Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To assess
the feasibility of a new technique based on diffusion anisotropy to
segment white and grey matter of the brain. To use this technique to
measure the mean diffusivity (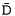 ) and magnetisation transfer ratio (MTR) of normal appearing white matter (NAWM) and grey matter (NAGM) from patients with multiple sclerosis.
METHODS—Dual echo
turbo spin echo, MT, and diffusion weighted scans of the brain were
obtained from 30 patients with multiple sclerosis and 18 sex and age
matched healthy controls. After image coregistration and removal of T2
visible lesions, white and grey matter were segmented from 10 supratentorial slices using diffusion anisotropy thresholds. Histograms
of the average MTR and
) and magnetisation transfer ratio (MTR) of normal appearing white matter (NAWM) and grey matter (NAGM) from patients with multiple sclerosis.
METHODS—Dual echo
turbo spin echo, MT, and diffusion weighted scans of the brain were
obtained from 30 patients with multiple sclerosis and 18 sex and age
matched healthy controls. After image coregistration and removal of T2
visible lesions, white and grey matter were segmented from 10 supratentorial slices using diffusion anisotropy thresholds. Histograms
of the average MTR and 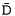 were created for normal white and grey matter of controls and NAWM and NAGM of
patients with multiple sclerosis.
RESULTS—All the MTR
histogram derived metrics of the NAWM from patients with multiple
sclerosis were significantly lower than those of white matter from
controls. The peak height of the
were created for normal white and grey matter of controls and NAWM and NAGM of
patients with multiple sclerosis.
RESULTS—All the MTR
histogram derived metrics of the NAWM from patients with multiple
sclerosis were significantly lower than those of white matter from
controls. The peak height of the 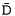 histogram of NAWM from patients with multiple sclerosis was also
significantly different from that of normal white matter. The average
MTR, the peak location of the MTR histogram, and peak height of the
histogram of NAWM from patients with multiple sclerosis was also
significantly different from that of normal white matter. The average
MTR, the peak location of the MTR histogram, and peak height of the
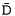 histogram of the NAGM of patients
with multiple sclerosis were significantly lower than the corresponding
quantities of grey matter from controls.
CONCLUSIONS—A
technique was developed for segmenting white and grey matter with the
potential for improving the understanding of the pathophysiology of
many neurological conditions. Its application to the study of multiple
sclerosis confirms the presence of a diffuse tissue damage in the NAWM
of these patients and suggests that subtle changes also occur in the NAGM.
histogram of the NAGM of patients
with multiple sclerosis were significantly lower than the corresponding
quantities of grey matter from controls.
CONCLUSIONS—A
technique was developed for segmenting white and grey matter with the
potential for improving the understanding of the pathophysiology of
many neurological conditions. Its application to the study of multiple
sclerosis confirms the presence of a diffuse tissue damage in the NAWM
of these patients and suggests that subtle changes also occur in the NAGM.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (152.2 KB).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWNELL B., HUGHES J. T. The distribution of plaques in the cerebrum in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Nov;25:315–320. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.4.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basser P. J., Mattiello J., LeBihan D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basser P. J., Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B. 1996 Jun;111(3):209–219. doi: 10.1006/jmrb.1996.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp S. J., Stevenson V. L., Thompson A. J., Miller D. H., Borras C., Auriacombe S., Brochet B., Falautano M., Filippi M., Hérissé-Dulo L. Cognitive function in primary progressive and transitional progressive multiple sclerosis: a controlled study with MRI correlates. Brain. 1999 Jul;122(Pt 7):1341–1348. doi: 10.1093/brain/122.7.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cercignani M., Iannucci G., Rocca M. A., Comi G., Horsfield M. A., Filippi M. Pathologic damage in MS assessed by diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology. 2000 Mar 14;54(5):1139–1144. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.5.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen P., Gideon P., Thomsen C., Stubgaard M., Henriksen O., Larsson H. B. Increased water self-diffusion in chronic plaques and in apparently normal white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1993 Mar;87(3):195–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1993.tb04100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogan A. G., Clark C. A., Werring D. J., Barker G. J., McDonald W. I., Miller D. H. Comparison of multiple sclerosis clinical subgroups using navigated spin echo diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999 Jun;17(5):653–661. doi: 10.1016/s0730-725x(99)00011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Campi A., Dousset V., Baratti C., Martinelli V., Canal N., Scotti G., Comi G. A magnetization transfer imaging study of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1995 Mar;45(3 Pt 1):478–482. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Horsfield M. A., Adèr H. J., Barkhof F., Bruzzi P., Evans A., Frank J. A., Grossman R. I., McFarland H. F., Molyneux P. Guidelines for using quantitative measures of brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in monitoring the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1998 Apr;43(4):499–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410430414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Tortorella C., Bozzali M. Normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis: the contribution of magnetic resonance techniques. Mult Scler. 1999 Aug;5(4):273–282. doi: 10.1177/135245859900500414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Tortorella C., Rovaris M., Bozzali M., Possa F., Sormani M. P., Iannucci G., Comi G. Changes in the normal appearing brain tissue and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000 Feb;68(2):157–161. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.68.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Yousry T., Baratti C., Horsfield M. A., Mammi S., Becker C., Voltz R., Spuler S., Campi A., Reiser M. F. Quantitative assessment of MRI lesion load in multiple sclerosis. A comparison of conventional spin-echo with fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. Brain. 1996 Aug;119(Pt 4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1093/brain/119.4.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N. C., Jenkins R., Leary S. M., Stevenson V. L., Losseff N. A., Crum W. R., Harvey R. J., Rossor M. N., Miller D. H., Thompson A. J. Progressive cerebral atrophy in MS: a serial study using registered, volumetric MRI. Neurology. 2000 Feb 22;54(4):807–812. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawne-Cain M. L., O'Riordan J. I., Thompson A. J., Moseley I. F., Miller D. H. Multiple sclerosis lesion detection in the brain: a comparison of fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and conventional T2-weighted dual spin echo. Neurology. 1997 Aug;49(2):364–370. doi: 10.1212/wnl.49.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnal J. V., Doran M., Hall A. S., Collins A. G., Oatridge A., Pennock J. M., Young I. R., Bydder G. M. MR imaging of anisotropically restricted diffusion of water in the nervous system: technical, anatomic, and pathologic considerations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):1–18. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199101000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfield M. A., Lai M., Webb S. L., Barker G. J., Tofts P. S., Turner R., Rudge P., Miller D. H. Apparent diffusion coefficients in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 1996 Sep;36(3):393–400. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910360310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. K., Horsfield M. A., Simmons A. Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1999 Sep;42(3):515–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd D., Barkhof F., McConnell R., Algra P. R., Allen I. V., Revesz T. Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1999 Jan;122(Pt 1):17–26. doi: 10.1093/brain/122.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson H. B., Thomsen C., Frederiksen J., Stubgaard M., Henriksen O. In vivo magnetic resonance diffusion measurement in the brain of patients with multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging. 1992;10(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(92)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bihan D., Turner R., Moonen C. T., Pekar J. Imaging of diffusion and microcirculation with gradient sensitization: design, strategy, and significance. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1991 Jan-Feb;1(1):7–28. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lexa F. J., Grossman R. I., Rosenquist A. C. Dyke Award paper. MR of wallerian degeneration in the feline visual system: characterization by magnetization transfer rate with histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994 Feb;15(2):201–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loevner L. A., Grossman R. I., Cohen J. A., Lexa F. J., Kessler D., Kolson D. L. Microscopic disease in normal-appearing white matter on conventional MR images in patients with multiple sclerosis: assessment with magnetization-transfer measurements. Radiology. 1995 Aug;196(2):511–515. doi: 10.1148/radiology.196.2.7617869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin F. D., Reingold S. C. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology. 1996 Apr;46(4):907–911. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.4.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Grossman R. I., Udupa J. K., Wei L., Kolson D. L., Mannon L. J., Grossman M. Isolated U-fiber involvement in MS: preliminary observations. Neurology. 1998 May;50(5):1301–1306. doi: 10.1212/wnl.50.5.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Barkhof F., Berry I., Kappos L., Scotti G., Thompson A. J. Magnetic resonance imaging in monitoring the treatment of multiple sclerosis: concerted action guidelines. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Aug;54(8):683–688. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.8.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Barkhof F., Nauta J. J. Gadolinium enhancement increases the sensitivity of MRI in detecting disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1993 Oct;116(Pt 5):1077–1094. doi: 10.1093/brain/116.5.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyser J. M., Edwards K. R., Poser C. M., Filskov S. B. Cognitive function in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1980 Sep;37(9):577–579. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500580073013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli C., Basser P. J. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med. 1996 Dec;36(6):893–906. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910360612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike G. B., de Stefano N., Narayanan S., Francis G. S., Antel J. P., Arnold D. L. Combined magnetization transfer and proton spectroscopic imaging in the assessment of pathologic brain lesions in multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999 May;20(5):829–837. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovaris M., Filippi M., Calori G., Rodegher M., Campi A., Colombo B., Comi G. Intra-observer reproducibility in measuring new putative MR markers of demyelination and axonal loss in multiple sclerosis: a comparison with conventional T2-weighted images. J Neurol. 1997 Apr;244(4):266–270. doi: 10.1007/s004150050083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studholme C., Hill D. L., Hawkes D. J. Automated three-dimensional registration of magnetic resonance and positron emission tomography brain images by multiresolution optimization of voxel similarity measures. Med Phys. 1997 Jan;24(1):25–35. doi: 10.1118/1.598130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortorella C., Viti B., Bozzali M., Sormani M. P., Rizzo G., Gilardi M. F., Comi G., Filippi M. A magnetization transfer histogram study of normal-appearing brain tissue in MS. Neurology. 2000 Jan 11;54(1):186–193. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.1.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavasour I. M., Whittall K. P., MacKay A. L., Li D. K., Vorobeychik G., Paty D. W. A comparison between magnetization transfer ratios and myelin water percentages in normals and multiple sclerosis patients. Magn Reson Med. 1998 Nov;40(5):763–768. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910400518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werring D. J., Clark C. A., Barker G. J., Thompson A. J., Miller D. H. Diffusion tensor imaging of lesions and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1999 May 12;52(8):1626–1632. doi: 10.1212/wnl.52.8.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buchem M. A., McGowan J. C., Kolson D. L., Polansky M., Grossman R. I. Quantitative volumetric magnetization transfer analysis in multiple sclerosis: estimation of macroscopic and microscopic disease burden. Magn Reson Med. 1996 Oct;36(4):632–636. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910360420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Waesberghe J. H., Kamphorst W., De Groot C. J., van Walderveen M. A., Castelijns J. A., Ravid R., Lycklama à Nijeholt G. J., van der Valk P., Polman C. H., Thompson A. J. Axonal loss in multiple sclerosis lesions: magnetic resonance imaging insights into substrates of disability. Ann Neurol. 1999 Nov;46(5):747–754. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199911)46:5<747::aid-ana10>3.3.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


