Abstract
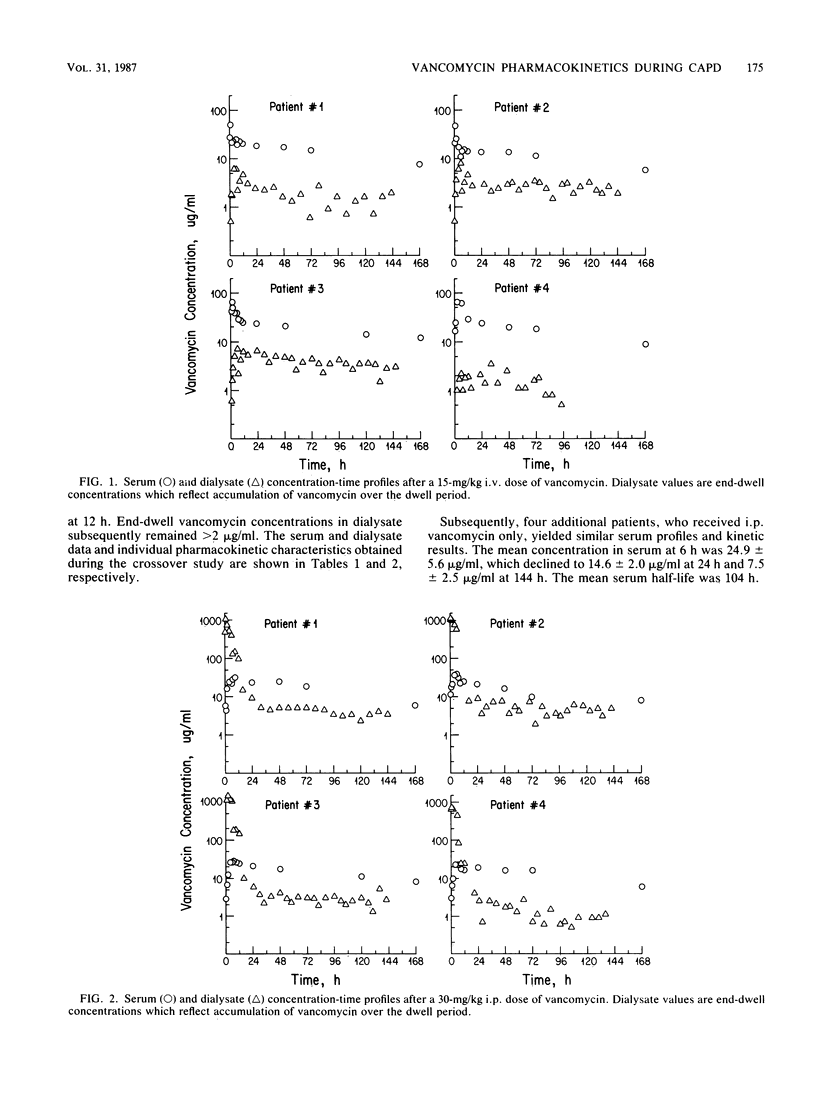
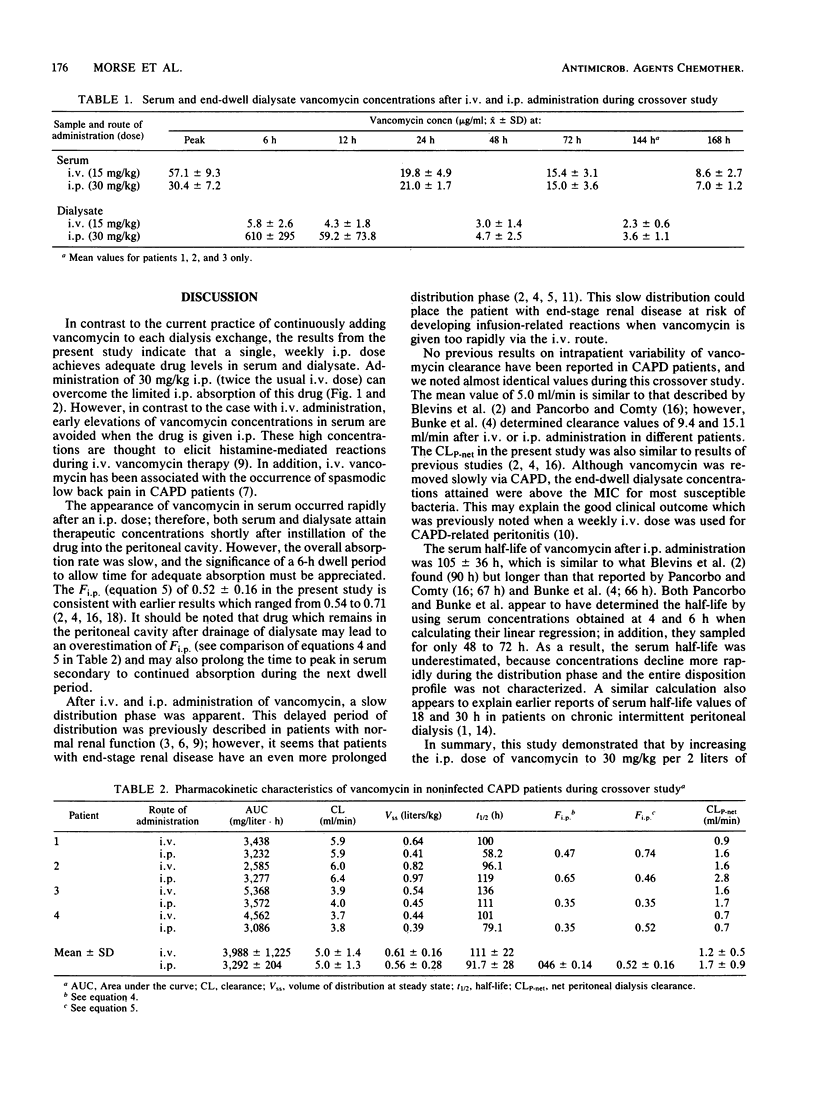
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of vancomycin were investigated in eight patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. A crossover design was used. Four noninfected patients received both a 15-mg/kg (body weight) intravenous dose and a 30-mg/kg intraperitoneal (i.p.) dose. Bioavailability ranged from 0.35 to 0.65 after i.p. administration. i.p. absorption was rapid, with concentrations in serum of 8.8 +/- 6 micrograms/ml noted at 1 h peak values of 30.4 +/- 7 micrograms/ml at 6 h. A slow distribution phase was apparent, with a terminal elimination phase emerging after 12 to 24 h. Vancomycin was eliminated slowly, with a mean total clearance of 5.0 +/- 1.3 ml/min, and concentrations in serum were 7.0 +/- 1.2 micrograms/ml at 168 h. The mean serum half-life was 91.7 +/- 28.1 h, and similar pharmacokinetics were noted after intravenous administration. Subsequently, four patients with catheter-related exit site or tunnel infections received a 30-mg/kg i.p. dose of vancomycin and displayed a similar kinetic pattern. This method of administering vancomycin achieved therapeutic serum and end-dwell dialysate concentrations over a 1-week period, represents a simple, cost-effective therapy which avoids the possibility of infusion-related toxicity, and deserves further investigation in patients with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayus J. C., Eneas J. F., Tong T. G., Benowitz N. L., Schoenfeld P. Y., Hadley K. L., Becker C. E., Humphreys M. H. Peritoneal clearance and total body elimination of vancomycin during chronic intermittent peritoneal dialysis. Clin Nephrol. 1979 Mar;11(3):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins R. D., Halstenson C. E., Salem N. G., Matzke G. R. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):603–606. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin R. A., Bauer L. A., Miller D. D., Record K. E., Griffen W. O., Jr Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in normal and morbidly obese subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):575–580. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunke C. M., Aronoff G. R., Brier M. E., Sloan R. S., Luft F. C. Vancomycin kinetics during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Nov;34(5):631–637. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler N. R., Narang P. K., Lesko L. J., Ninos M., Power M. Vancomycin disposition: the importance of age. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Dec;36(6):803–810. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatterer G. Spasmodic low back pain in a patient receiving intravenous vancomycin during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Clin Pharm. 1984 Jan-Feb;3(1):87–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jehl F., Gallion C., Thierry R. C., Monteil H. Determination of vancomycin in human serum by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):503–507. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Moellering R. C., Jr, Greenblatt D. J. Single-dose kinetics of intravenous vancomycin. J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;20(4 Pt 1):197–201. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1980.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krothapalli R. K., Senekjian H. O., Ayus J. C. Efficacy of intravenous vancomycin in the treatment of gram-positive peritonitis in long-term peritoneal dialysis. Am J Med. 1983 Aug;75(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magera B. E., Arroyo J. C., Rosansky S. J., Postic B. Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in patients with peritonitis on peritoneal dialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):710–714. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain J. B., Bongiovanni R., Brown S. Vancomycin quantitation by high-performance liquid chromatography in human serum. J Chromatogr. 1982 Sep 10;231(2):463–466. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81873-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse G., Janicke D., Cafarell R., Piontek K., Apicella M., Jusko W. J., Walshe J. Moxalactam epimer disposition in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Aug;38(2):150–156. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. E., Sørensen I., Hansen H. E. Peritoneal transport of vancomycin during peritoneal dialysis. Nephron. 1979;24(6):274–277. doi: 10.1159/000181735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancorbo S., Comty C. Peritoneal transport of vancomycin in 4 patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Nephron. 1982;31(1):37–39. doi: 10.1159/000182611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocci M. L., Jr, Jusko W. J. LAGRAN program for area and moments in pharmacokinetic analysis. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Jun;16(3):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogge M. C., Johnson C. A., Zimmerman S. W., Welling P. G. Vancomycin disposition during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a pharmacokinetic analysis of peritoneal drug transport. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):578–582. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenzer K. S., Wang C. H., Anhalt J. P. Automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay for monitoring vancomycin. Ther Drug Monit. 1983;5(3):341–345. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198309000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I. Microbiologic aspects of chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 1983 Jan;23(1):83–92. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. J., Morse G. D., Janicke D. M., Apicella M. A. Crossover pharmacokinetic analysis comparing intravenous and intraperitoneal administration of tobramycin. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):796–799. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Treatment of infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):376–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



