Abstract
Objective: To investigate the extent and the nature of white matter tissue damage of patients with Alzheimer's disease using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging (DT-MRI).
Background: Although Alzheimer's disease pathology mainly affects cortical grey matter, previous pathological and MRI studies showed that also the brain white matter of patients is damaged. However, the nature of Alzheimer's disease associated white matter damage is still unclear.
Methods: Conventional and DT-MRI scans were obtained from16 patients with Alzheimer's disease and 10 sex and age matched healthy volunteers. The mean diffusivity (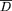 ), fractional anisotropy (FA), and inter-voxel coherence (C) of several white matter regions were measured.
), fractional anisotropy (FA), and inter-voxel coherence (C) of several white matter regions were measured.
Results: 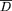 was higher and FA lower in the corpus callosum, as well as in the white matter of the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes from patients with Alzheimer's disease than in the corresponding regions from healthy controls.
was higher and FA lower in the corpus callosum, as well as in the white matter of the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes from patients with Alzheimer's disease than in the corresponding regions from healthy controls. 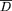 and FA of the white matter of the occipital lobe and internal capsule were not different between patients and controls. C values were also not different between patients and controls for any of the regions studied. Strong correlations were found between the mini mental state examination score and the average overall white matter
and FA of the white matter of the occipital lobe and internal capsule were not different between patients and controls. C values were also not different between patients and controls for any of the regions studied. Strong correlations were found between the mini mental state examination score and the average overall white matter 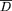 (r=0.92, p<0.001) and FA (r=0.78; p<0.001).
(r=0.92, p<0.001) and FA (r=0.78; p<0.001).
Conclusions: White matter changes in patients with Alzheimer's disease are likely to be secondary to wallerian degeneration of fibre tracts due to neuronal loss in cortical associative areas.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (167.3 KB).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basser P. J., Mattiello J., LeBihan D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B. C., Barker W. W., Loewenstein D. A., Sheldon J., Duara R. MR signal abnormalities in memory disorder and dementia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzali M., Franceschi M., Falini A., Pontesilli S., Cercignani M., Magnani G., Scotti G., Comi G., Filippi M. Quantification of tissue damage in AD using diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology. 2001 Sep 25;57(6):1135–1137. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.6.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzao A., Floris R., Baviera M. E., Apruzzese A., Simonetti G. Diffusion and perfusion MR imaging in cases of Alzheimer's disease: correlations with cortical atrophy and lesion load. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Jun-Jul;22(6):1030–1036. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun A., Englund E. A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a pathoanatomical study. Ann Neurol. 1986 Mar;19(3):253–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fama R., Sullivan E. V., Shear P. K., Marsh L., Yesavage J. A., Tinklenberg J. R., Lim K. O., Pfefferbaum A. Selective cortical and hippocampal volume correlates of Mattis Dementia Rating Scale in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 1997 Jun;54(6):719–728. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1997.00550180039010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Cercignani M., Inglese M., Horsfield M. A., Comi G. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2001 Feb 13;56(3):304–311. doi: 10.1212/wnl.56.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foundas A. L., Leonard C. M., Mahoney S. M., Agee O. F., Heilman K. M. Atrophy of the hippocampus, parietal cortex, and insula in Alzheimer's disease: a volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol. 1997 Apr;10(2):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N. C., Freeborough P. A., Rossor M. N. Visualisation and quantification of rates of atrophy in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1996 Jul 13;348(9020):94–97. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)05228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel H., Teipel S. J., Alexander G. E., Horwitz B., Teichberg D., Schapiro M. B., Rapoport S. I. Corpus callosum atrophy is a possible indicator of region- and cell type-specific neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer disease: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Arch Neurol. 1998 Feb;55(2):193–198. doi: 10.1001/archneur.55.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanyu H., Asano T., Sakurai H., Imon Y., Iwamoto T., Takasaki M., Shindo H., Abe K. Diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer imaging of the corpus callosum in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1999 Aug 1;167(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(99)00135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanyu H., Shindo H., Kakizaki D., Abe K., Iwamoto T., Takasaki M. Increased water diffusion in cerebral white matter in Alzheimer's disease. Gerontology. 1997;43(6):343–351. doi: 10.1159/000213874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. K., Horsfield M. A., Simmons A. Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1999 Sep;42(3):515–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantarci K., Jack C. R., Jr, Xu Y. C., Campeau N. G., O'Brien P. C., Smith G. E., Ivnik R. J., Boeve B. F., Kokmen E., Tangalos E. G. Mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease: regional diffusivity of water. Radiology. 2001 Apr;219(1):101–107. doi: 10.1148/radiology.219.1.r01ap14101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bihan D., Turner R., Moonen C. T., Pekar J. Imaging of diffusion and microcirculation with gradient sensitization: design, strategy, and significance. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1991 Jan-Feb;1(1):7–28. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Campbell M. J., Terry R. D., Morrison J. H. Laminar and regional distributions of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative study of visual and auditory cortices. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1799–1808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01799.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys D., Pruvo J. P., Parent M., Vermersch P., Soetaert G., Steinling M., Delacourte A., Défossez A., Rapoport A., Clarisse J. Could Wallerian degeneration contribute to "leuko-araiosis" in subjects free of any vascular disorder? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Jan;54(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay S., Meyerhoff D. J., Constans J. M., Norman D., Fein G., Weiner M. W. Regional gray and white matter metabolite differences in subjects with AD, with subcortical ischemic vascular dementia, and elderly controls with 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Arch Neurol. 1996 Feb;53(2):167–174. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1996.00550020079018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. C., Esiri M. M., Hiorns R. W., Wilcock G. K., Powell T. P. Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4531–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferbaum A., Sullivan E. V., Hedehus M., Lim K. O., Adalsteinsson E., Moseley M. Age-related decline in brain white matter anisotropy measured with spatially corrected echo-planar diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2000 Aug;44(2):259–268. doi: 10.1002/1522-2594(200008)44:2<259::aid-mrm13>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli C., Basser P. J. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med. 1996 Dec;36(6):893–906. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910360612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Morrison J. H. Quantitative morphology and regional and laminar distributions of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2801–2808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02801.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. E., Chen F., Chalk J. B., Zelaya F. O., Strugnell W. E., Benson M., Semple J., Doddrell D. M. Loss of connectivity in Alzheimer's disease: an evaluation of white matter tract integrity with colour coded MR diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000 Oct;69(4):528–530. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.69.4.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovaris M., Inglese M., van Schijndel R. A., Sormani M. P., Rodegher M., Comi G., Filippi M. Sensitivity and reproducibility of volume change measurements of different brain portions on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2000 Dec;247(12):960–965. doi: 10.1007/s004150070054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandson T. A., Felician O., Edelman R. R., Warach S. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999 Mar-Apr;10(2):166–171. doi: 10.1159/000017099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studholme C., Hill D. L., Hawkes D. J. Automated three-dimensional registration of magnetic resonance and positron emission tomography brain images by multiresolution optimization of voxel similarity measures. Med Phys. 1997 Jan;24(1):25–35. doi: 10.1118/1.598130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi G., Bertolino A., Lundbom N., Bonavita S., Patronas N. J., Duyn J. H., Metman L. V., Chase T. N., Di Chiro G. Cortical and subcortical chemical pathology in Alzheimer's disease as assessed by multislice proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Neurology. 1996 Sep;47(3):696–704. doi: 10.1212/wnl.47.3.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermersch P., Roche J., Hamon M., Daems-Monpeurt C., Pruvo J. P., Dewailly P., Petit H. White matter magnetic resonance imaging hyperintensity in Alzheimer's disease: correlations with corpus callosum atrophy. J Neurol. 1996 Mar;243(3):231–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00868519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods R. P., Grafton S. T., Holmes C. J., Cherry S. R., Mazziotta J. C. Automated image registration: I. General methods and intrasubject, intramodality validation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998 Jan-Feb;22(1):139–152. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199801000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


