurons in the hilus of kindled, wild-type animals (C), with no alterations in the knock-out mice (D), as compared with corresponding controls (A and B, respectively). Mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05, Student's unpaired t test (n = 10 for GFRα2 +/+ and n = 7 for −/− mice). Bar = 160 μm.
At 24 h after the last test stimulation, the number of somatostatin-immunoreactive hilar interneurons was similarly increased, compared with nonstimulated controls in wild-type and knock-out mice. Also, these animals did not differ in the number of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the CA1 or dentate gyrus, NeuN-immunoreactive interneurons in the dentate gyrus, or calretinin-immunoreactive interneurons in the CA1 or mossy cells in the dentate hilus. Significantly fewer calretinin-positive cells were observed in the dentate subgranular layer in test-stimulated GFRα2 −/− as compared with +/+ mice (1306 ± 155 and 2045 ± 264, respectively). These cells are probably newly generated granule cells (32). Whether their lower number after seizures reflects reduced rate of neurogenesis or impaired regulation of calretinin levels is not known.
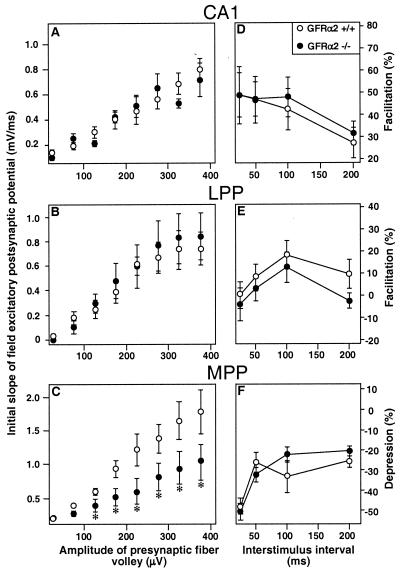
To explore whether lack of GFRα2 may influence synaptic transmission, we assessed basal synaptic properties in CA1 and dentate granule cell layer (Fig. 5 A–C). The field excitatory postsynaptic potential slope for a given size of presynaptic fiber volley was significantly decreased at MPP-granule cell synapses in GFRα2 −/− as compared with +/+ mice (Fig. 5C). This decrease indicates that basal excitatory transmission at these synapses is impaired in GFRα2 −/− mice. However, this impairment is not a general phenomenon because there were no differences between GFRα2 −/−and +/+ mice in the relation between presynaptic fiber volley and field excitatory postsynaptic potential slope at Schaffer collateral-CA1 and LPP-granule cell synapses (Fig. 5 A and B).
Figure 5.
Basal properties of MPP-dentate granule cell synapses are altered in GFRα2 −/− mice. The initial slope of the field excitatory postsynaptic potential plotted against the presynaptic fiber volley for Schaffer collateral-CA1 (A) and LPP- and MPP-dentate granule cell synapses (B and C, respectively). Note the significantly lower efficacy of excitatory transmission in MPP-granule cell synapses in GFRα2 −/− mice. No differences are observed between wild-type and knock-out animals for Schaffer collateral-CA1 and LPP-granule cell synapses. Paired-pulse facilitation in Schaffer collateral-CA1 (D) and LPP-granule cell synapses (E), and PPD in MPP-dentate granule cell synapses (F), respectively, are not altered in GFRα2 −/− mice. *, P < 0.05, Student's unpaired t test. Data are obtained from four to six slices of GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice, respectively.
We also investigated synaptic plasticity in CA1 and dentate gyrus. No significant differences in paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) at Schaffer collateral-CA1 and LPP-granule cell synapses or in paired-pulse depression (PPD) at MPP-granule cell synapses were detected between wild-type and knock-out mice (Fig. 5 D, E, and F). Also, tetanus-induced long-term potentiation (LTP) at Schaffer collateral-CA1 or at MPP- or LPP-granule cell synapses was not altered in GFRα2 −/− mice.
Finally, whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from subicular pyramidal neurons showed that PPD of inhibitory postsynaptic currents, which is considered a measure of presynaptic function (33), as well as inhibitory postsynaptic currents evoked by high frequency stimulation, did not differ between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice.
Discussion
The present study shows that lack of GFRα2 in mice leads to suppressed seizure development and reduced maintenance of hyperexcitability in hippocampal kindling. This deficit is associated with impairment of basal excitatory synaptic transmission at MPP-granule cell synapses and lack of seizure-induced down-regulation of NPY immunoreactivity in hilar interneurons. Whether these alterations in GFRα2 −/− mice are due to acute deficits in GDNF and NRTN signaling in the adult brain or caused by lack of the coreceptor during development is not known. Several lines of evidence argue against the possibility that the effects on kindling are due to developmentally related structural abnormalities. First, no changes in the number of interneurons or other morphological alterations were detected in the hippocampal formation. Second, GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice did not differ in the expression of different seizure grades. Third, gene expression for GDNF family ligands and receptors is regulated by seizure activity in the adult brain (21). Fourth, although there was no change in the basal expression of NPY, GFRα2 −/− mice exhibited a specific absence of the seizure-induced decrease of NPY levels in hilar interneurons.
Neurotrophins may promote epileptogenesis by influencing synaptic plasticity and potentiating excitatory and suppressing inhibitory transmission in cortical and hippocampal neurons (34). Whether GDNF family ligands also operate via these mechanisms is not known. Arguing for an effect of GFRα2-mediated signaling on specific synapses, basal properties of MPP-granule cell synapses were impaired in GFRα2 −/− mice. There was no deficit in PPD at these synapses. Because PPD is most likely due to a presynaptic alteration, our result suggests that the impairment is mainly due to postsynaptic changes. Could this impairment contribute to the retardation of kindling? Kindling stimulations activate the hippocampal-parahippocampal loop. The dentate gyrus is considered to serve as a gate for the passage of electrical activity through this loop and generates paroxysmal activity in response to kindling stimulations. This so-called maximal dentate activation increases AD duration and promotes propagation of seizure activity to other limbic and extralimbic areas (35). Alterations at MPP-granule cell synapses could interfere with the mechanisms of maximal dentate activation, leading to delayed kindling epileptogenesis. Because secondary ADs are manifestations of seizure reverberation in the hippocampal-parahippocampal loop (36), their shorter duration in GFRα2 −/− mice might also be a consequence of the deficit at MPP-granule cell synapses.
It has been suggested that LTP is involved in kindling epileptogenesis (37). In agreement, BDNF knock-out mice that exhibit kindling retardation (9) show deficits in LTP at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses (38). This finding is in contrast to the present observation in GFRα2 −/− mice, which exhibit no impairment of LTP either at Schaffer collateral-CA1 or at MPP- or LPP-granule cell synapses. Our findings argue against the possibility that BDNF and GDNF family ligands act by inducing similar alterations of synaptic plasticity during kindling epileptogenesis.
Although both GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice had been fully kindled, the long-term seizure susceptibility was lower in the knock-out animals. It is unlikely that this impairment is a consequence of the retarded kindling development, because BDNF and neurotrophin-3 knock-out mice exhibit similar retardation with no influence on kindling persistence (9, 10). Also, Dennison et al. (3) reported that the number of ADs required to reach the kindled state do not affect its maintenance.
The lower long-term hyperexcitability in GFRα2 −/− mice might be due to impairment of NPY mechanisms in the dentate gyrus. At 24 h after the last seizure, the number of NPY-immunoreactive hilar interneurons was reduced in GFRα2 +/+ mice but unchanged in −/− mice. This difference was most likely due to decreased NPY immunoreactivity and not to neuronal loss. Fluoro-Jade staining showed no degenerating neurons in the kindled animals. Moreover, there was no difference in the number of NeuN-positive hilar neurons between kindled and control mice. Most hippocampal NPY-positive neurons also express somatostatin (39), and the last seizure gave rise to the same increase in the number of somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in both strains. The reduction of NPY immunoreactivity was specific for hilar interneurons. Thus, the seizure-induced increase of NPY immunoreactivity in mossy fibers did not differ between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice.
The NPY-positive hilar interneurons have efferent connections only with granule cell dendrites in the molecular layer (40). These dendrites express NPY Y1 and Y5 receptors, which should mediate the direct effects of the NPY-positive hilar interneurons on seizure susceptibility. The majority of studies indicate that signaling through Y1 and Y5 receptors has pro- and antiepileptic actions, respectively (41–44). Hypothetically, if the seizure-evoked reduction of NPY immunoreactivity is associated with increased release of NPY from hilar interneurons, the more pronounced hyperexcitability in GFRα2 +/+ mice could be mediated through enhanced activation of proepileptic Y1 receptors. This effect might be counteracted by down-regulation of Y1 mRNA in granule cells and decrease of Y1 receptor binding in the molecular layer reported after hippocampal kindling in rats (45). Alternatively, the high levels of NPY immunoreactivity after seizures in GFRα2 −/− mice could suggest a compensatory elevated synthesis because of high NPY release. If this is the case, the lower seizure susceptibility in these animals might be due to increased stimulation of antiepileptic Y5 receptors, which are up-regulated in dentate granule cells after hippocampal seizures (46). Whether there are differences between GFRα2 +/+ and −/− mice in NPY levels of hilar interneurons also during the original kindling process remains to be elucidated.
It is currently unclear how lack of GFRα2 signaling leads to functional changes in hilar interneurons and at MPP-granule cell synapses. Neurturin and GDNF are probably released from either granule cell dendrites or mossy fiber collaterals. On hilar interneurons, which express c-Ret and GFRα1 but not α2, NRTN and GDNF signaling cannot be mediated by conventional interaction between GFRα2 and c-Ret (47, 48). Instead, GFRα2 on mossy fiber collaterals (see Fig. 3) might form complex with GDNF or NRTN, and thereby regulate their release and subsequent signaling on c-Ret-GFRα1-expressing hilar interneurons. Alternatively, GFRα2 and the ligands might signal “in trans” to the hilar interneurons from the mossy fiber collaterals. Such interaction between c-Ret and ligand/GFRα complex has been shown only in vitro (47). At MPP-granule cell synapses, GDNF family ligands may bind to GFRα2 receptors located either on the granule cells themselves or on afferents from the entorhinal cortex. However, c-Ret has not yet been detected on these synapses, and it is unclear whether NRTN and GDNF may act only through GFRα2, similar to what has been demonstrated for GDNF and GFRα1 (49, 50).
Alterations in extrahippocampal limbic structures could also play an important role for the kindling deficits. Hippocampal kindling stimulations increase the expression of GFRα2 mRNA in the piriform cortex (21), which is important for the spread of seizure activity to cortical and subcortical structures (51). The delay in the progression to generalized seizures in GFRα2 −/− mice might, at least partly, be explained by the lack of the GFRα2 in the piriform cortex.
In conclusion, the present findings indicate that a cascade of changes in the signaling of a variety of neurotrophic factors, including not only the neurotrophins but also the members of the GDNF family, plays a role for the progressive increase of excitability during epileptogenesis. Of major importance is, as our data show, that neurotrophic factors are also involved in mechanisms determining the long-term stability of the elevated seizure susceptibility. It seems highly warranted to clarify these mechanisms in detail, not least because such knowledge may provide a framework for the development of new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of complex partial seizures in humans.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council; the Academy of Finland; Biocentrum Helsinki; the Sigrid Juselius, Crafoord, Wiberg, Kock, and Elsa and Thorsten Segerfalk Foundations; the Medical Faculty of the University of Lund; the Royal Physiographic Society; and European Union Biomed Grant BMH4-97-2157. A.N. and P.M. were supported by scholarships from the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and Natural Sciences and from the Engineering Research Council of Canada, respectively.
Abbreviations
- AD
after discharge
- BDNF
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- GDNF
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
- GFR
GDNF family receptor
- LPP
lateral perforant path
- LTP
long-term potentiation
- MPP
medial perforant path
- NPY
neuropeptide Y
- NRTN
neurturin
- PPD
paired-pulse depression
References
- 1.McNamara J O, Bonhaus D W, Shin C. In: Epilepsy: Models, Mechanisms and Concepts. Schwartzkroin P A, editor. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press; 1993. pp. 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goddard G V, McIntyre D C, Leech C K. Exp Neurol. 1969;25:295–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dennison Z, Teskey G C, Cain D P. Epilepsy Res. 1995;21:171–182. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(95)00025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gall C, Isackson P J. Science. 1989;24:758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Humpel C, Wetmore C, Olson L. Neuroscience. 1993;53:909–918. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90476-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ernfors P, Bengzon J, Kokaia Z, Persson H, Lindvall O. Neuron. 1991;7:165–176. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90084-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Elmér E, Kokaia Z, Kokaia M, Carnahan J, Nawa H, Lindvall O. Neuroscience. 1998;83:351–362. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Binder D K, Routbort M J, Ryan T E, Yancopoulos G D, McNamara J O. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1424–1436. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01424.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kokaia M, Ernfors P, Kokaia Z, Elmér E, Jaenisch R, Lindvall O. Exp Neurol. 1995;133:215–224. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1995.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Elmér E, Kokaia M, Ernfors P, Ferencz I, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Exp Neurol. 1997;145:93–103. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1997.6478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Bengzon J, Elmér E, Kokaia M. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:490–496. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lin L F, Doherty D H, Lile J D, Bektesh S, Collins F. Science. 1993;260:1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.8493557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kotzbauer P T, Lampe P A, Heuckeroth R O, Golden J P, Creedon D J, Johnson E M, Jr, Milbrandt J. Nature (London) 1996;384:467–470. doi: 10.1038/384467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martin D, Miller G, Rosendahl M, Russell D A. Brain Res. 1995;683:172–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Akerud P, Alberch J, Eketjall S, Wagner J, Arenas E. J Neurochem. 1999;73:70–78. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Horger B, Nishimura M, Armanini M, Wang L-C, Poulsen K, Rosenblad C, Kirik D, Moffat B, Simmons L, Johnson E, Milbrandt J, Rosenthal A, Björklund A, Vandlen R, Hynes M, Phillips H. J Neurosci. 1998;18:4929–4937. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-13-04929.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Airaksinen M S, Titievsky A, Saarma M. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;13:313–325. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1999.0754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baloh R H, Enomoto H, Johnson E M, Milbrandt J. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:103–110. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(99)00048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Trupp M, Raynoschek C, Ibanez C F. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;11:47–63. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1998.0667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sanicola M, Hession C, Worley D, Carmillo P, Ehrenfels C, Walus L, Robinson S, Jaworski G, Wei H, Tizard R, Whitty A, Pepinsky R B, Cate R L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:6238–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kokaia Z, Airaksinen M S, Nanobashvili A, Larsson E, Kujamaki E, Lindvall O, Saarma M. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:1202–1216. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Golden J P, Baloh R H, Kotzbauer P T, Lampe P A, Osborne P A, Milbrandt J, Johnson E M., Jr J Comp Neurol. 1998;398:139–150. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19980817)398:1<139::aid-cne9>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rossi J, Luukko K, Poteryaev D, Laurikainen A, Sun Y F, Laakso T, Eerikainen S, Tuominen R, Lakso M, Rauvala H, et al. Neuron. 1999;22:243–252. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Franklin K B J, Paxinos G. Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. San Diego: Academic; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Racine R J. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972;32:281–294. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kokaia Z, Andsberg G, Martinez-Serrano A, Lindvall O. Neuroscience. 1998;84:1113–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schmued L C, Albertson C, Slikker W J. Brain Res. 1997;751:37–46. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01387-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Larsson E, Nanobashvili A, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:1220–1228. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199911000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kokaia M, Asztély F, Olofsdotter K, Sindreu C B, Kullmann D M, Lindvall O. J Neurosci. 1998;18:8730–8739. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-21-08730.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Asztély F, Kokaia M, Olofsdotter K, Örtegren U, Lindvall O. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:662–669. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kokaia, M. (2000) Hippocampus10, in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 32.Seki T, Arai Y. J Neurosci. 1993;13:2351–2358. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02351.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wilcox K S, Dichter M A. J Neurosci. 1994;14:1775–1788. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01775.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McAllister A K, Katz L C, Lo D C. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999;22:295–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lothman E W, Bertram E H, 3rd, Stringer J L. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;37:1–82. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Leung L W. Brain Res. 1987;419:173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90581-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Maru E, Goddard G V. Exp Neurol. 1987;96:19–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(87)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:8856–8860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Köhler C, Eriksson L G, Davies S, Chan-Palay V. Neurosci Lett. 1987;78:1–6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90551-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Deller T, Leranth C. J Comp Neurol. 1990;300:433–447. doi: 10.1002/cne.903000312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Erickson J C, Clegg K E, Palmiter R D. Nature (London) 1996;381:415–418. doi: 10.1038/381415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Woldbye D P D, Larsen P J, Mikkelsen J D, Klemp K, Madsen T M, Bolwig T G. Nat Med. 1997;3:761–764. doi: 10.1038/nm0797-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gariboldi M, Conti M, Cavaleri D, Samanin R, Vezzani A. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:757–759. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Brooks P A, Kelly J S, Allen J M, Smith D A, Stone T W. Brain Res. 1987;408:295–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90391-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gobbi M, Gariboldi M, Piwko C, Hoyer D, Sperk G, Vezzani A. J Neurochem. 1998;70:1615–1622. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70041615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kopp J, Nanobashvili A, Kokaia A, Lindvall O, Hökfelt T. Mol Brain Res. 1999;72:17–29. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(99)00191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yu T, Scully S, Yu Y, Fox G M, Jing S, Zhou R. J Neurosci. 1998;18:4684–4696. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-12-04684.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Trupp M, Belluardo N, Funakoshi H, Ibanez C F. J Neurosci. 1997;17:3554–3567. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-10-03554.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Poteryaev D, Titievsky A, Sun Y F, Thomas-Crusells J, Lindahl M, Billaud M, Arumae U, Saarma M. FEBS Lett. 1999;463:63–66. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01590-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Trupp M, Scott R, Whittemore S R, Ibanez C F. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20885–20894. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.30.20885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Löscher W, Ebert U. Prog Neurobiol. 1996;50:427–481. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(96)00036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]