Abstract
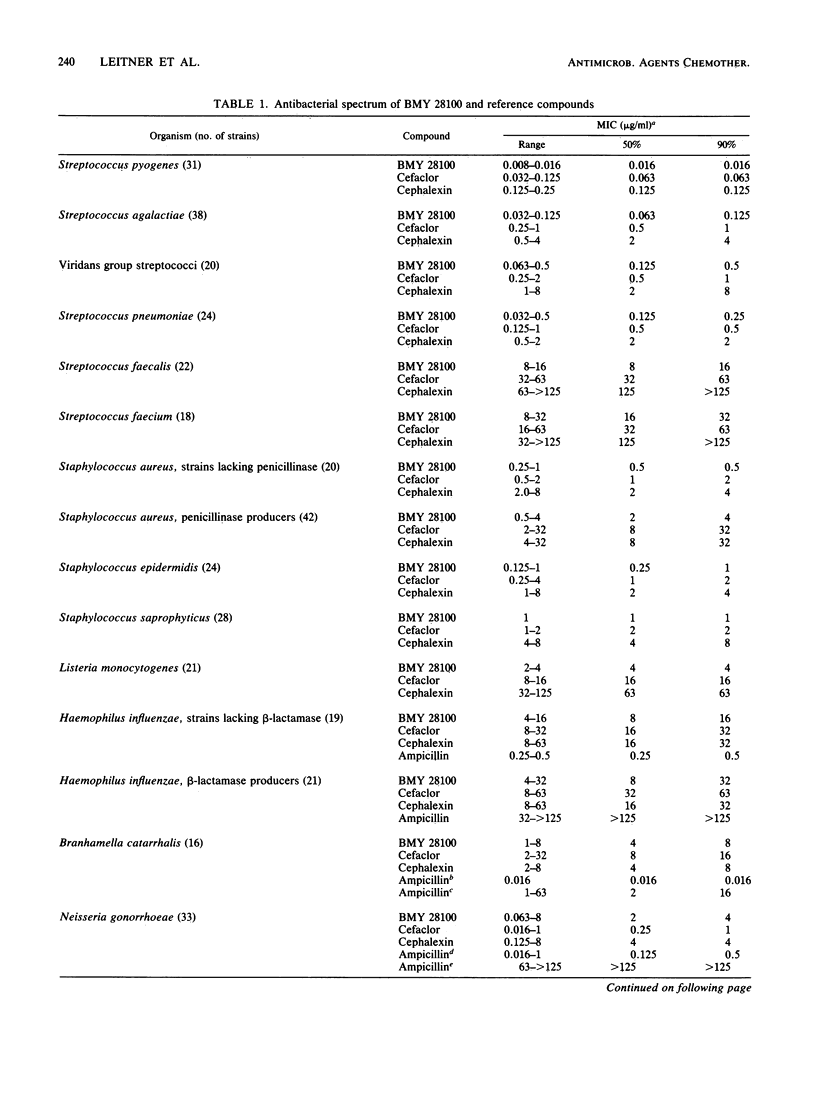
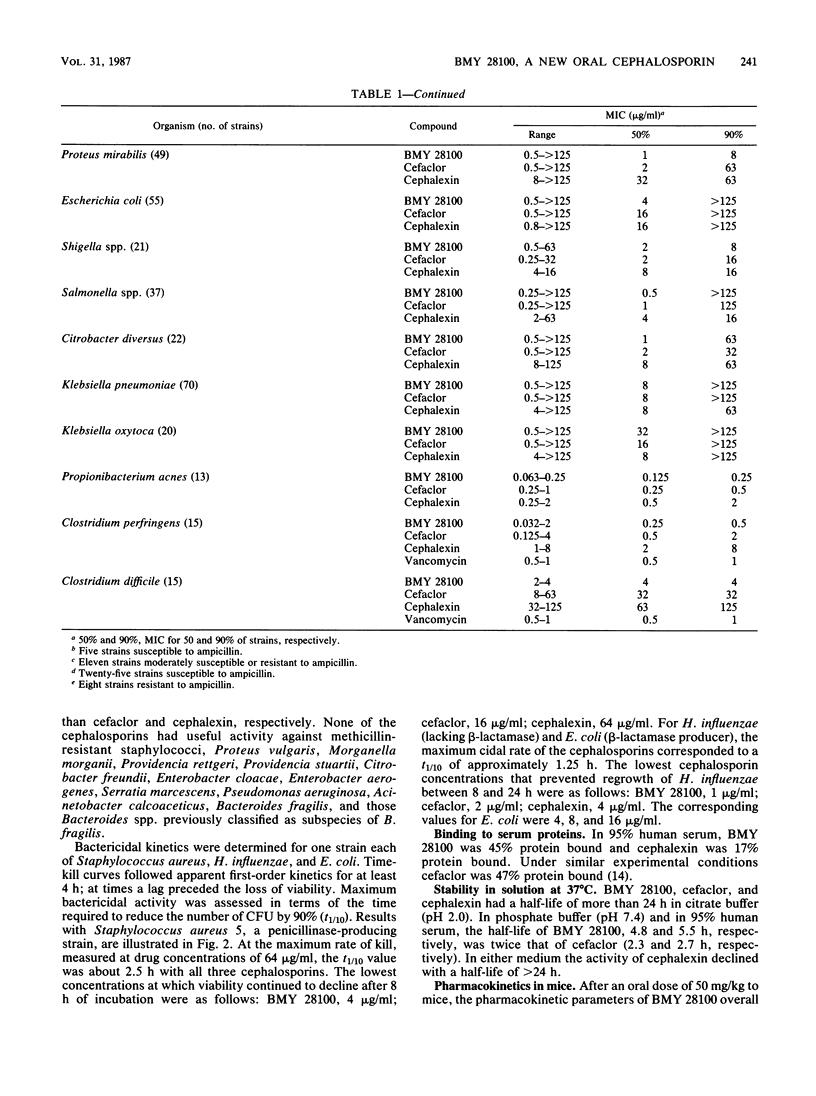
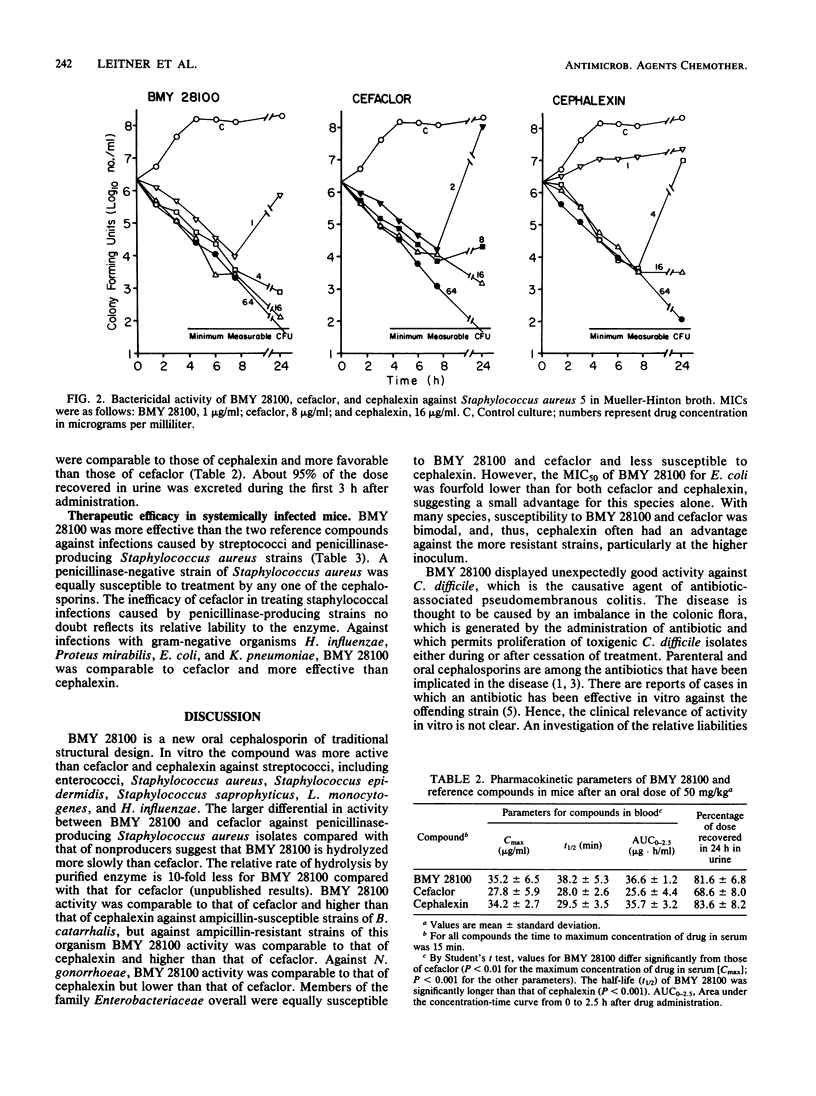
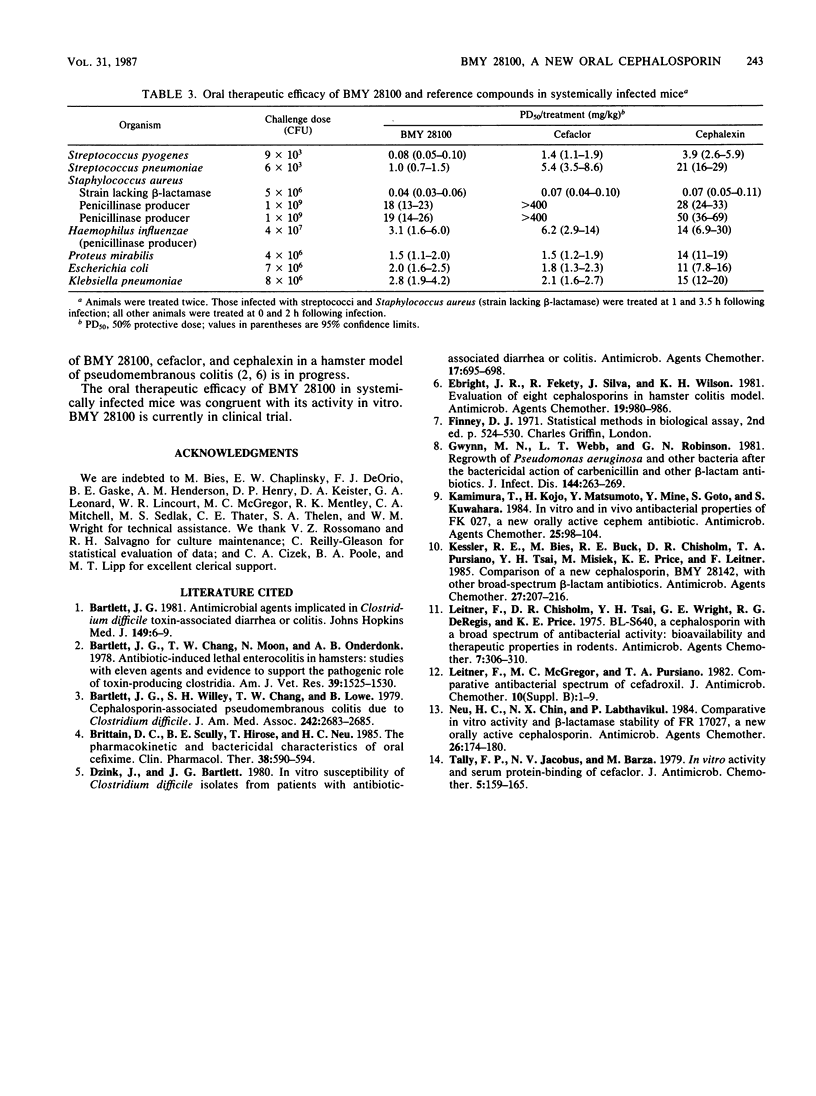
BMY 28100, a new oral cephalosporin with a (Z)-propenyl side chain at the 3 position and a p-hydroxyphenylglycyl substituent at the 7 position, was evaluated in comparison with cefaclor and cephalexin and, when appropriate, ampicillin and vancomycin. In vitro, BMY 28100 was more active than the reference cephalosporins against streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Listeria monocytogenes, Haemophilus influenzae, Propionibacterium acnes, Clostridium perfringens, and Clostridium difficile. BMY 28100 was comparable to cefaclor and more active than cephalexin against Staphylococcus saprophyticus and ampicillin-susceptible strains of Branhamella catarrhalis; but against ampicillin-resistant strains of B. catarrhalis, BMY 28100 was comparable to cephalexin and more active than cefaclor. Against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, BMY 28100 was comparable to cephalexin, but less active than cefaclor. Members of the family Enterobacteriaceae overall were equally susceptible to BMY 28100 and cefaclor but were less susceptible to cephalexin. In human serum, BMY 28100 was 45% protein bound. After an oral dose to mice, 82% of the drug was recovered in urine. The oral therapeutic efficacy of BMY 28100 in systemically infected mice reflected its activity in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G. Antimicrobial agents implicated in Clostridium difficile toxin-associated diarrhea of colitis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1981 Jul;149(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Moon N., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-induced lethal enterocolitis in hamsters: studies with eleven agents and evidence to support the pathogenic role of toxin-producing Clostridia. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Sep;39(9):1525–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Willey S. H., Chang T. W., Lowe B. Cephalosporin-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to Clostridium difficile. JAMA. 1979 Dec 14;242(24):2683–2685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain D. C., Scully B. E., Hirose T., Neu H. C. The pharmacokinetic and bactericidal characteristics of oral cefixime. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Nov;38(5):590–594. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzink J., Bartlett J. G. In vitro susceptibility of Clostridium difficile isolates from patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhea or colitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):695–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright J. R., Fekety R., Silva J., Wilson K. H. Evaluation of eight cephalosporins in hamster colitis model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):980–986. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynn M. N., Webb T. L., Rolinson G. N. Regrowth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria after the bactericidal action of carbenicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):263–269. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura T., Kojo H., Matsumoto Y., Mine Y., Goto S., Kuwahara S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial properties of FK 027, a new orally active cephem antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Bies M., Buck R. E., Chisholm D. R., Pursiano T. A., Tsai Y. H., Misiek M., Price K. E., Leitner F. Comparison of a new cephalosporin, BMY 28142, with other broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F., Chisholm D. R., Tsai Y. H., Wright G. E., Deregis R. G., Price K. E. BL-S640, a cephalosporin with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity: bioavailability and therapeutic properties in rodents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):306–310. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F., McGregor M. C., Pursiano T. A. Comparative antibacterial spectrum of cefadroxil. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Sep;10 (Suppl B):1–9. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity and beta-lactamase stability of FR 17027, a new orally active cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):174–180. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Barza M. In vitro activity and serum protein-binding of cefaclor. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Mar;5(2):159–165. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



